1. 定义
HashTable、HashMap,是Dictionary类的一种散列表实现方式
散列算法:尽可能快地在数据结构中找到一个值
散列函数:给定一个键值,然后返回值在表中的地址
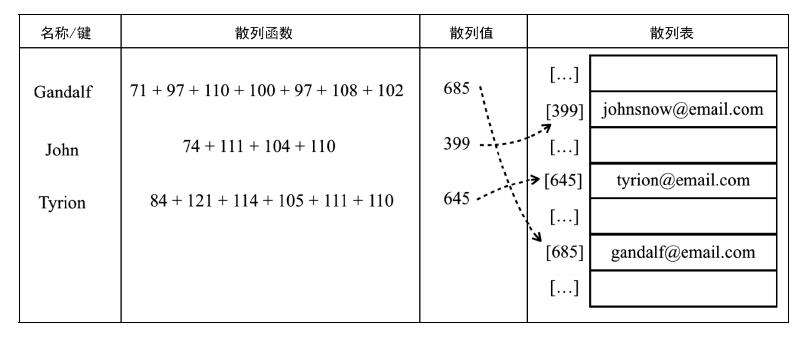
2. 具体操作
创建
创建散列函数
方法
-
put(key,value):向散列表增加一个新的项(也能更新散列表)
-
remove(key):根据键值从散列表中移除值
-
get(key):返回根据键值检索到的特定的值。
3. 使用
散列表和散列集合
类似
散列集合由一个集合构成,插入、移除或获取元素时,使用的是hashCode函数
4. 处理散列表的冲突
当键有相同的散列值时,不同的值在散列表中对应着相同的位置,后面添加的值会覆盖前面的,称为冲突。
处理冲突的几种方法: 分离链接、线性探查和双散列法
1. 分离链接
解决冲突的最简单的方法
分离链接法包括为散列表的每一个位置创建一个链表并将元素存储在里面
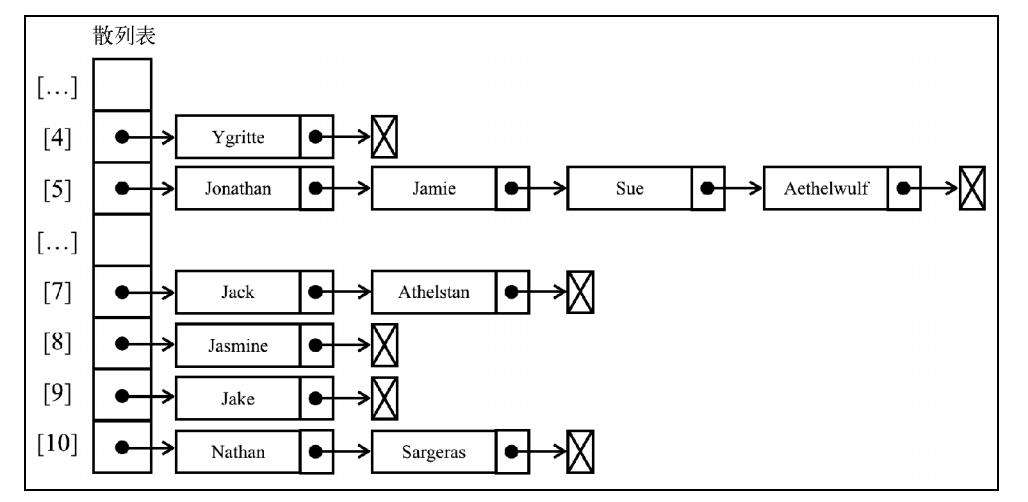
创建
方法
-
put(key,value):向散列表增加一个新的项(也能更新散列表)
-
remove(key):根据键值从散列表中移除值
-
get(key):返回根据键值检索到的特定的值
2. 线性探查
将元素直接存储到表中
当想向表中添加一个新元素的时候,如果索引为position的位置被占据,以此寻找position+1、position+2……直到有空的位置
删除键值对:
-
软删除: 使用特殊的值(标记)来表示键值对被删除,并不是真的删除
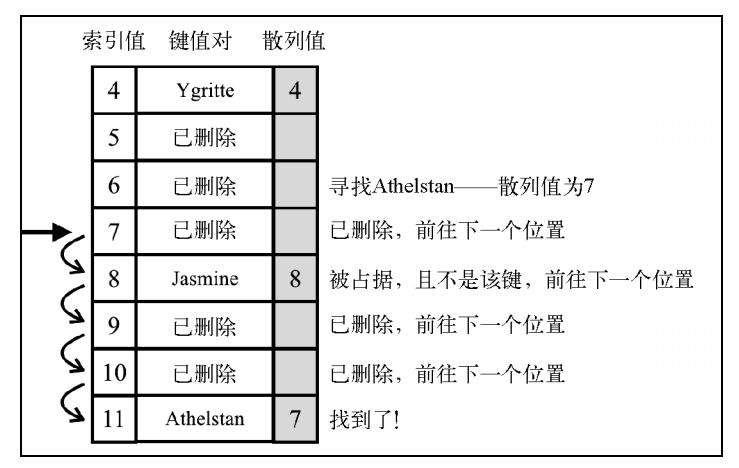
-
检验是否有必要将一个或多个元素移动到之前的位置。当搜索一个键的时候,这种方法可以避免找到一个空位置
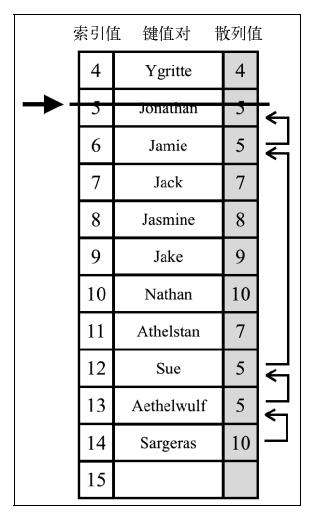
方法
-
put(key,value):向散列表增加一个新的项(也能更新散列表)
-
remove(key):根据键值从散列表中移除值
-
get(key):返回根据键值检索到的特定的值
5. ES2015Map类
6. ES2105 WeakMap类和WeakSet类
除了Set和Map这两种新的数据结构,ES2015还增加了它们的弱化版本,WeakSet和WeakMap
区别:
- WeakSet或WeakMap类没有entries、keys和values等方法
- 只能用对象作为键
创建和使用这两个类主要是为了性能,WeakSet和WeakMap是弱化的(用对象作为键),没有强引用的键。这使得JavaScript的垃圾回收器可以从中清除整个入口。
必须用键才可以取出值。这些类没有entries、keys和values等迭代器方法,因此,除非你知道键,否则没有办法取出值。
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!