redux是一个可预测的状态管理工具,唯一可以改变state的方式就是dispatch一个action,action描述了以何种方式改变state,交由reducer去改变state。
创建redux应用
npm i redux
src/index.js:
import {createStore} from 'redux'
const initState = {
list: []
}
// reducer,createStore的第一个参数,当store初始化的时候redux会调用reducer,传入state为undefined,action.type为一个@@redux/INIT开头的随机字符串
// 所以在这里可以设置state的默认值,防止下次reducer改变数据的时候报错
// reducer应当返回一个state,来作为新的state。
function todo(state = initState, action){
switch(action.type){
case 'todoAdd':
return {
list: state.list.concat(action.text)
}
case 'todoRemove':
return {
list: state.list.filter((v) => v !== action.text)
}
default:
return state
}
}
let store = createStore(todo)
//订阅store更新
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log(store.getState())
})
//派发action,这个action会被传入到reducer的第二个参数
store.dispatch({
type: 'todoAdd',
text: '吃饭',
})
store.dispatch({
type: 'todoAdd',
text: '睡觉',
})
store.dispatch({
type: 'todoAdd',
text: '打豆豆',
})
store.dispatch({
type: 'todoRemove',
text: '睡觉',
})
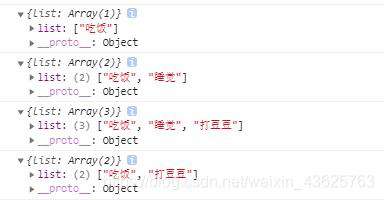
控制台打印结果为:
合并reducer
假如说有多个reducer,一个是todo,另外一个是用户数据,我们可以使用redux提供的combineReducers来合并reducer,src下新建一个文件夹为store,src/store/index.js为创建的store,src/store/todo.js和src/store/user.js分别为todo的reducer和user的reducer。 src/store/index.js代码为:
import {createStore, combineReducers} from 'redux'
import todo from './todo'
import user from './user'
const reducer = combineReducers({
todo,
user,
})
const store = createStore(reducer)
export default store
src/store/user.js代码为
const initState = {
name: 'xiaobai',
age: 18,
}
function user(state = initState, action){
switch(action.type){
case 'userAgeAdd':
return {
...state,
age: state.age + 1,
}
case 'userNameChange':
return {
...state,
name: action.name,
}
default:
return state
}
}
export default user
现在在src/index.js里面增加一段代码
store.dispatch({
type: 'userNameChange',
name: 'xiaohei',
})
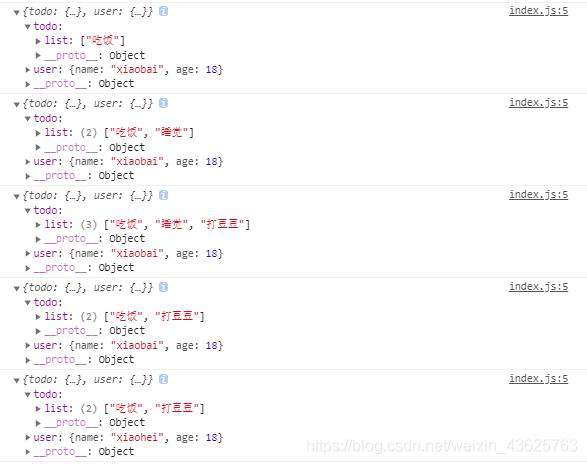
打印结果
创建action生成函数
上面的写法dispatch每次都要写一个action,可是试想一下如果我们封装成一个函数来返回一个action的话会更方便一点,就以user这个reducer开始封装生成action的函数。 src/store/user.js增加两个函数
export function userNameChange(name){
return {
type: 'userNameChange',
name,
}
}
export function userAgeAdd(){
return {
type: 'userAgeAdd',
}
}
src/index.js修改为:
import store from './store'
import {userNameChange} from './store/user'
//订阅store更新
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log(store.getState())
})
store.dispatch(userNameChange('xiaohei'))
打印结果看到user.name已经被修改为'xiaohei'
创建异步action生成函数
reducer是一个纯函数,不应该修改传入的参数,不应该有执行有副作用的API 请求和路由跳转,不能调用非纯函数。只要传入参数相同,返回计算得到的下一个 state 就一定相同,单纯执行计算。 那么怎么执行异步操作呢,这时候就要用到一个插件redux-thunk。通过使用redux提供的applyMiddleware,action创建函数除了返回 action 对象外还可以返回函数,当返回函数时,这个函数会被执行,接收一个参数为dispatch。这个函数并不需要保持纯净。
npm i redux-thunk
继续修改src/store/user.js导出的userNameChange
export function userNameChange(name){
return (dispatch) => { //返回的函数会被执行,并被传入dispatch
setTimeout(() => { //模拟api请求
console.log('一秒后dispatch一个action')
dispatch({
type: 'userNameChange',
name,
})
},2000)
}
}
/src/store/index.js
import {createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import reduxThunk from 'redux-thunk'
import todo from './todo'
import user from './user'
const reducer = combineReducers({
todo,
user,
})
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(
reduxThunk
))
export default store
现在打开控制台刷新页面,一秒之后打印结果正常,说明我们已经做好了action的异步操作。 redux-thunk并不是redux处理异步操作唯一的解决方式,当你读完下一章节你也可以写一个自定义的middleware
Middleware分析
middleware 是指可以被嵌入在框架接收请求到产生响应过程之中的代码。例如,Express 或者 Koa 的 middleware 可以完成添加 CORS headers、记录日志、内容压缩等工作。middleware 最优秀的特性就是可以被链式组合。你可以在一个项目中使用多个独立的第三方 middleware。 Redux middleware 它提供的是位于 action 被发起之后,到达 reducer 之前的扩展点。 你可以利用 Redux middleware 来进行日志记录、创建崩溃报告、调用异步接口或者路由等等。
手动记录日志
假如我们没有redux提供的applyMiddleware,如果想记录redux日志的话,可能会需要这样写来手动记录。 src/store/user.js修改为原来的userNameChange,src/store/index.js删除middleware。 src/index.js
import store from './store'
import {userNameChange} from './store/user'
let action = userNameChange('xiaohei')
console.log('dispatch', action.type)
store.dispatch(action)
console.log('newState', store.getState())
重写dispatch
上面的方法虽然可以实现记录日志的功能,但是需要每次dispatch都需要记录。既然改变数据就一定会用dispatch,我们可以尝试重写dispatch,在保留原来dispatch完整功能的情况下,增加一些我们自己需要做的操作。 src/index.js
import store from './store'
import {userNameChange} from './store/user'
let next = store.dispatch //保存原来的dispatch完整功能
store.dispatch = (action) => { //重写dispatch,接收一个action
console.log('dispatch', action.type)
let result = next(action) //执行原来的dispatch功能
console.log('newState', store.getState())
return result
}
let action = userNameChange('xiaohei')
store.dispatch(action)
现在打开控制台,不管在哪里dispatch,都已经可以正常的记录日志了,
新增middleware
实际开发中捕获异常也是很重要的,现在如果需要新增功能的话,在原来重写的dispatch上面写新功能会让代码看起来很乱,我们完全可以写成两个独立的功能。 src/index.js
import store from './store'
import {userNameChange} from './store/user'
const logMiddleware = (store) => {
let next = store.dispatch
store.dispatch = (action) => {
console.log('dispatch', action.type)
let result = next(action)
console.log('newState', store.getState())
return result
}
}
const errMiddlware = (store) => {
let next = store.dispatch
store.dispatch = (action) => {
try {
return next(action)
}catch(err){
console.log('redux抛出异常')
throw err
}
}
}
logMiddleware(store)
errMiddlware(store)
let action = userNameChange('xiaohei')
store.dispatch(action)
//为了试验异常捕获,dispatch不传参数。
store.dispatch()
现在打开控制台打印结果为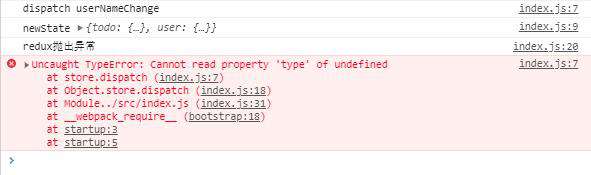 不出所料,两个中间件功能全部实现了,整个代码运行流程为:执行logMiddleware,传入createStore生成的store,logMiddleware对store的dispatch方法进行重写;执行errMiddlware,传入dispatch方法已经被logMiddleware方法重写过的store,errMiddlware在保留原来被处理过的完整的dispatch方法之上,继续添加新的功能。
不出所料,两个中间件功能全部实现了,整个代码运行流程为:执行logMiddleware,传入createStore生成的store,logMiddleware对store的dispatch方法进行重写;执行errMiddlware,传入dispatch方法已经被logMiddleware方法重写过的store,errMiddlware在保留原来被处理过的完整的dispatch方法之上,继续添加新的功能。
applyMiddleware源码
通过研究redux提供的applyMiddleware源码
function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
//createStore会判断如果执行applyMiddleware返回函数,创建store的工作就交由下面的代码来执行
//返回一个处理过dispatch的store,现在的...args为我们传入的reducer。
//createStore的代码为 enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)
return (createStore) => (...args) => {
const store = createStore(...args)
let dispatch = () => {
throw new Error(
'Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. ' +
'Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.'
)
}
const middlewareAPI = { //中间件可访问的参数
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (...args) => dispatch(...args)
}
const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI)), //接收next,返回dispatch的函数组成的数组。
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch) //原始dispatch传入compose生成的函数被链式处理。
return {
...store,
dispatch //被处理过的dispatch
}
}
}
下面为compose:
export default function compose(...funcs) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
return arg => arg
}
if (funcs.length === 1) {
return funcs[0]
}
return funcs.reduce((a, b) => {
return (...args) => a(b(...args))
})
}
//compose 的作用是:传入一组任意数量的函数,比如 funcA, funcB,funcC,
//可生成一个新的函数 (...args) => funcA(funcB(funcC(...args)))
//它的含义是每个函数均以上一个函数的返回值为参数传入,并将自己计算得到的返回值作为下一个函数的参数。
通过以上源码不难发现,其实middleware就是一个接收middlewareAPI的函数,返回的函数接收一个参数next,返回一个函数作为下一个中间件的next。
使用applyMiddleware
先改写logMiddleware和errMiddlware src/store/index.js
import {createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import reduxThunk from 'redux-thunk'
import todo from './todo'
import user from './user'
const reducer = combineReducers({
todo,
user,
})
const logMiddleware = (store) => { //store为applyMiddleware传出的middlewareAPI
return (next) => { //返会函数接收next,执行返回dispatch作为下一个middleware的next参数
return (action) => { //dispatch
console.log('dispatch', action.type)
let result = next(action)
console.log('newState', store.getState())
return result
}
}
}
const errMiddlware = (store) => { //middlewareAPI
return (next) => { //logMiddleware返回的dispatch
return (action) => { //返回dispatch,作为下一个middleware的next
try {
return next(action)
}catch(err){
console.log('redux抛出异常')
throw err
}
}
}
}
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(
//middlewares
logMiddleware,
errMiddlware,
))
export default store
src/index.js删除对dispatch的处理。
import store from './store'
import {userNameChange} from './store/user'
store.dispatch(userNameChange('xiaohei'))
//为了试验异常捕获,dispatch不传参数。
store.dispatch()
现在打开控制台,既打印了redux日志,也有异常捕获,说明我们middleware写法是正确的,现在对他们进行柯里化。
const logMiddleware = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log('dispatch', action.type)
let result = next(action)
console.log('newState', store.getState())
return result
}
const errMiddlware = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
try {
return next(action)
}catch(err){
console.log('redux抛出异常')
throw err
}
}
异步action
上面以优雅的写法增加了logMiddleware和errMiddleware,现在还不能支持异步action的写法,继续增加一个middleware让action可以返回一个函数,函数处理异步操作最终dispatch一个action来改变数据。 src/store/user.js增加一个异步action
export function userAgeAddSync(){
return (dispatch) => { //接收dispatch用来异步操作完成后的派发动作
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(userAgeAdd())
}, 1000)
}
}
刷新页面发现redux抛出异常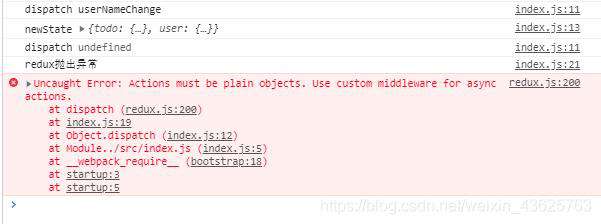 因为执行userAgeAddSync得到的是一个接收dispatch的函数,action.type为undefined的原因也是如此,因此需要增加一个中间件来处理这个异步action。
src/store/index.js增加一个middleware并应用到applyMiddleware中
因为执行userAgeAddSync得到的是一个接收dispatch的函数,action.type为undefined的原因也是如此,因此需要增加一个中间件来处理这个异步action。
src/store/index.js增加一个middleware并应用到applyMiddleware中
const syncMiddlware = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
if(typeof action === 'function'){ //如果action是一个函数,就直接执行这个函数,传入dispatch
action(store.dispatch)
}else{
return next(action)
}
}
现在来看打印结果
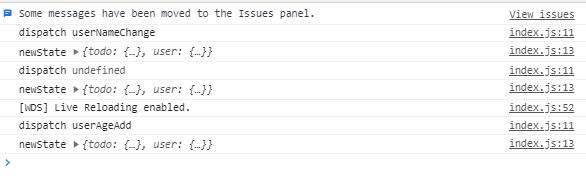 现在一秒之后派发userAgeAdd我们已经做到了,但是中间有一个步骤打印action.type为undefined,如果你对middleware链式调用理解的还不错的话,你已经知道什么原因了。因为在我们执行store.dispatch(userAgeAddSync())的时候,userAgeAddSync()返回的函数被logMiddleware处理,打印action.type一定会是undefined,现在只需要在logMiddleware里面座一层判断,如果action为函数的话,直接执行action,传入dispatch,如果不是的话执行原来的记录日志逻辑。
修改logMiddleware代码为
现在一秒之后派发userAgeAdd我们已经做到了,但是中间有一个步骤打印action.type为undefined,如果你对middleware链式调用理解的还不错的话,你已经知道什么原因了。因为在我们执行store.dispatch(userAgeAddSync())的时候,userAgeAddSync()返回的函数被logMiddleware处理,打印action.type一定会是undefined,现在只需要在logMiddleware里面座一层判断,如果action为函数的话,直接执行action,传入dispatch,如果不是的话执行原来的记录日志逻辑。
修改logMiddleware代码为
const logMiddleware = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
let result
if(typeof action === 'function'){
action(store.dispatch)
}else{
console.log('dispatch', action.type)
result = next(action)
console.log('newState', store.getState())
return result
}
}
现在打开控制台,页面加载完毕只有userNameChange的日志,一秒后打印userAgeAdd的日志,这正是我们想要的结果。后期如果有时间的话我会基于这套代码进行封装,应用到React上面。本篇博客代码和所有的章节提交记录我放在了Gitee上面,链接链接: Gitee,有兴趣的同学可以下载研究。
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!