前言
这段时间利用课余时间夹杂了很多很多事把 Vue2 源码学习了一遍,但很多都是跟着视频大概过了一遍,也都画了自己的思维导图。但还是对详情的感念模糊不清,故这段时间对源码进行了总结梳理。
目录结构
├── benchmarks 性能、基准测试
├── dist 构建打包的输出目录
├── examples 案例目录
├── flow flow 语法的类型声明
├── packages 一些额外的包,比如:负责服务端渲染的包 vue-server-renderer、配合 vue-loader 使用的的 vue-template-compiler,还有 weex 相关的
│ ├── vue-server-renderer
│ ├── vue-template-compiler
│ ├── weex-template-compiler
│ └── weex-vue-framework
├── scripts 所有的配置文件的存放位置,比如 rollup 的配置文件
├── src vue 源码目录
│ ├── compiler 编译器
│ ├── core 运行时的核心包
│ │ ├── components 全局组件,比如 keep-alive
│ │ ├── config.js 一些默认配置项
│ │ ├── global-api 全局 API,比如熟悉的:Vue.use()、Vue.component() 等
│ │ ├── instance Vue 实例相关的,比如 Vue 构造函数就在这个目录下
│ │ ├── observer 响应式原理
│ │ ├── util 工具方法
│ │ └── vdom 虚拟 DOM 相关,比如熟悉的 patch 算法就在这儿
│ ├── platforms 平台相关的编译器代码
│ │ ├── web
│ │ └── weex
│ ├── server 服务端渲染相关
├── test 测试目录
├── types TS 类型声明
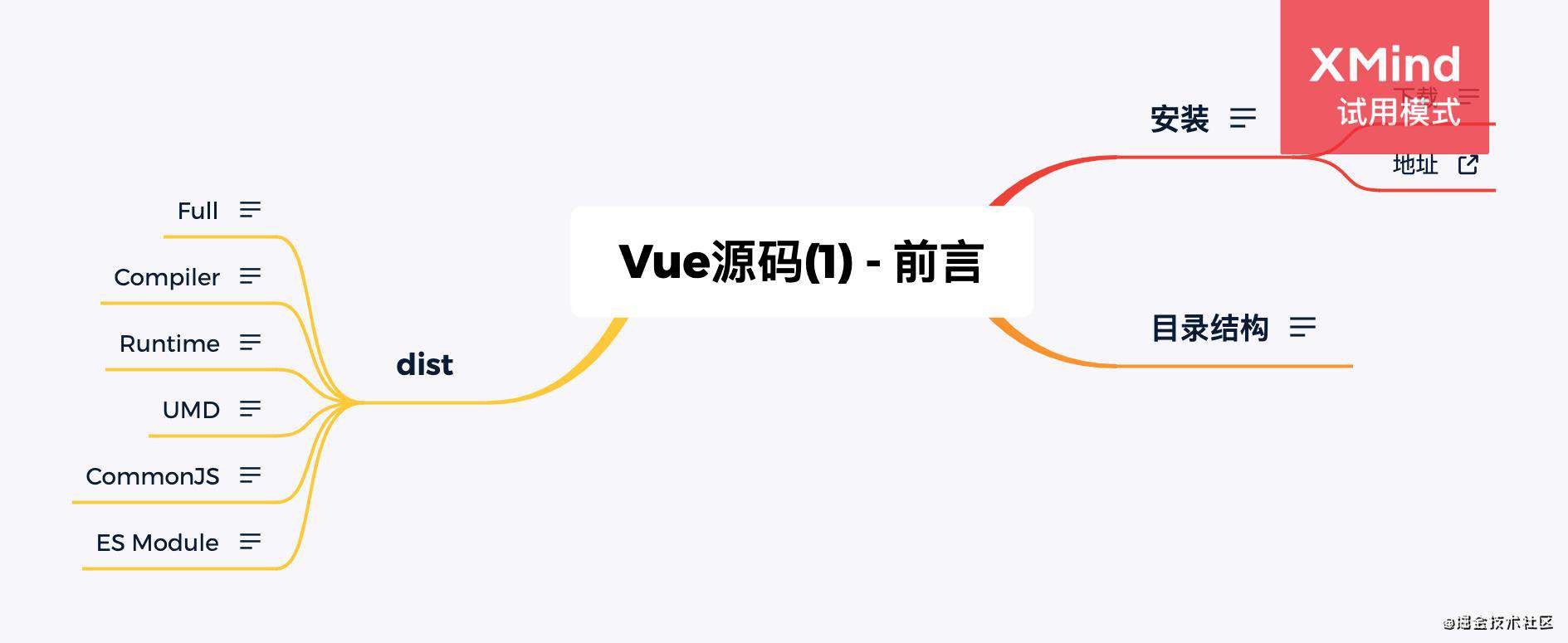
Vue 初始化
入口
// Vue 的构造函数
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
// 在 /src/core/instance/init.js,
// 1.初始化组件实例关系属性
// 2.自定义事件的监听
// 3.插槽和渲染函数
// 4.触发 beforeCreate 钩子函数
// 5.初始化 inject 配置项
// 6.初始化响应式数据,如 props, methods, data, computed, watch
// 7.初始化解析 provide
// 8.触发 created 钩子函数
this._init(options)
}
核心代码
源码核心代码顺序以深度遍历形式
initMixin
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
// 负责 Vue 的初始化过程
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
vm._self = vm // 将 vm 挂载到实例 _self 上
// 初始化组件实例关系属性,比如 $parent、$children、$root、$refs...
initLifecycle(vm)
// 自定义事件的监听:谁注册,谁监听
initEvents(vm)
// 插槽信息:vm.$slot
// 渲染函数:vm.$createElement(创建元素)
initRender(vm)
// beforeCreate 钩子函数
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
// 初始化组件的 inject 配置项
initInjections(vm)
// 数据响应式:props、methods、data、computed、watch
initState(vm)
// 解析实例 vm.$options.provide 对象,挂载到 vm._provided 上,和 inject 对应。
initProvide(vm)
// 调用 created 钩子函数
callHook(vm, 'created')
}
}
致命五问
致命五答
一答
二答
三答
四答
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
五答
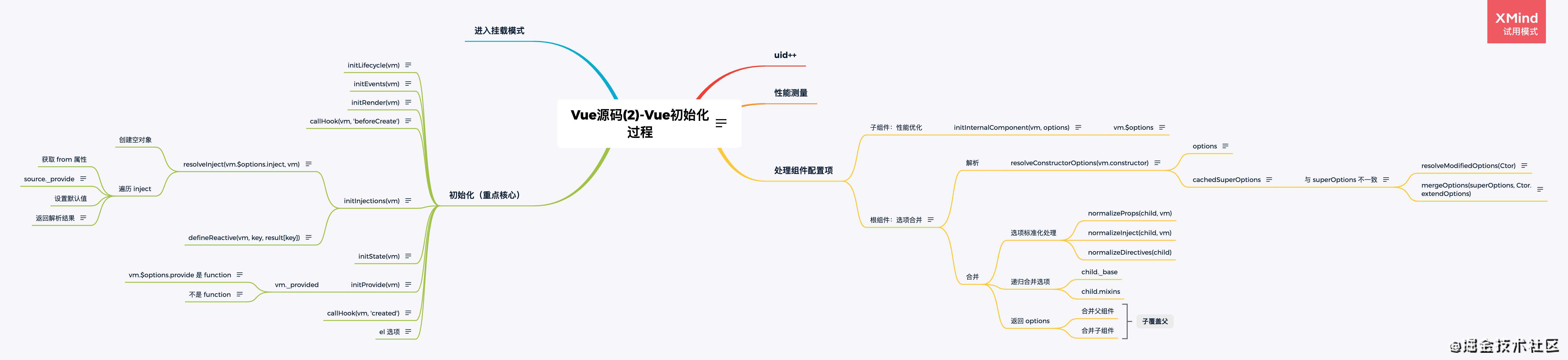
响应式原理
入口
// 初始化数据响应式:props、methods、data、computed、watch
export function initState (vm: Component) {
// 初始化当前实例的 watchers 数组
vm._watchers = []
// 拿到上边初始化合并后的 options 配置项
const opts = vm.$options
// props 响应式,挂载到 vm
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
// 1. 判断 methods 是否为函数
// 2. 方法名与 props 判重
// 3. 挂载到 vm
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
// 初始化 data 并挂载到 vm
initData(vm)
} else {
// 响应式 data 上的数据
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
// 1. 创建 watcher 实例,默认是懒执行,并挂载到 vm 上
// 2. computed 与上列 props、methods、data 判重
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
// 1. 处理 watch 对象与 watcher 实例的关系(一对一、一对多)
// 2. watch 的格式化和配置项
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}
核心代码
源码核心代码顺序以深度遍历形式
observe
// 为对象创建观察者 Observe
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
// 非对象和 VNode 实例不做响应式处理
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
// 若 value 对象上存在 __ob__ 属性并且实例是 Observer 则表示已经做过观察了,直接返回 __ob__ 属性。
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
} else if (
// 一堆判断对象的条件
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
// 创建观察者实例
ob = new Observer(value)
}
//
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
}
Observer
// 监听器类
export class Observer {
// ... 配置
constructor (value: any) {
this.value = value
// 实例化一个发布者 Dep
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this)
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
// ...处理数组
} else {
// value 为对象,为对象的每个属性设置响应式
// 也就是为啥响应式对象属性的对象也是响应式
this.walk(value)
}
}
// 值为对象时
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
// 设置响应式对象
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}
// 值为数组时
observeArray (items: Array<any>) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
// 判断,优化,创建观察者实例
observe(items[i])
}
}
}
Dep
// 订阅器类
export default class Dep {
constructor () {
// 该 dep 发布者的 id
this.id = uid++
// 存放订阅者
this.subs = []
}
// 添加订阅者
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
// 添加订阅者
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
// 向订阅者中添加当前 dep
// 在 Watcher 中也有这个操作,实现双向绑定
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
// 通知 dep 中的所有 watcher,执行 watcher.update() 方法
notify () {
// ...省略代码
}
}
Watcher
// 订阅者类,一个组件一个 watcher,订阅的数据改变时执行相应的回调函数
export default class Watcher {
...代码省略:constructor() 构造配置一个 watcher
get () {
// 打开 Dep.target,Dep.target = this
pushTarget(this)
// value 为回调函数执行的结果
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
// 这里执行 updateComponent,进入 patch 阶段更新视图。
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
// ...捕获异常
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
// 最后清除 watcher 实例的各种依赖收集
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
// watcher 订阅着 dep 发布者并进行缓存判重
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
// 缓存 dep 发布者
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
// 发布者收集订阅者 watcher
// 在 dep 中也有这个操作,实现双向绑定
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
/**
* Clean up for dependency collection.
*/
cleanupDeps () {
// ...代码省略
// 清除 dep 发布者的依赖收集
}
// 订阅者 update() 更新
update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
// // 懒执行如 computed
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
// 同步执行,watcher 实例的一个配置项
} else if (this.sync) {
// 同步执行,在使用 vm.$watch 或者 watch 选项时可以传一个 sync 选项,
this.run()
} else {
// 大部分 watcher 更新进入 watcher 的队列
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
// 1. 同步执行时会调用
// 2. 浏览器异步队列刷新 flushSchedulerQueue() 会调用
run () {
// ...代码省略,active = false 直接返回
// 使用 this.get() 获取新值来更新旧值
// 并且执行 cb 回调函数,将新值和旧值返回。
}
// 订阅者 watcher 懒执行
evaluate () {
this.value = this.get()
this.dirty = false
}
/**
* Depend on all deps collected by this watcher.
*/
depend () {
// 调用当前 watcher 依赖的所有 dep 发布者的 depend()
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
/**
* Remove self from all dependencies' subscriber list.
*/
teardown () {
// ...销毁该 watcher 实例
}
}
defineReactive
// 设置响应式对象
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
...省略
// 响应式核心
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
// get 拦截对象的读取操作
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
// 依赖收集并通知实现发布者 dep 和订阅者 watcher 的双向绑定
dep.depend()
// 依赖收集对象属性中的对象
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
// 数组情况
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
// 为数组项为对象的项添加依赖
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
// set 拦截对对象的设置操作
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
// 无新值,不用更新则直接 return
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
// 没有 setter,只读属性,则直接 return
if (getter && !setter) return
// 设置新值
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
// 将新值进行响应式
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
// dep 发布者通知更新
dep.notify()
}
})
}
proxy
const sharedPropertyDefinition = {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: noop,
set: noop
}
// 为每个属性设置拦截代理,并且挂载到 vm 上(target)
// 如 proxy(vm, `_props`, key)、proxy(vm, `_data`, key)
export function proxy (target: Object, sourceKey: string, key: string) {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = function proxyGetter () {
return this[sourceKey][key]
}
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function proxySetter (val) {
this[sourceKey][key] = val
}
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition)
}
致命五问
致命五答
一答
二答
三答
四答
五答
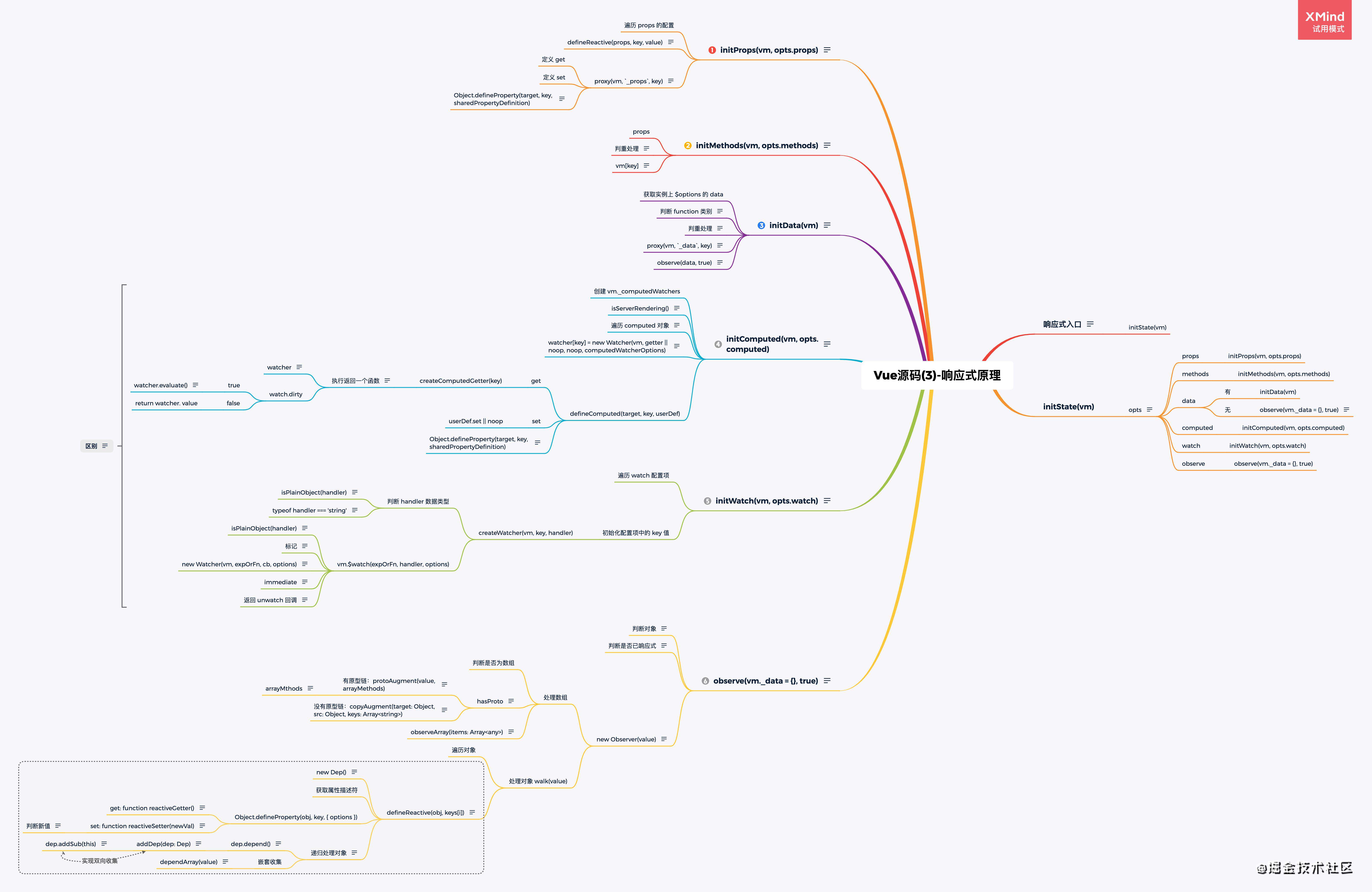
异步更新
Vue 源码的异步更新也就是响应式原理的进一步深入,下面引用以下官方对于异步更新的介绍来进一步了解这个概念。
入口
// watcher 异步更新入口
update () {
// computed 懒加载走这
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
// 当给 watcher 实例设置同步选项,也就是不走异步更新队列,直接执行 this.run() 调用更新
// 这个属性在官方文档中没有出现
this.run()
} else {
// 大部分都走 queueWatcher() 异步更新队列
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
核心代码
源码核心代码顺序以深度遍历形式
queueWatcher
// 将当前 watcher 放入 watcher 的异步更新队列
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id
// 避免重复添加相同 watcher 进异步更新队列
if (has[id] == null) {
// 缓存标记
has[id] = true
// flushing 正在刷新队列
if (!flushing) {
// 直接入队
queue.push(watcher)
} else {
// 正在刷新队列
// 将 watcher 按 id 递增顺序放入更新队列中。
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
// 用数组切割方法
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)
}
// queue the flush
// 正在刷新队列
if (!waiting) {
// 设置标记,确保只有一条异步更新队列
waiting = true
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
// 直接刷新队列:
// 1.异步更新队列 queue 升序排序,确保按 id 顺序执行
// 2.遍历队列调用每个 watcher 的 before()、run() 方法并清除当前 watcher 缓存(也就是 id 置为空)
// 3.调用 resetSchedulerState(),重置异步更新队列,等待下一次更新。(也就是清除缓存,初始化下标,俩标志设为 false)
flushSchedulerQueue()
return
}
// 也就是 vm.$nextTick、Vue.nextTick
// 做了两件事:
// 1.将回调函数(flushSchedulerQueue) 放入 callbacks 数组。
// 2.向浏览器任务队列中添加 flushCallbacks 函数,达到下次 DOM 渲染更新后立即调用
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
}
}
}
run
/**
* 由 刷新队列函数 flushSchedulerQueue 调用,如果是同步 watch,则由 this.update 直接调用,完成如下几件事:
* 1、执行实例化 watcher 传递的第二个参数,updateComponent 或者 获取 this.xx 的一个函数(parsePath 返回的函数)
* 2、更新旧值为新值
* 3、执行实例化 watcher 时传递的第三个参数,比如用户 watcher 的回调函数
*/
run () {
if (this.active) {
// 调用 watcher.get() 获取当前 watcher 的值。
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// 更新值
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
// 若果是用户定义的 watcher,执行用户 cb 函数,传递新值和旧值。
if (this.user) {
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
}
} else {
// 其余走渲染 watcher,this.cb 默认为 noop(空函数)
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}
nextTick
const callbacks = []
let pending = false
// cb 函数是 flushSchedulerQueue 异步函数队列
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
// callbacks 数组推进 try/catch 封装的 cb(避免异步队列中某个 watcher 回调函数发生错误无法排查)
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
// 执行了 flushCallbacks() 函数,表示当前浏览器异步任务队列无 flushCallbacks 函数
if (!pending) {
pending = true
// nextTick() 的重点!
// 执行 timerFunc,重新在浏览器的异步任务队列中放入 flushCallbacks 函数
timerFunc()
}
// 做 Promise 异常处理
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}
// timerFunc 将 flushCallbacks 函数放入浏览器的异步任务队列中。
// 关键在于放入浏览器异步任务队列的优先级!
// 1.Promise.resolve().then(flushCallbacks)
// 2.new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)
// 3.setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
// 4.setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
let timerFunc
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
// 第一选 Promise.resolve().then() 放入 flushCallbacks
p.then(flushCallbacks)
// 若挂掉了,采用添加空计时器来“强制”刷新微任务队列。
if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
// PhantomJS and iOS 7.x
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
// Use MutationObserver where native Promise is not available,
// e.g. PhantomJS, iOS7, Android 4.4
// (#6466 MutationObserver is unreliable in IE11)
let counter = 1
// 第二选 new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)
// 创建并返回一个新的 MutationObserver 它会在指定的DOM发生变化时被调用。
// [MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/MutationObserver)
const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)
const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter))
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
})
timerFunc = () => {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2
textNode.data = String(counter)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
// 第三选 setImmediate()
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
}
} else {
// 第四选 setTimeout() 定时器
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}
// 最终一条浏览器异步队列执行 callbacks 数组中的方法来达到 nextTick() 异步更新调用方法。
function flushCallbacks () {
// 设置标记,开启下一次浏览器异步队列更新
pending = false
const copies = callbacks.slice(0)
// 清空 callbacks 数组
callbacks.length = 0
// 执行异步更新队列其中存储的每个 flushSchedulerQueue 函数
for (let i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]()
}
}
致命五问
致命五答
一答
二答
三答
四答
五答
Vue 全局 API
入口
// 初始化全局配置和 API
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// 全局配置 config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => {
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
// 给 Vue 挂载全局配置,并拦截。
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
// Vue 的全局工具方法: Vue.util.xx
Vue.util = {
// 警告
warn,
// 选项扩展
extend,
// 选项合并
mergeOptions,
// 设置响应式
defineReactive
}
// Vue.set()
Vue.set = set
// Vue.delete()
// 处理操作与下列 set() 基本一致。
// target 为对象时,采用运算符 delete
Vue.delete = del
// Vue.nextTick()
// 不多 BB 就是上节 异步更新原理中的 nextTick
// 1.将回调函数(flushSchedulerQueue) 放入 callbacks 数组。
// 2.向浏览器任务队列中添加 flushCallbacks 函数,达到下次 DOM 渲染更新后立即调用
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
// Vue.observable() 响应式方法
// 也不多 BB 就是上上节 响应式原理中的 observe
// 为对象创建一个 Oberver 监听器实例,并监听
Vue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => {
observe(obj)
return obj
}
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
// ASSET_TYPES = ['component', 'directive', 'filter']
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
// 初始化挂载 Vue.options.xx 实例对象
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
// Vue.options._base 挂载 Vue 的构造函数
Vue.options._base = Vue
// 在 Vue.options.components 中扩展内置组件,比如 keep-alive
// 在 /src/shared/utils.js:(for in 挂载)
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
// Vue.use 全局 API:安装 plugin 插件
// 1.installedPlugins 缓存判断当前 plugin 是否已安装
// 2.调用 plugin 的安装并缓存
initUse(Vue)
// Vue.mixin 全局 API:混合配置
// this.options = mergeOptions(this.options, mixin)
// 出现相同配置项时,子选项会覆盖父选项的配置:options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key)
initMixin(Vue)
// Vue.extend 全局 API:扩展一些公共配置或方法
initExtend(Vue)
// Vue.component/directive/filter 全局 API:创造组件实例注册方法
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}
核心代码
源码核心代码顺序以深度遍历形式
set()
// 通过 vm.$set() 方法给对象或数组设置响应式
export function set (target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any {
// ...省略代码:警告
// 更新数组通过 splice 方法实现响应式更新:vm.$set(array, idx, val)
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.length = Math.max(target.length, key)
target.splice(key, 1, val)
return val
}
// 更新已有属性,直接更新最新值:vm.$set(obj, key, val)
if (key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
// 设置未定义的对象值
// 获取当前 target 对象的 __ob__,判断是否已被 observer 设置为响应式对象。
const ob = (target: any).__ob__
// ...省略代码:不能向 _isVue 和 ob.vmCount = 1 的根组件添加新值
// 若 target 不是响应式对象,直接往 target 设置静态属性
if (!ob) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
// 若 target 是响应式对象
// defineReactive() 添加上响应式属性
// 立即调用对象上的订阅器 dep 派发更新
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val)
ob.dep.notify()
return val
}
initExtend
export function initExtend (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// 每个实例构造函数(包括Vue)都有一个唯一的 cid。这使我们能够创建包装的“子对象”,用于原型继承和缓存它们的构造函数。
Vue.cid = 0
let cid = 1
// Vue 去扩展子类
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions: Object): Function {
extendOptions = extendOptions || {}
const Super = this
const SuperId = Super.cid
// 缓存多次 Vue.extend 使用同一个配置项时
const cachedCtors = extendOptions._Ctor || (extendOptions._Ctor = {})
if (cachedCtors[SuperId]) {
return cachedCtors[SuperId]
}
// 是否为有效的配置项名,避免重复
const name = extendOptions.name || Super.options.name
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && name) {
validateComponentName(name)
}
// 定义 Sub 构造函数,准备合并
const Sub = function VueComponent(options) {
// 就是 Vue 实例初始化的 init() 方法
this._init(options)
}
// 通过原型继承的方式继承 Vue
Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype)
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub
// 唯一标识
Sub.cid = cid++
// 选项合并
Sub.options = mergeOptions(
Super.options,
extendOptions
)
// 挂载自己的父类
Sub['super'] = Super
// 将上边合并的配置项初始化配置代理到 Sub.prototype._props/_computed 对象上
// 方法在下边
if (Sub.options.props) {
initProps(Sub)
}
if (Sub.options.computed) {
initComputed(Sub)
}
// 实现多态方法
Sub.extend = Super.extend
Sub.mixin = Super.mixin
Sub.use = Super.use
// 实现 component、filter、directive 三个静态方法
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
Sub[type] = Super[type]
})
// 递归组件的原理并注册
if (name) {
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
}
// 在扩展时保留对基类选项的引用,可以检查 Super 的选项是否是最新。
Sub.superOptions = Super.options
Sub.extendOptions = extendOptions
Sub.sealedOptions = extend({}, Sub.options)
// 缓存
cachedCtors[SuperId] = Sub
return Sub
}
}
function initProps (Comp) {
const props = Comp.options.props
for (const key in props) {
proxy(Comp.prototype, `_props`, key)
}
}
function initComputed (Comp) {
const computed = Comp.options.computed
for (const key in computed) {
defineComputed(Comp.prototype, key, computed[key])
}
}
initAssetRegisters
export function initAssetRegisters (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// ASSET_TYPES = ['component', 'directive', 'filter']
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
// 每个 Vue 上挂载实例注册方法
Vue[type] = function (
id: string,
definition: Function | Object
): Function | Object | void {
// 无方法
if (!definition) {
// 返回空
return this.options[type + 's'][id]
} else {
if (type === 'component' && isPlainObject(definition)) {
// 组件若为 name,默认为 id
definition.name = definition.name || id
// 调用 Vue.extend,将该组件进行扩展,也就是可以实例化该组件
definition = this.options._base.extend(definition)
}
// bind 绑定和 update 更新指令均调用该 defintion 方法
if (type === 'directive' && typeof definition === 'function') {
definition = { bind: definition, update: definition }
}
// this.options.components[id] = definition || this.options.directives[id] = definition || this.options.filter[id] = definition
this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition
return definition
}
}
})
}
致命六问
致命六答
一答
答:
1.Vue 初始化了全局的 config 配置并设为响应式。
2.暴露一些工具方法,如日志、选项扩展、选项合并、设置对象响应式
3.暴露全局初始化方法,如 Vue.set、Vue.delete、Vue.nextTick、Vue.observable
4.暴露组件配置注册方法,如 Vue.options.components、Vue.options.directives、Vue.options.filters、Vue.options._base
5.暴露全局方法,如 Vue.use、Vue.mixin、Vue.extend、Vue.initAssetRegisters()
二答
三答
四答
五答
六答
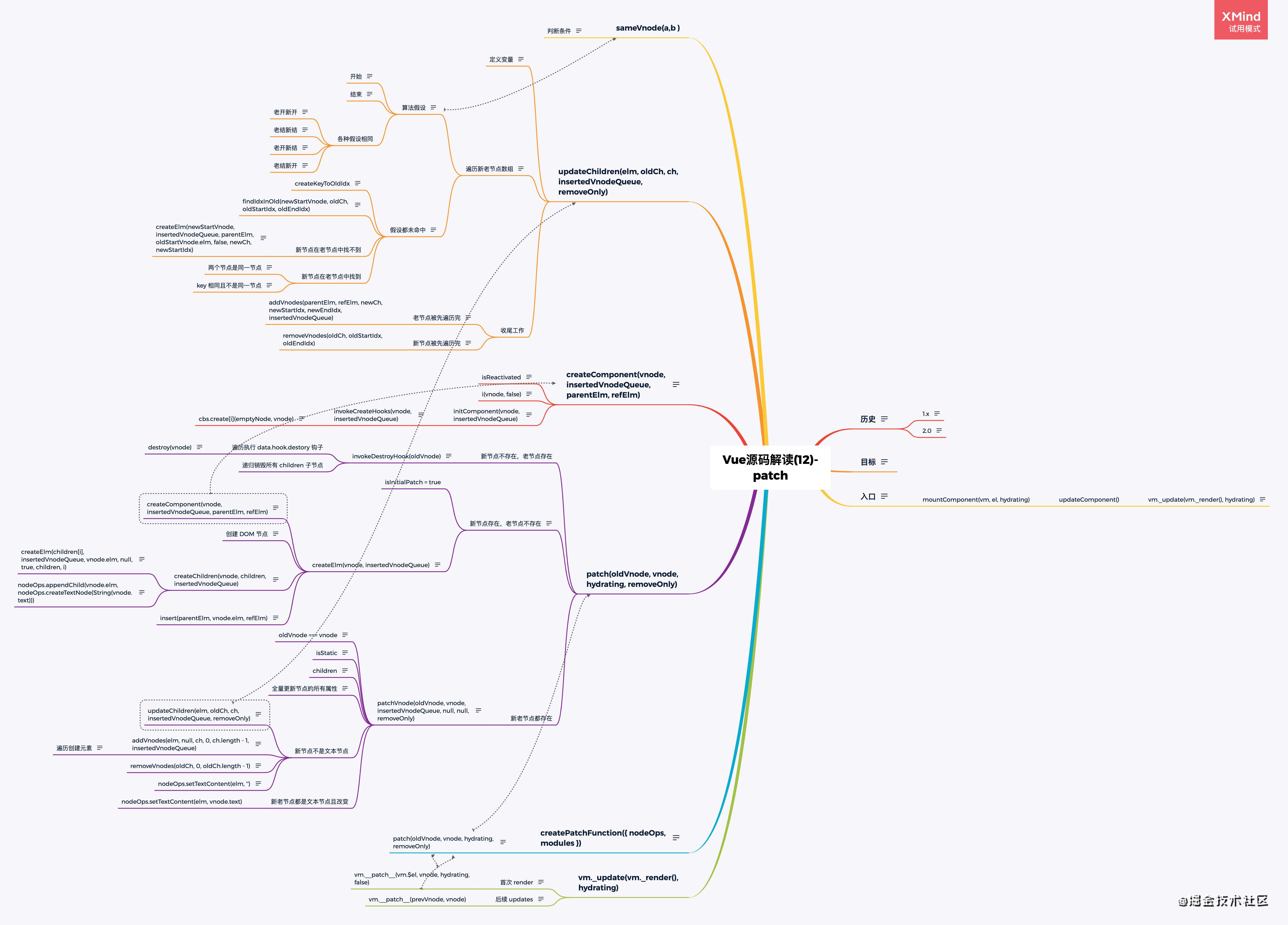
Vue patch 渲染更新
入口
// patch 渲染更新的入口
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
const prevEl = vm.$el
// vm._vnode 由 vm._render() 生成
// 老虚拟节点
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const restoreActiveInstance = setActiveInstance(vm)
// 新虚拟节点
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) {
// 只有新虚拟节点,即为首次渲染,初始化页面时走这里
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */)
} else {
// 有新老节点,即为更新数据渲染,更新页面时走这里
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
// 缓存虚拟节点
restoreActiveInstance()
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
}
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
// 当父子节点的虚拟节点一致,也更新父节点的 $el
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}
核心代码
源码核心代码顺序以深度遍历形式
patch()
// patch 方法,hydrating 是否服务端渲染,removeOnly 是否使用了 <transition group> 过渡组
// 1.vnode 不存在,则摧毁 oldVnode
// 2.vnode 存在且 oldVnode 不存在,表示组件初次渲染,添加标示且创建根节点
// 3.vnode 和 oldVnode 都存在时
// 3.1.oldVnode 不是真实节点表示更新阶段(都是虚拟节点),执行 patchVnode,生成 vnode
// 3.2.oldVnode 是真实元素,表示初始化渲染,执行 createElm 基于 vnode 创建整棵 DOM 树并插入到 body 元素下,递归更新父占位符节点元素,完成更新后移除 oldnode。
// 4.最后 vnode 插入队列并生成返回 vnode
function patch(oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {
// vnode 不存在,表示删除节点,则摧毁 oldVnode
if (isUndef(vnode)) {
// 执行 oldVnode 也就是未更新组件生命周期 destroy 钩子
// 执行 oldVnode 各个模块(style、class、directive 等)的 destroy 方法
// 如果有 children 递归调用 invokeDestroyHook
if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
let isInitialPatch = false
const insertedVnodeQueue = []
// vnode 存在且 oldVnode 不存在
if (isUndef(oldVnode)) {
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root element
// 组件初次渲染,创建根节点
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
// 判断 oldVnode 是否为真实元素
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
// 不是真实元素且 oldVnode 和 vnode 是同一个节点,执行 patchVnode 直接更新节点
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly)
// 真实元素或者新老节点不相同
} else {
if (isRealElement) {
// mounting to a real element
// check if this is server-rendered content and if we can perform
// a successful hydration.
// oldVnode 是元素节点且有服务器渲染的属性
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR)
hydrating = true
}
// ...省略代码,服务端渲染执行 invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true)
// either not server-rendered, or hydration failed.
// create an empty node and replace it
// 不是服务端渲染,或 hydration 失败,创建一个空的 vnode 节点
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode)
}
// 拿到 oldVnode /父 oldVnode 的真实元素
const oldElm = oldVnode.elm
const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm)
// 基于 vnode 创建整棵 DOM 树并插入到 body 元素下
createElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
// extremely rare edge case: do not insert if old element is in a
// leaving transition. Only happens when combining transition +
// keep-alive + HOCs. (#4590)
oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
)
// 递归更新父占位符节点元素
if (isDef(vnode.parent)) {
let ancestor = vnode.parent
const patchable = isPatchable(vnode)
while (ancestor) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) {
cbs.destroy[i](ancestor)
}
ancestor.elm = vnode.elm
if (patchable) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, ancestor)
}
// #6513
// invoke insert hooks that may have been merged by create hooks.
// e.g. for directives that uses the "inserted" hook.
const insert = ancestor.data.hook.insert
if (insert.merged) {
// start at index 1 to avoid re-invoking component mounted hook
for (let i = 1; i < insert.fns.length; i++) {
insert.fns[i]()
}
}
} else {
registerRef(ancestor)
}
ancestor = ancestor.parent
}
}
// 完成更新,移除 oldVnode
// 当有父节点时,指定范围删除自己
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes([oldVnode], 0, 0)
// 没有父节点时
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
}
}
}
// 将虚拟节点插入队列中
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch)
return vnode.elm
}
createElm
// 基于 vnode 创建真实 DOM 树
function createElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
parentElm,
refElm,
nested,
ownerArray,
index
) {
// 直接复制缓存的 vnode
if (isDef(vnode.elm) && isDef(ownerArray)) {
vnode = ownerArray[index] = cloneVNode(vnode)
}
vnode.isRootInsert = !nested // for transition enter check
// 创建 vnode 组件
if (createComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)) {
return
}
// 获取 data 对象
const data = vnode.data
// 所有的孩子节点
const children = vnode.children
const tag = vnode.tag
if (isDef(tag)) {
// ...省略代码:当标签未知时发出警告
// 创建新节点
vnode.elm = vnode.ns
? nodeOps.createElementNS(vnode.ns, tag)
: nodeOps.createElement(tag, vnode)
setScope(vnode)
// 递归创建所有子节点(普通元素、组件)
createChildren(vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue)
if (isDef(data)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
}
// 将节点插入父节点
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && data && data.pre) {
creatingElmInVPre--
}
// 处理注释节点并插入父节点
} else if (isTrue(vnode.isComment)) {
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createComment(vnode.text)
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
// 处理文本节点并插入父节点
} else {
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createTextNode(vnode.text)
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
}
patchVnode
// 更新节点
// 1.新老节点相同,直接返回
// 2.静态节点,克隆复用
// 3.全部遍历更新 vnode.data 上的属性
// 4.若是文本节点,直接更新文本
// 5.若不是文本节点
// 5.1 都有孩子,则递归执行 updateChildren 方法(diff 算法更新)
// 5.2 ch 有 oldCh 没有,则表明新增节点 addVnodes
// 5.3 ch 没有 oldCh 有,则表明删除节点 removeVnodes
function patchVnode(
oldVnode,
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
ownerArray,
index,
removeOnly
) {
// 老节点和新节点相同,直接返回
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return
}
// 缓存过的 vnode,直接克隆 vnode
if (isDef(vnode.elm) && isDef(ownerArray)) {
// clone reused vnode
vnode = ownerArray[index] = cloneVNode(vnode)
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm
// 异步占位符节点
if (isTrue(oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder)) {
if (isDef(vnode.asyncFactory.resolved)) {
hydrate(oldVnode.elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true
}
return
}
// reuse element for static trees.
// note we only do this if the vnode is cloned -
// if the new node is not cloned it means the render functions have been
// reset by the hot-reload-api and we need to do a proper re-render.
if (isTrue(vnode.isStatic) &&
isTrue(oldVnode.isStatic) &&
vnode.key === oldVnode.key &&
(isTrue(vnode.isCloned) || isTrue(vnode.isOnce))
) {
// 新旧节点都是静态的而且两个节点的 key 一样,并且新节点被克隆了或者新节点有 v-once 指令,则用 oldVnode 的组件节点,且跳出,不进行 diff 更新
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance
return
}
// 执行组件的 prepatch 钩子
let i
const data = vnode.data
if (isDef(data) && isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.prepatch)) {
i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
// 孩子
const oldCh = oldVnode.children
const ch = vnode.children
// 更新 vnode 上的属性
if (isDef(data) && isPatchable(vnode)) {
// 全部遍历更新(Vue3 做了大量优化)
for (i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i) cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode)
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.update)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
// 新节点不是文本节点
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
// 如果 oldCh 和 ch 不同,开始更新子节点(也就是 diff 算法)
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)
// 只有 ch
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 检查是否有重复 key 值,给予警告
checkDuplicateKeys(ch)
}
// oldVnode 中有文本信息,创建文本节点并添加
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 只有 oldCh
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
// 删除节点的操作
removeVnodes(oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
// oldVnode 上有文本
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
// 置空文本
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
// vnode 是文本,若 oldVnode 和 vnode 文本不相同
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
// 更新文本节点
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
// 还有 data 数据,执行组件的 prepatch 钩子
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.postpatch))
i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
}
removeVnodes
// 删除 vnode 节点
function removeVnodes(vnodes, startIdx, endIdx) {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
const ch = vnodes[startIdx]
// 有子节点
if (isDef(ch)) {
// 不是文本节点
if (isDef(ch.tag)) {
// patch() 方法中有说明
removeAndInvokeRemoveHook(ch)
invokeDestroyHook(ch)
} else { // Text node
// 直接移除该元素
removeNode(ch.elm)
}
}
}
}
updateChildren
// 更新子节点采用了 diff 算法
// 做了四种假设,假设新老节点开头结尾有相同节点的情况,一旦命中假设,就避免了一次循环,以提高执行效率
// 如果不幸没有命中假设,则执行遍历,从老节点中找到新开始节点
// 找到相同节点,则执行 patchVnode,然后将老节点移动到正确的位置
// 如果老节点先于新节点遍历结束,则剩余的新节点执行新增节点操作
// 如果新节点先于老节点遍历结束,则剩余的老节点执行删除操作,移除这些老节点
function updateChildren(parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
// 为 diff 算法假设做初始化:新老子节点的头尾下标和对应值
let oldStartIdx = 0
let newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm
// <transition-group> 的标识符
const canMove = !removeOnly
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 若重复 key 则发出警告
checkDuplicateKeys(newCh)
}
// 遍历新老节点数组,直到一方取完值
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
// 老开始节点无值,表示更新过,向右移动下标(往后看)
if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // Vnode has been moved left
// 老结束节点无值,表示更新过,向左移动下标(往后看)
} else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
// 新老的开始/结束节点是相同节点,返回 patchVnode 阶段,不更新比较
// 因为两个都不比较,同时移动下标
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
// 新尾和老头/新头和老尾相等
// 一样需要移动下标,进行 ch 数组下个节点的判断
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // Vnode moved right
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx)
// <transtion-group> 包裹的组件时使用,如轮播图情况。
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm))
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
// 四种常规 web 操作假设都不成立,则不能优化,开始遍历更新
} else {
// 当老节点的 key 对应不上 idx 时
// 在指定 idx 的范围内,找到 key 在老节点中的下标位置
// 形成 map = { key1: id1, key2: id2, ...}
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
// 若新开始节点有 key 值,在老节点的 key 和 id 映射表 map 中找到返回对应的 id 下标值
// 若新开始节点没有 key 值,则找到老节点数组中新开始节点的值,返回 id 下标
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
// 若新开始节点不存在老节点中,那就是新建元素
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) { // New element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
// 新开始节点存在老节点中,开始判断情况更新
} else {
vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
// 如果两个节点不但 key 相同,节点也是相同,则直接返回 patchVnode
if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
// 将该老节点置为 空,避免新节点反复找到同一个节点
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined
// 还是判断 <transition-group> 标签的情况
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
} else {
// 两个节点虽然 key 相等,但节点不相等,看作新元素,创建节点
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
}
}
// 老节点向后移动一个
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
}
// 新老节点某个数组被遍历完了
// 新的有多余,那就是新增
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 老的有多余,那就是删除
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
}
致命七问
致命七答
一答
二答
三答
四答
五答
六答
七答
最后
class VNode {
tag: string | void;
data: VNodeData | void;
children: ?Array<VNode>;
text: string | void;
elm: Node | void;
ns: string | void;
context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scope
key: string | number | void;
componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void;
componentInstance: Component | void; // component instance
parent: VNode | void; // component placeholder node
// strictly internal
raw: boolean; // contains raw HTML? (server only)
isStatic: boolean; // hoisted static node
isRootInsert: boolean; // necessary for enter transition check
isComment: boolean; // empty comment placeholder?
isCloned: boolean; // is a cloned node?
isOnce: boolean; // is a v-once node?
asyncFactory: Function | void; // async component factory function
asyncMeta: Object | void;
isAsyncPlaceholder: boolean;
ssrContext: Object | void;
fnContext: Component | void; // real context vm for functional nodes
fnOptions: ?ComponentOptions; // for SSR caching
devtoolsMeta: ?Object; // used to store functional render context for devtools
fnScopeId: ?string; // functional scope id support
constructor (
tag?: string,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: ?Array<VNode>,
text?: string,
elm?: Node,
context?: Component,
componentOptions?: VNodeComponentOptions,
asyncFactory?: Function
) {
this.tag = tag
this.data = data
this.children = children
this.text = text
this.elm = elm
this.ns = undefined
this.context = context
this.fnContext = undefined
this.fnOptions = undefined
this.fnScopeId = undefined
this.key = data && data.key
this.componentOptions = componentOptions
this.componentInstance = undefined
this.parent = undefined
this.raw = false
this.isStatic = false
this.isRootInsert = true
this.isComment = false
this.isCloned = false
this.isOnce = false
this.asyncFactory = asyncFactory
this.asyncMeta = undefined
this.isAsyncPlaceholder = false
}
// DEPRECATED: alias for componentInstance for backwards compat.
/* istanbul ignore next */
get child (): Component | void {
return this.componentInstance
}
}
思维导图
- Vue源码(1) - 前言
- Vue源码(2)-初始化
- Vue源码(3)-响应式原理
- Vue源码(4)-异步更新
- Vue源码(5)-全局API
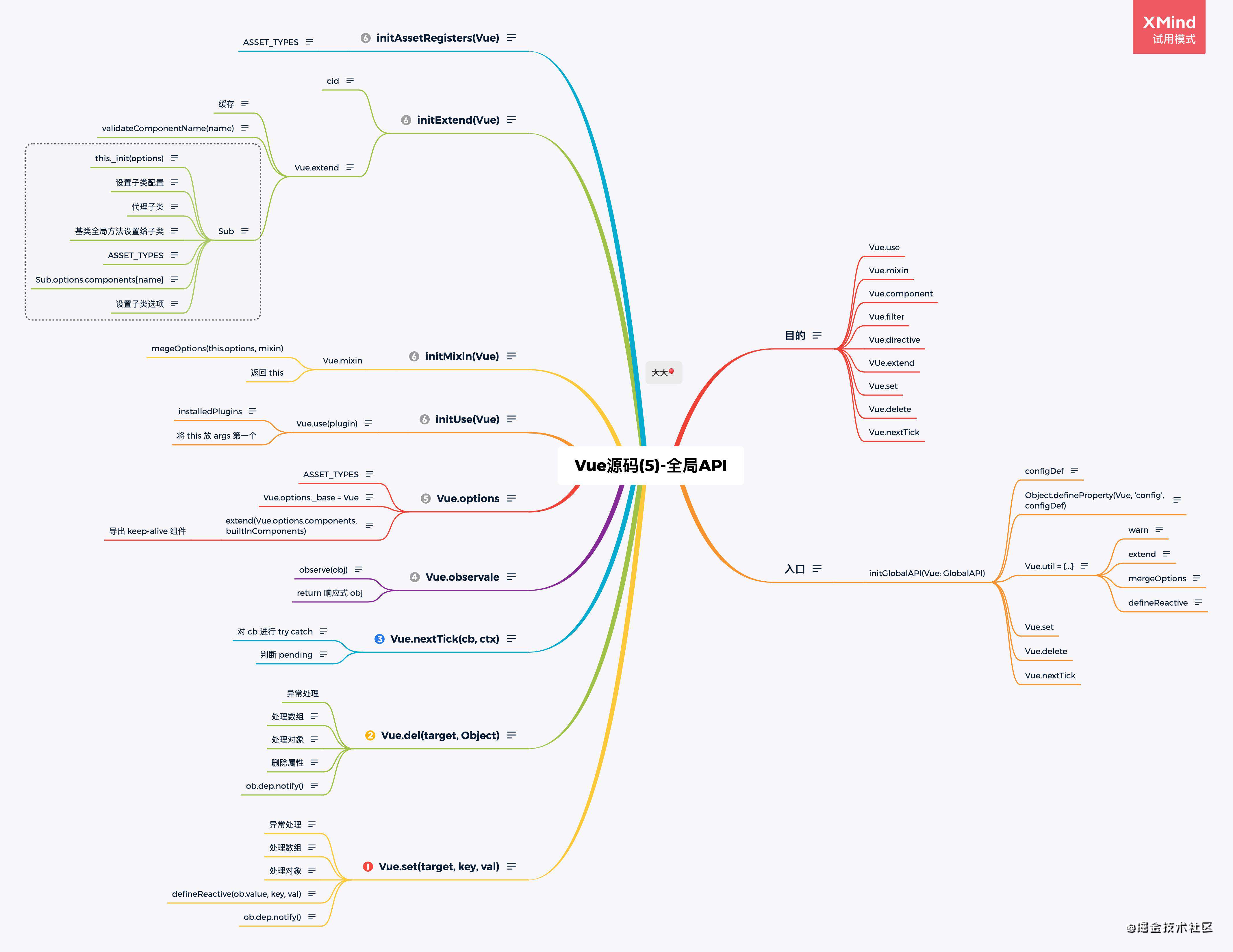
- Vue源码(6)-实例方法
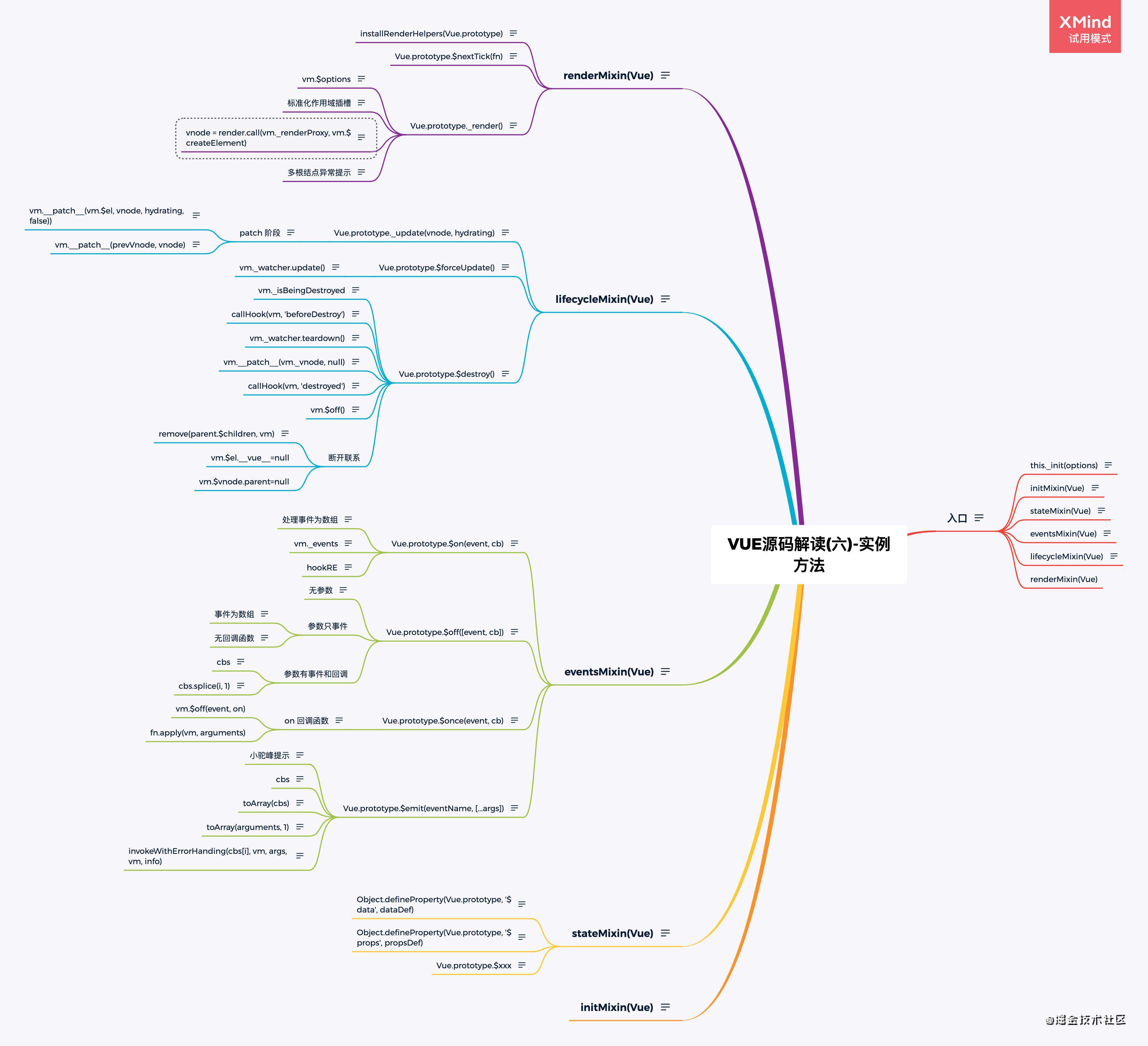
- Vue源码(7)-Hook Event
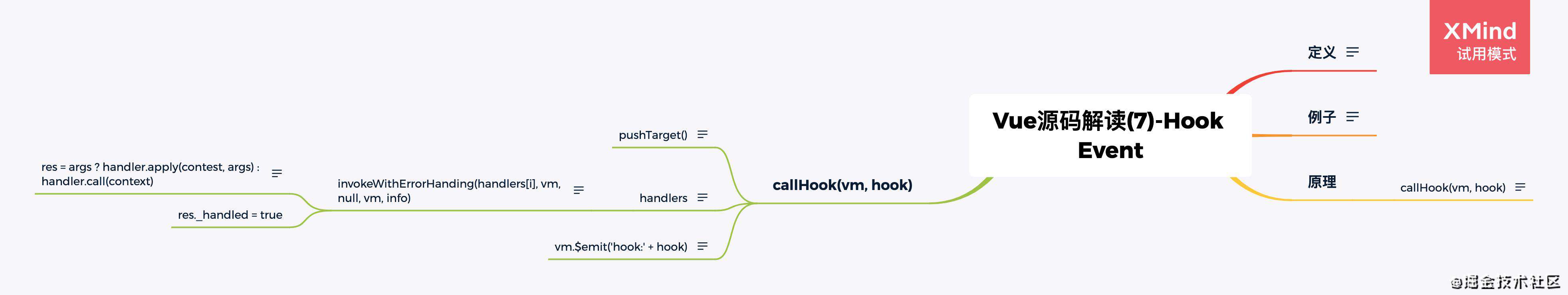
- Vue源码(8)-编译器(解析)
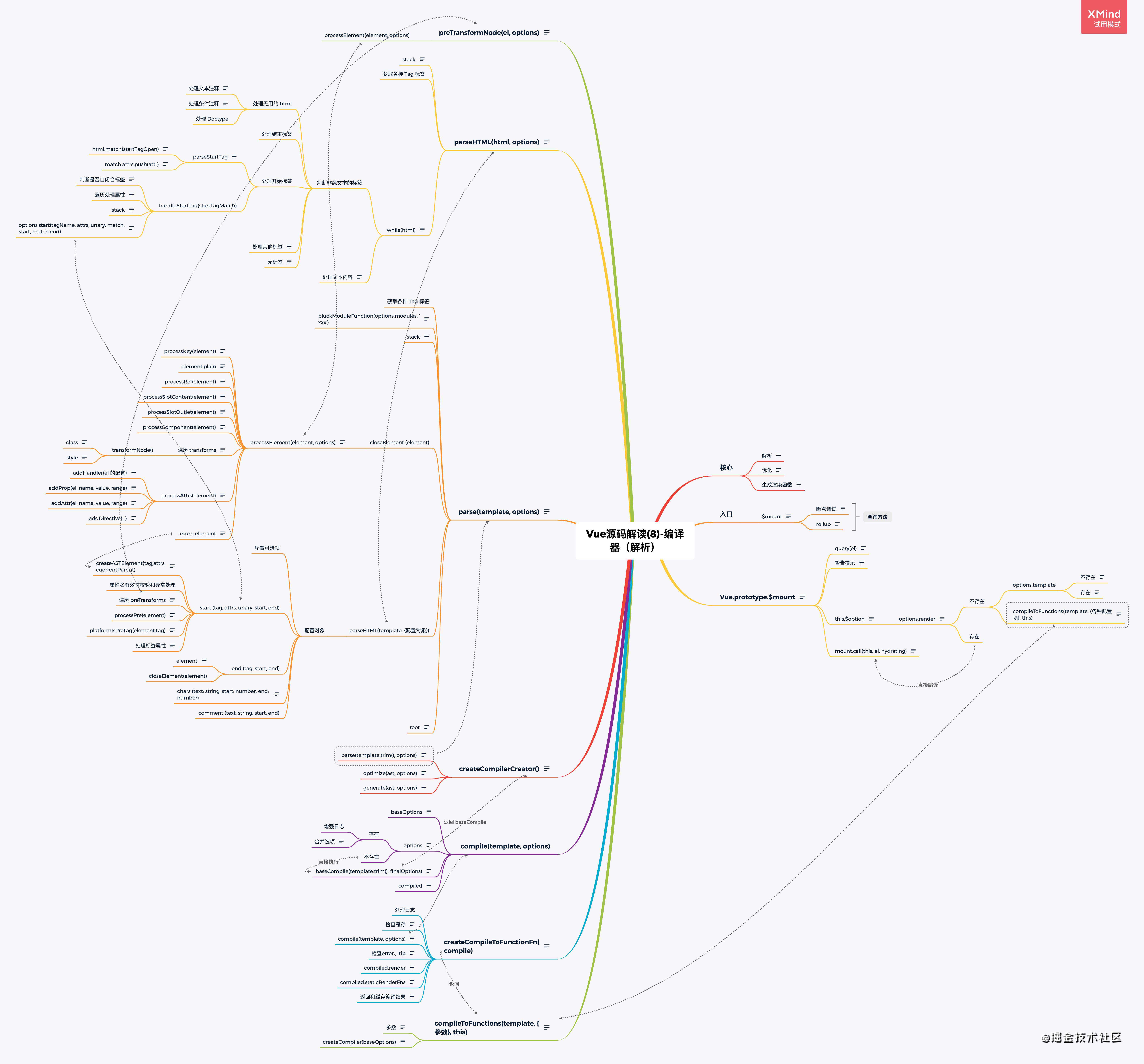
- Vue源码(9)-编译器之优化
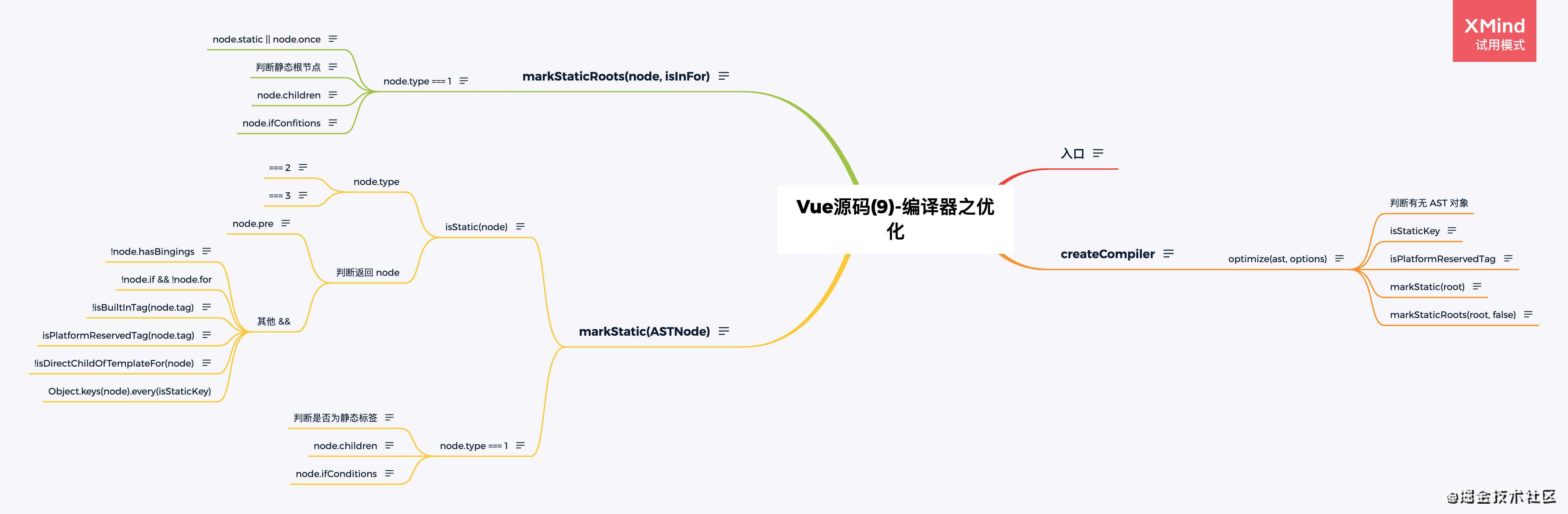
- Vue源码(10)—编译器之生成渲染函数
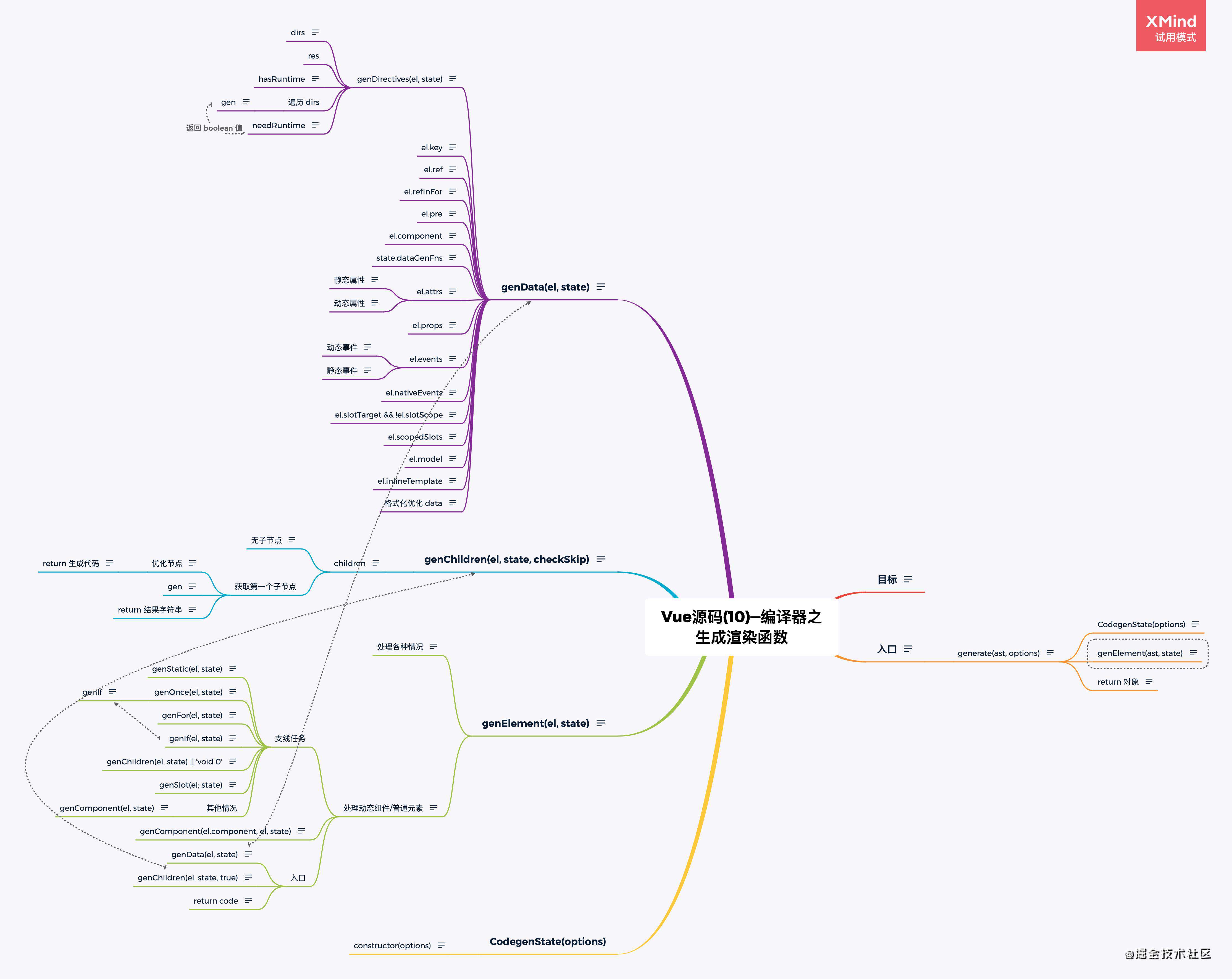
- Vue源码(11)-render helper
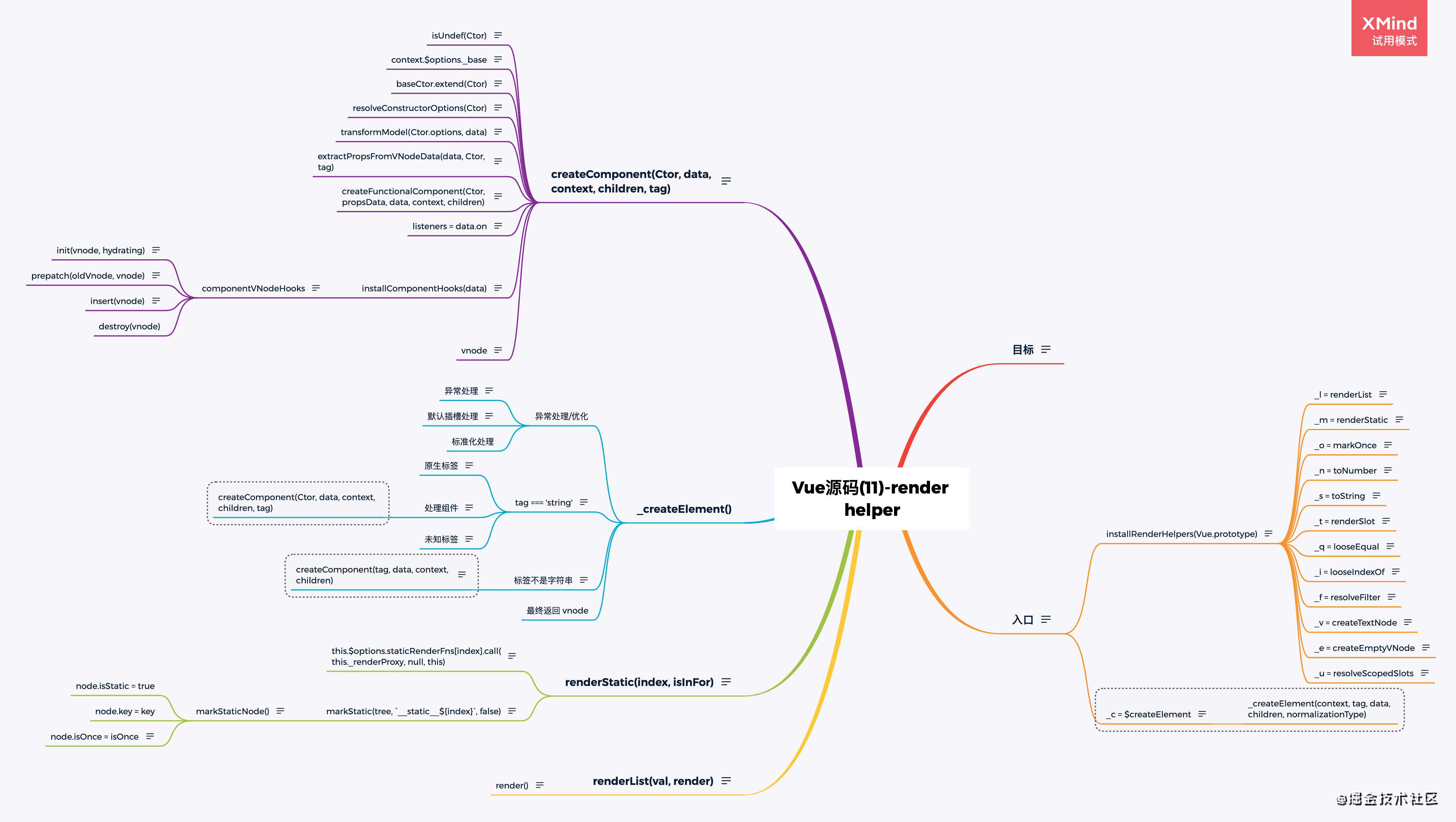
- Vue源码(12)-patch
结尾
最后希望这篇源码总结对小伙伴们有所帮助噢!若有纰漏或瑕疵,麻烦指教一二!
? 点赞关注(暗示)
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!