单向链表和双向链表
单向链表
- 只能从头遍历到尾或者从尾遍历到头(一般从头到尾)。
- 链表相连的过程是单向的,实现原理是上一个节点中有指向下一个节点的引用。
- 单向链表有一个比较明显的缺点:可以轻松到达下一个节点,但回到前一个节点很难,在实际开发中, 经常会遇到需要回到上一个节点的情况。
双向链表
- 既可以从头遍历到尾,也可以从尾遍历到头。
- 链表相连的过程是双向的。实现原理是一个节点既有向前连接的引用,也有一个向后连接的引用。
- 双向链表可以有效的解决单向链表存在的问题。
- 双向链表缺点:
- 每次在插入或删除某个节点时,都需要处理四个引用,而不是两个,实现起来会困难些。
- 相对于单向链表,所占内存空间更大一些。
- 但是,相对于双向链表的便利性而言,这些缺点微不足道。
双向链表结构
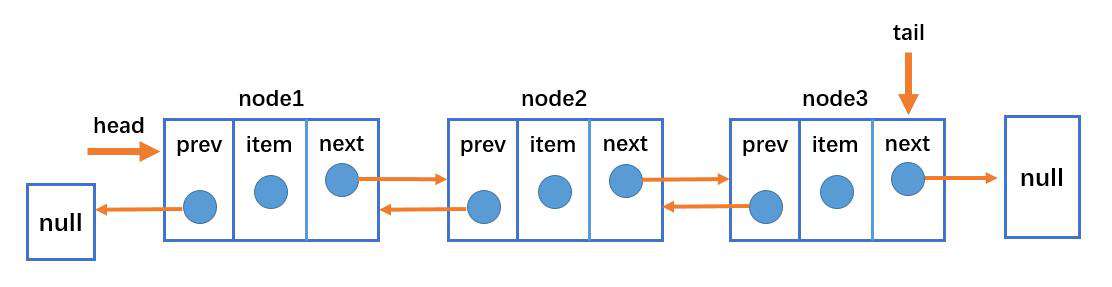
- 双向链表不仅有 head 指针指向第一个节点,而且有 tail 指针指向最后一个节点。
- 每一个节点由三部分组成:item 储存数据、prev 指向前一个节点、next 指向后一个节点。
- 双向链表的第一个节点的 prev 指向 null。
- 双向链表的最后一个节点的 next 指向 null。
双向链表常见的操作
append(element)向链表尾部追加一个新元素。insert(position, element)向链表的指定位置插入一个新元素。getElement(position)获取指定位置的元素。indexOf(element)返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素就返回 -1。update(position, element)修改指定位置上的元素。removeAt(position)从链表中的删除指定位置的元素。remove(element)从链表删除指定的元素。isEmpty()如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回trun,如果链表长度大于 0 则返回false。size()返回链表包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似。toString()由于链表项使用了 Node 类,就需要重写继承自 JavaScript 对象默认的toString方法,让其只输出元素的值。forwardString()返回正向遍历节点字符串形式。backwordString()返回反向遍历的节点的字符串形式。
双向链表的封装
创建双向链表类 DoublyLinkedList
- DoublyNode 类继承单向链表的 Node 类,新添加
this.prev属性,该属性用于指向上一个节点。 - DoublyLinkedList 类继承 LinkedList 类,新添加
this.tail属性,该属性指向末尾的节点。
// 双向链表的节点类(继承单向链表的节点类)
class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element) {
super(element);
this.prev = null;
}
}
// 双向链表类继承单向链表类
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
}
append(element)
// append(element) 往双向链表尾部追加一个新的元素
// 重写 append()
append(element) {
// 1、创建双向链表节点
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 2、追加元素
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// !!跟单向链表不同,不用通过循环找到最后一个节点
// 巧妙之处
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
insert(position, element)
// insert(position, data) 插入元素
// 重写 insert()
insert(position, element) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2、创建新的双向链表节点
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 3、判断多种插入情况
if (position === 0) { // 在第 0 个位置插入
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
//== 巧妙之处:相处腾出 this.head 空间,留个 newNode 来赋值 ==//
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.perv = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 在最后一个位置插入
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else { // 在 0 ~ this.length 位置中间插入
let targetIndex = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
// 找到要插入位置的节点
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 交换节点信息
previousNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = previousNode;
newNode.next = currentNode;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
insert(position, element)
// insert(position, data) 插入元素
// 重写 insert()
insert(position, element) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2、创建新的双向链表节点
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 3、判断多种插入情况
if (position === 0) { // 在第 0 个位置插入
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
//== 巧妙之处:相处腾出 this.head 空间,留个 newNode 来赋值 ==//
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.perv = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 在最后一个位置插入
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else { // 在 0 ~ this.length 位置中间插入
let targetIndex = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
// 找到要插入位置的节点
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 交换节点信息
previousNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = previousNode;
newNode.next = currentNode;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
removeAt(position)
// removeAt() 删除指定位置的节点
// 重写 removeAt()
removeAt(position) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length - 1) return null;
// 2、根据不同情况删除元素
let currentNode = this.head;
if (position === 0) { // 删除第一个节点的情况
if (this.length === 1) { // 链表内只有一个节点的情况
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else { // 链表内有多个节点的情况
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) { // 删除最后一个节点的情况
currentNode = this.tail;
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
} else { // 删除 0 ~ this.length - 1 里面节点的情况
let targetIndex = 0;
let previousNode = null;
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next.perv = previousNode;
}
this.length--;
return currentNode.data;
}
update(position, data)
// update(position, data) 修改指定位置的节点
// 重写 update()
update(position, data) {
// 1、删除 position 位置的节点
const result = this.removeAt(position);
// 2、在 position 位置插入元素
this.insert(position, data);
return result;
}
forwardToString()
// forwardToString() 链表数据从前往后以字符串形式返回
forwardToString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = '';
// 遍历所有的节点,拼接为字符串,直到节点为 null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + '--';
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
backwardString()
// backwardString() 链表数据从后往前以字符串形式返回
backwardString() {
let currentNode = this.tail;
let result = '';
// 遍历所有的节点,拼接为字符串,直到节点为 null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + '--';
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return result;
}
其他方法的实现
双向链表的其他方法通过继承单向链表来实现。
完整实现
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
// ------------ 链表的常见操作 ------------ //
// append(element) 往双向链表尾部追加一个新的元素
// 重写 append()
append(element) {
// 1、创建双向链表节点
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 2、追加元素
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// !!跟单向链表不同,不用通过循环找到最后一个节点
// 巧妙之处
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
// insert(position, data) 插入元素
// 重写 insert()
insert(position, element) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2、创建新的双向链表节点
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 3、判断多种插入情况
if (position === 0) {
// 在第 0 个位置插入
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
//== 巧妙之处:相处腾出 this.head 空间,留个 newNode 来赋值 ==//
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.perv = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) {
// 在最后一个位置插入
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// 在 0 ~ this.length 位置中间插入
let targetIndex = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
// 找到要插入位置的节点
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 交换节点信息
previousNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = previousNode;
newNode.next = currentNode;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
// getData() 继承单向链表
getData(position) {
return super.getData(position);
}
// indexOf() 继承单向链表
indexOf(data) {
return super.indexOf(data);
}
// removeAt() 删除指定位置的节点
// 重写 removeAt()
removeAt(position) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length - 1) return null;
// 2、根据不同情况删除元素
let currentNode = this.head;
if (position === 0) {
// 删除第一个节点的情况
if (this.length === 1) {
// 链表内只有一个节点的情况
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
// 链表内有多个节点的情况
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) {
// 删除最后一个节点的情况
currentNode = this.tail;
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
} else {
// 删除 0 ~ this.length - 1 里面节点的情况
let targetIndex = 0;
let previousNode = null;
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next.perv = previousNode;
}
this.length--;
return currentNode.data;
}
// update(position, data) 修改指定位置的节点
// 重写 update()
update(position, data) {
// 1、删除 position 位置的节点
const result = this.removeAt(position);
// 2、在 position 位置插入元素
this.insert(position, data);
return result;
}
// remove(data) 删除指定 data 所在的节点(继承单向链表)
remove(data) {
return super.remove(data);
}
// isEmpty() 判断链表是否为空
isEmpty() {
return super.isEmpty();
}
// size() 获取链表的长度
size() {
return super.size();
}
// forwardToString() 链表数据从前往后以字符串形式返回
forwardToString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = "";
// 遍历所有的节点,拼接为字符串,直到节点为 null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + "--";
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
// backwardString() 链表数据从后往前以字符串形式返回
backwardString() {
let currentNode = this.tail;
let result = "";
// 遍历所有的节点,拼接为字符串,直到节点为 null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + "--";
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return result;
}
}
代码测试
const doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList();
// append() 测试
doublyLinkedList.append("ZZ");
doublyLinkedList.append("XX");
doublyLinkedList.append("CC");
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// insert() 测试
doublyLinkedList.insert(0, "00");
doublyLinkedList.insert(2, "22");
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// getData() 测试
console.log(doublyLinkedList.getData(1)); //--> ZZ
// indexOf() 测试
console.log(doublyLinkedList.indexOf("XX")); //--> 3
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// removeAt() 测试
doublyLinkedList.removeAt(0);
doublyLinkedList.removeAt(1);
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// update() 测试
doublyLinkedList.update(0, "111111");
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// remove() 测试
console.log(doublyLinkedList.remove("111111"));
console.log(doublyLinkedList.remove("22222"));
console.log(doublyLinkedList);
// forwardToString() 测试
console.log(doublyLinkedList.forwardToString());
// backwardString() 测试
console.log(doublyLinkedList.backwardString());
专辑系列
- 从 0 开始学习 JavaScript 数据结构与算法(一)前言
- 从 0 开始学习 JavaScript 数据结构与算法(二)数组
- 从 0 开始学习 JavaScript 数据结构与算法(三)栈
- 从 0 开始学习 JavaScript 数据结构与算法(四)队列
- 从 0 开始学习 JavaScript 数据结构与算法(五)优先队列
- 从 0 开始学习 JavaScript 数据结构与算法(六)单向链表
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!