babel分享
babel介绍
babel 是源码 => 源码的过程
1. parse 代码 => ast
2. transform 操作语法书 增删改 ast => ast (修改后的)
3. generate 修改后的 ast => 新的代码
抽象语法书 (Abstract Syntax Tree,AST)以树形结构表达 编程语言 的语法
ast语法树 代码是从 经过词法分析 和 语法分析 最终生成ast
举一个例子
我是张三 词法分析的过程就相当于 我、是、张三
语法分析 是 一个赋值语句 张三 赋值给 我
me = 'zhangsan'
词法分析过程最终生成结果 token (不能再拆分的单词)
me、= 、'zhangsan'
语法分析的过程 发现 有一个等号(operator 操作符) 发现是赋值操作
left 是 me (标识符 identifier)right 是 (字符串字面量 StringLiteral) 'xiaomenggang '
- 举个例子
astexplorer.net/
javascript:
console.log(1)
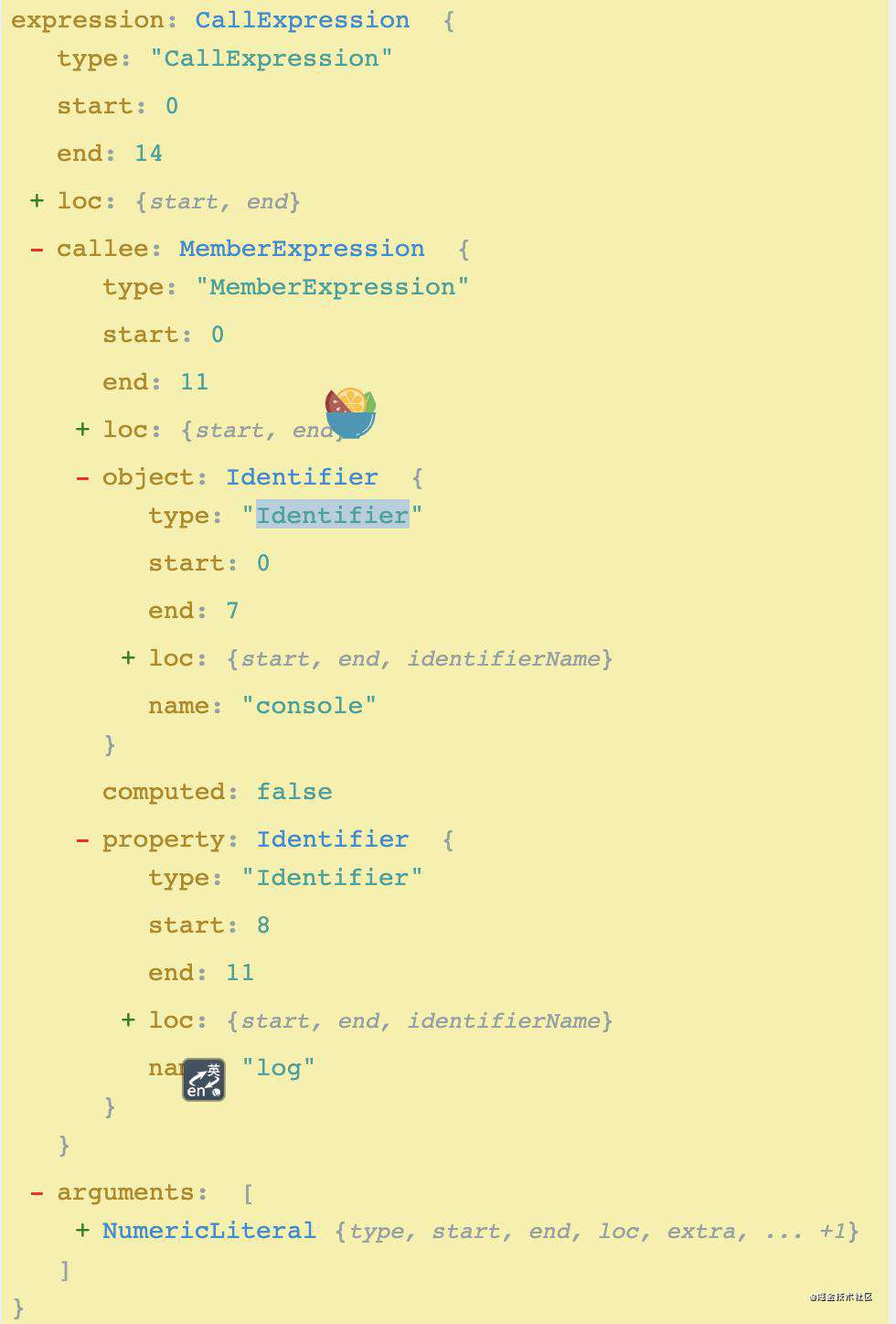
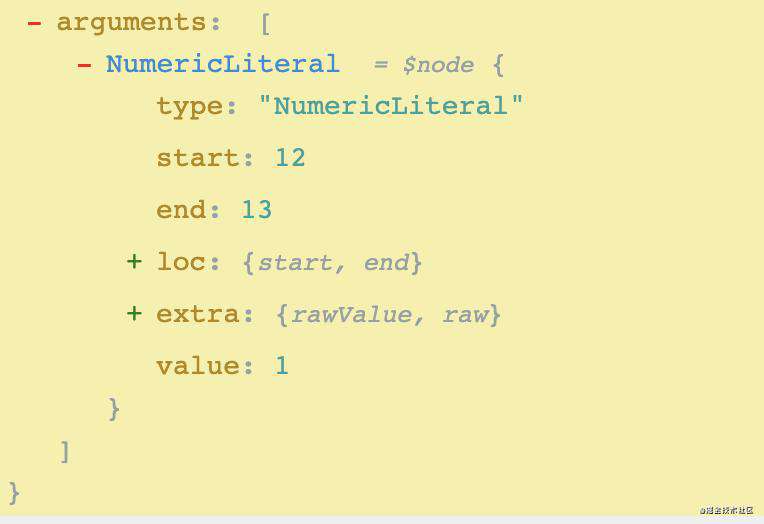
他的树形结构是这样的
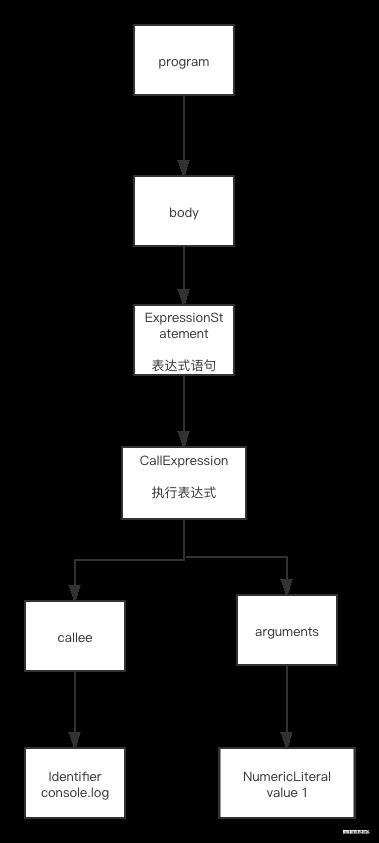
ast 常见节点
Statement 语句
| 代码 | 节点名称 | 中文名 | for | ForStatement | 循环语句 | while | WhileStatement | while语句 | continue | ContinueStatement | continue语句 | Switch | SwitchStatement | Switch语句 |
|---|
| 代码 | 节点名称 | 中文名 | var a = 'xmg'; | variableDeclaratio | 变量声明 | function fn(){} | functionDeclaratio | 函数声明 | import d from 'e'; | importDeclaratio | 导出声明 | Switch | SwitchStatement | Switch语句 |
|---|
| 代码 | 节点名称 | 中文名 | [1,2,3] | ArrayExpression | 数组表达式 | a = 1 | AssignmentExpression | 赋值表达式 | 1 + 2 | BinaryExpression | 二元表达式 | funciton () {} | FunctionExpression | 函数表达式 | () => {} | ArrowFunctionExpression | 箭头函数表达式 |
|---|
超级微小编译器
github.com/jamiebuilds…
简单的从 词法分析 到 语法分析的一个简单实现过程
我们先来看下babel 的api
parse
parse @babel/parser 将代码转换成 ast
参数 plugin,souseType(script script 则不解析 es module 语法 module 是解析 es module 语法 unambiguous 根据环境自动判断 )
transform @babel/traverse 遍历AST 使用访问者 模式 对ast修改
traverse(ast, visitor)
visitor: {
StringLiteral(path) {
debugger
console.log(path.node.value)
}
}
path 上面有很多方法 比如 path.node 当前节点 比如 path.parent 获取父级节点 path.insertBefore 向前插入 path.repalceWith 替换 path.remove 删除 path.stop 停止遍历
generate @babel/generate 将代码 从 ast 转成 code
@babel/types 提供快速生成 ast 和 断言的方法 创建 ast和判断ast的节点类型 比如 types.IfStatement()
if(1){}
types.ifStatement(types.NumericLiteral(1),types.blockStatement([]))
types.isIfStatement():boolean
我们再来做一个例子 删除console代码
const parser = require('@babel/parser');
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default;
const generate = require('@babel/generator').default;
const types = require('@babel/types');
// console.log(types.ifStatement(types.NumericLiteral(1),types.blockStatement([])))
// console.log(generate(types.ifStatement(types.NumericLiteral(1),types.blockStatement([]))))
const sourceCode = `
console.log(1);
function func() {
var a = 2
console.info(a);
}
export default class Clazz {
say() {
var b = 3
console.debug(b);
}
render() {
let bbb = 333
console.log(bbb)
return <div>{bbb}</div>
}
}
`;
const ast = parser.parse(sourceCode, {
sourceType: 'unambiguous',
plugins: ['jsx']
});
traverse(ast, {
StringLiteral(path) {
debugger
console.log(path)
},
CallExpression(path) {
// if(path.scope) {
// path.scope.generateUid('maidian')
// console.log(path.scope.generateUid('maidian'))
// }
// types.ifStatement
if ( types.isMemberExpression(path.node.callee)
&& path.node.callee.object.name === 'console'
) {
path.remove()
}
}
});
const { code, map } = generate(ast);
console.log(code);
我们再来做一个例子 实现代码混淆
我们要说下 path 上的 scope 是作用域信息 生成作用域的就是模块、函数、块 作用域之间会形成嵌套关系,也就是作用域链
scope.bindings 当前作用域内声明的所有变量
const parser = require('@babel/parser');
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default;
const generate = require('@babel/generator').default;
const types = require('@babel/types');
let num=0;
const string = `abcdefghigklsisysjsks`
const sourceCode = `
function getScr() {
const num1 = 3
const num3 = num1**num1
const num5 = num3**num3
function add () {
return num5 + num3
}
const sum = add()
return sum
}
`;
const ast = parser.parse(sourceCode, {
sourceType: 'unambiguous',
});
traverse(ast, {
StringLiteral(path) {
console.log(path)
},
Scopable(path, state) {
if(path.scope.bindings) {
Object.entries(path.scope.bindings).forEach(([key,binding] )=> {
binding.scope.rename(key,binding.scope.generateUid(string[num++]))
})
}
}
});
const { code, map } = generate(ast);
console.log(code);
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!