前言
前一篇文章介绍了 fastify 通过 schema 来序列化 JSON,为 Node.js 服务提升性能的方法。今天的文章会介绍 fastify 使用的路由库,翻阅其源码(lib/route.js)可以发现,fastify 的路由库并不是内置的,而是使用了一个叫做 find-my-way 的路由库。
这个路由库的简介也很有意思,号称“超级无敌快”的 HTTP 路由。
看上去 fastify 像是依赖了第三方的路由库,其实这两个库的作者是同一批人。

如何使用
find-my-way 通过 on 方法绑定路由,并且提供了 HTTP 所有方法的简写。
const router = require('./index')()
router.on('GET', '/a', (req, res, params) => {
res.end('{"message": "GET /a"}')
})
router.get('/a/b', (req, res, params) => {
res.end('{"message": "GET /a/b"}')
}))
其实内部就是通过遍历所有的 HTTP 方法名,然后在原型上扩展的。
Router.prototype.on = function on (method, path, opts, handler) {
if (typeof opts === 'function') {
// 如果 opts 为函数,表示此时的 opts 为 handler
handler = opts
opts = {}
}
// ...
}
for (var i in http.METHODS) {
const m = http.METHODS[i]
const methodName = m.toLowerCase()
// 扩展方法简写
Router.prototype[methodName] = function (path, handler) {
return this.on(m, path, handler)
}
}
绑定的路由可以通过 lookup 调用,只要将原生的 req 和 res 传入 lookup 即可。
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 只要将原生的 req 和 res 传入 lookup 即可
router.lookup(req, res)
})
server.listen(3000)
find-my-way 会通过 req.method/req.url 找到对应的 handler,然后进行调用。
Router.prototype.lookup = function lookup (req, res) {
var handle = this.find(req.method, sanitizeUrl(req.url))
if (handle === null) {
return this._defaultRoute(req, res, ctx)
}
// 调用 hendler
return handle.handler(req, res, handle.params)
}
路由的添加和查找都基于树结构来实现的,下面我们来看看具体的实现。
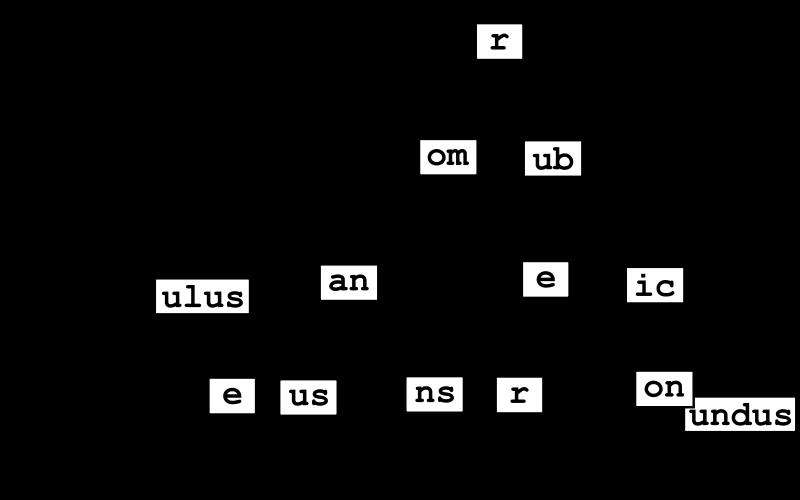
Radix Tree
find-my-way 采用了名为 Radix Tree(基数树) 的算法,也被称为 Prefix Tree(前缀树)。Go 语言里常用的 web 框架echo和gin都使用了Radix Tree作为路由查找的算法。
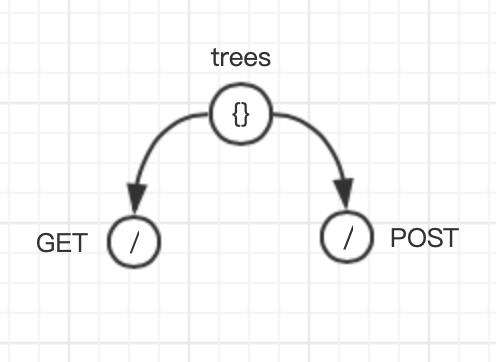
在 find-my-way 中每个 HTTP 方法(GET、POST、PUT ...)都会对应一棵前缀树。
// 方法有所简化...
function Router (opts) {
opts = opts || {}
this.trees = {}
this.routes = []
}
Router.prototype.on = function on (method, path, opts, handler) {
if (typeof opts === 'function') {
// 如果 opts 为函数,表示此时的 opts 为 handler
handler = opts
opts = {}
}
this._on(method, path, opts, handler)
}
Router.prototype._on = function on (method, path, opts, handler) {
this.routes.push({
method, path, opts, handler,
})
// 调用 _insert 方法
this._insert(method, path, handler)
}
Router.prototype._insert = function _insert (method, path, handler) {
// 取出方法对应的 tree
var currentNode = this.trees[method]
if (typeof currentNode === 'undefined') {
// 首次插入构造一个新的 Tree
currentNode = new Node({ method })
this.trees[method] = currentNode
}
while(true) {
// 为 currentNode 插入新的节点...
}
}
每个方法对应的树在第一次获取不存在的时候,都会先创建一个根节点,根节点使用默认字符(/)。
每个节点的数据结构如下:
// 只保留了一些重要参数,其他的暂时忽略
function Node(options) {
options = options || {}
this.prefix = options.prefix || '/' // 去除公共前缀之后的字符,默认为 /
this.label = this.prefix[0] // 用于存放其第一个字符
this.method = options.method // 请求的方法
this.handler = options.handler // 请求的回调
this.children = options.children || {} // 存放后续的子节点
}
当我们插入了几个路由节点后,树结构的具体构造如下:
router.on('GET', '/a', (req, res, params) => {
res.end('{"message":"hello world"}')
})
router.on('GET', '/aa', (req, res, params) => {
res.end('{"message":"hello world"}')
})
router.on('GET', '/ab', (req, res, params) => {
res.end('{"message":"hello world"}')
})
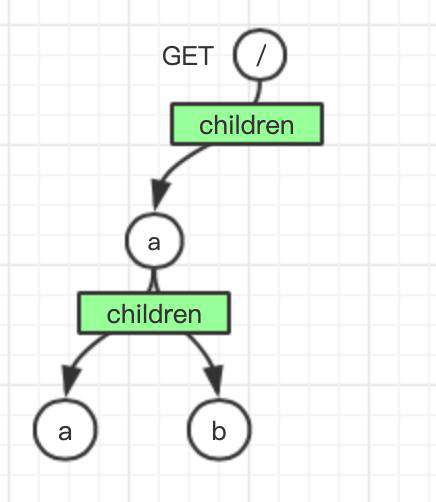
Node {
label: 'a',
prefix: 'a',
method: 'GET',
children: {
a: Node {
label: 'a',
prefix: 'a',
method: 'GET',
children: {},
handler: [Function]
},
b: Node {
label: 'b',
prefix: 'b',
method: 'GET',
children: {},
handler: [Function]
}
},
handler: [Function]
}
如果我们绑定一个名为 /axxx 的路由,为了节约内存,不会生成三个 label 为x 的节点,只会生成一个节点,其 label 为 x,prefix 为 xxx。
router.on('GET', '/a', (req, res, params) => {
res.end('{"message":"hello world"}')
})
router.on('GET', '/axxx', (req, res, params) => {
res.end('{"message":"hello world"}')
})
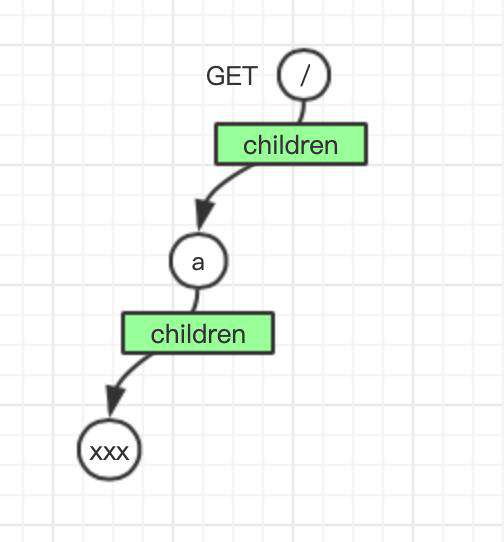
Node {
label: 'a',
prefix: 'a',
method: 'GET',
children: {
a: Node {
label: 'x',
prefix: 'xxx',
method: 'GET',
children: {},
handler: [Function]
}
},
handler: [Function]
}
插入路由节点
通过之前的代码可以看到, on 方法最后会调用内部的 _insert 方法插入新的节点,下面看看其具体的实现方式:
Router.prototype._insert = function _insert (method, path, handler) {
// 取出方法对应的 tree
var currentNode = this.trees[method]
if (typeof currentNode === 'undefined') {
// 首次插入构造一个新的 Tree
currentNode = new Node({ method })
this.trees[method] = currentNode
}
var len = 0
var node = null
var prefix = ''
var prefixLen = 0
while(true) {
prefix = currentNode.prefix
prefixLen = prefix.length
len = prefixLen
path = path.slice(len)
// 查找是否存在公共前缀
node = currentNode.findByLabel(path)
if (node) {
// 公共前缀存在,复用
currentNode = node
continue
}
// 公共前缀不存在,创建一个
node = new Node({ method: method, prefix: path })
currentNode.addChild(node)
}
}
插入节点会调用 Node 原型上的 addChild 方法。
Node.prototype.getLabel = function () {
return this.prefix[0]
}
Node.prototype.addChild = function (node) {
var label = node.getLabel() // 取出第一个字符做为 label
this.children[label] = node
return this
}
本质是遍历路径的每个字符,然后判断当前节点的子节点是否已经存在一个节点,如果存在就继续向下遍历,如果不存在,则新建一个节点,插入到当前节点。
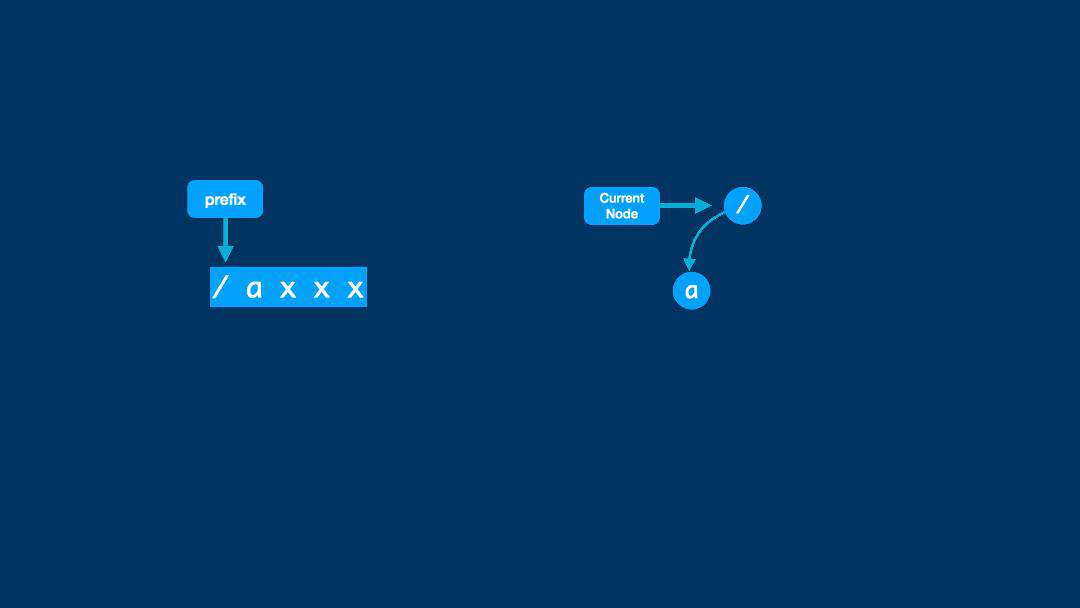
查找路由节点
find-my-way 对外提供了 lookup 方法,用于查找路由对应的方法并执行,内部是通过 find 方法查找的。
Router.prototype.find = function find (method, path, version) {
var currentNode = this.trees[method]
if (!currentNode) return null
while (true) {
var pathLen = path.length
var prefix = currentNode.prefix
var prefixLen = prefix.length
var len = prefixLen
var previousPath = path
// 找到了路由
if (pathLen === 0 || path === prefix) {
var handle = currentNode.handler
if (handle !== null && handle !== undefined) {
return {
handler: handle.handler
}
}
}
// 继续向下查找
path = path.slice(len)
currentNode = currentNode.findChild(path)
}
}
Node.prototype.findChild = function (path) {
var child = this.children[path[0]]
if (child !== undefined || child.handler !== null)) {
if (path.slice(0, child.prefix.length) === child.prefix) {
return child
}
}
return null
}
查找节点也是通过遍历树的方式完成的,找到节点之后还需要放到 handle 是否存在,存在的话需要执行回调。
总结
本文主要介绍了 fastify 的路由库通过 Radix Tree 进行提速的思路,相比于其他的路由库通过正则匹配(例如 koa-router 就是通过 path-to-regexp 来解析路径的),效率上还是高很多的。

常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!