Navigator 2.0作为新一代的路由提供了申明式的API,更加符合Flutter的风格。Navigator 2.0向前兼容,新增了一些新的API,使用的方式和Navigator 1.0相比有较大的差别。
本文将详细解析Navigator 2.0的底层逻辑,让大家对它有一个深入的了解,这样在使用上会更加的得心应手。
Navigator 2.0 诞生的背景
Flutter官方团队改造路由主要有几点原因:
- Navigator 1.0 只提供了一些
push(),pushNamed()和pop()等简单的API。实现压入或者弹出多个页面很困难,更难实现对栈内中间页面的移除,交换等操作; - Flutter随着2.0的到来实现了全平台的支持,这样也就新出现一些使用场景,譬如网页修改URL地址等,这些就需要新的API来支持;
- Navigator 2.0满足了嵌套路由的需求场景,这样开发者在使用时就更加的灵活和方便;
- Navigator 2.0提供的是申明式的API,解决了以前路由命令式编程的方式,让编程的风格统一。
Navigator 2.0的API虽然比较的多,但是逻辑还是比较清晰的,我们来一个个的进行介绍。
Page
Page代表页面不可变的的配置信息,代表一个页面,类似于Widget配置信息转换成Element, Page配置的信息会转换成Route。
abstract class Page<T> extends RouteSettings {
const Page({
this.key,
String? name,
Object? arguments,
this.restorationId,
}) : super(name: name, arguments: arguments);
bool canUpdate(Page<dynamic> other) {
return other.runtimeType == runtimeType &&
other.key == key;
}
@factory
Route<T> createRoute(BuildContext context);
}
RouteSettings
Page的父类RouteSettings仅仅用来保存name和arguments这两个值。
const RouteSettings({
this.name,
this.arguments,
});
Route
Route代表一个页面,是Navigator栈中真正管理的内容。
abstract class Route<T> {
// 1
RouteSettings get settings => _settings;
NavigatorState? get navigator => _navigator;
// 2
List<OverlayEntry> get overlayEntries => const <OverlayEntry>[];
// 3
void install() {}
TickerFuture didPush() {}
...
}
| 方法 | 调用时机 | install | 被插入navigator | didPush | 动画进入显示 | didAdd | 直接显示 | didReplace | 替换旧的route | didPop | 请求pop页面 | didComplete | pop完成后 | didPopNext | 当前route后面的route被pop | didChangeNext | 当前route后面的route被替换 | didChangePrevious | 当前route前面的route被替换 | changedInternalState | 当前route的state变化后 | changedExternalState | 当前route的navigator变化后 |
|---|
MaterialPage 和 _PageBasedMaterialPageRoute
我们可以直接使用系统给我们提供的Page类,也可以自定义继承自Page的类。我们来看看官方给我们提供的MaterialPage的逻辑。
MaterialPage的Route是_PageBasedMaterialPageRoute类,它的继承逻辑是:_PageBasedMaterialPageRoute -> PageRoute -> ModalRoute -> TransitionRoute -> OverlayRoute + LocalHistoryRoute -> Route。
LocalHistoryRoute
LocalHistoryRoute可以给Route添加一些LocalHistoryEntry。当LocalHistoryEntry不为空时,didPop方法调用的时候会移除最后一个LocalHistoryEntry,否则Route就要被pop了。
OverlayRoute
OverlayRoute主要是持有Route对应的OverlayEntry数组,这个数组是子类在被插入navigator的时候对其进行赋值的。
abstract class OverlayRoute<T> extends Route<T> {
@factory
Iterable<OverlayEntry> createOverlayEntries();
List<OverlayEntry> get overlayEntries => _overlayEntries;
void install() {
_overlayEntries.addAll(createOverlayEntries());
super.install();
}
}
TransitionRoute
TransitionRoute是主要是负责动画部分。
abstract class TransitionRoute<T> extends OverlayRoute<T> {
Animation<double>? get animation => _animation;
Animation<double>? get secondaryAnimation => _secondaryAnimation;
void install() {
_animation = createAnimation()
..addStatusListener(_handleStatusChanged);
super.install();
}
TickerFuture didPush() {
super.didPush();
return _controller!.forward();
}
void didAdd() {
super.didAdd();
_controller!.value = _controller!.upperBound;
}
bool didPop(T? result) {
_controller!.reverse();
return super.didPop(result);
}
void didPopNext(Route<dynamic> nextRoute) {
_updateSecondaryAnimation(nextRoute);
super.didPopNext(nextRoute);
}
void didChangeNext(Route<dynamic>? nextRoute) {
_updateSecondaryAnimation(nextRoute);
super.didChangeNext(nextRoute);
}
}
ModalRoute
ModalRoute主要的作用是阻止除最上层的Route之外的Route进行用户交互,其中的知识点也是非常丰富的。
abstract class ModalRoute<T> extends TransitionRoute<T> with LocalHistoryRoute<T> {
Iterable<OverlayEntry> createOverlayEntries() sync* {
yield _modalBarrier = OverlayEntry(builder: _buildModalBarrier);
yield _modalScope = OverlayEntry(builder: _buildModalScope, maintainState: maintainState);
}
}
Widget _buildModalScope(BuildContext context) {
return _modalScopeCache ??= Semantics(
sortKey: const OrdinalSortKey(0.0),
child: _ModalScope<T>(
key: _scopeKey,
route: this,
// _ModalScope calls buildTransitions() and buildChild(), defined above
)
);
}
Widget buildPage(BuildContext context, Animation<double> animation, Animation<double> secondaryAnimation);
Widget buildTransitions(
BuildContext context,
Animation<double> animation,
Animation<double> secondaryAnimation,
Widget child,
) {
return child;
}
我们接下来看看_ModalScope的_ModalScopeState的内容:
class _ModalScopeState<T> extends State<_ModalScope<T>> {
late Listenable _listenable;
final FocusScopeNode focusScopeNode = FocusScopeNode(debugLabel: '$_ModalScopeState Focus Scope');
void initState() {
super.initState();
final List<Listenable> animations = <Listenable>[
if (widget.route.animation != null) widget.route.animation!,
if (widget.route.secondaryAnimation != null) widget.route.secondaryAnimation!,
];
_listenable = Listenable.merge(animations);
if (widget.route.isCurrent) {
widget.route.navigator!.focusScopeNode.setFirstFocus(focusScopeNode);
}
}
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// 1 RestorationScope
return AnimatedBuilder(
animation: widget.route.restorationScopeId,
builder: (BuildContext context, Widget? child) {
return RestorationScope(
restorationId: widget.route.restorationScopeId.value,
child: child!,
);
},
// 2 _ModalScopeStatus
child: _ModalScopeStatus(
route: widget.route,
isCurrent: widget.route.isCurrent, // _routeSetState is called if this updates
canPop: widget.route.canPop, // _routeSetState is called if this updates
child: Offstage(
offstage: widget.route.offstage, // _routeSetState is called if this updates
child: PageStorage(
bucket: widget.route._storageBucket, // immutable
child: Builder(
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return Actions(
actions: <Type, Action<Intent>>{
DismissIntent: _DismissModalAction(context),
},
child: PrimaryScrollController(
controller: primaryScrollController,
child: FocusScope(
node: focusScopeNode, // immutable
// 3 RepaintBoundary
child: RepaintBoundary(
// 4. AnimatedBuilder
child: AnimatedBuilder(
animation: _listenable, // immutable
builder: (BuildContext context, Widget? child) {
// 5. buildTransitions
return widget.route.buildTransitions(
context,
widget.route.animation!,
widget.route.secondaryAnimation!,
AnimatedBuilder(
animation: widget.route.navigator?.userGestureInProgressNotifier ?? ValueNotifier<bool>(false),
builder: (BuildContext context, Widget? child) {
final bool ignoreEvents = _shouldIgnoreFocusRequest;
focusScopeNode.canRequestFocus = !ignoreEvents;
return IgnorePointer(
ignoring: ignoreEvents,
child: child,
);
},
child: child,
),
);
},
child: _page ??= RepaintBoundary(
key: widget.route._subtreeKey, // immutable
child: Builder(
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return widget.route.buildPage(
context,
widget.route.animation!,
widget.route.secondaryAnimation!,
);
},
),
),
),
),
),
),
);
},
),
),
),
),
);
}
_ModalScopeState的build方法是设计非常精妙的一个方法:
PageRoute
PageRoute主要就是让最上层下面的Route不可见,点击_modalBarrier不让当前Route从Navigator栈中弹出。
abstract class PageRoute<T> extends ModalRoute<T> {
@override
bool get opaque => true;
@override
bool get barrierDismissible => false;
}
_PageBasedMaterialPageRoute
_PageBasedMaterialPageRoute的作用是覆写了buildPage方法, 返回的是开发者写的界面;
class _PageBasedMaterialPageRoute<T> extends PageRoute<T> with MaterialRouteTransitionMixin<T> {
Widget buildContent(BuildContext context) {
return _page.child;
}
}
官方为我们提供了默认的pop和push动画,它们就在混入的MaterialRouteTransitionMixin中实现的。MaterialRouteTransitionMixin会根据不同的平台有不同的实现,iOS是左右的动画,Android是上下的动画,web也是左右动画。
我们以iOS为例,其最后使用的是CupertinoPageTransition这个类的方法:
SlideTransition(
position: _secondaryPositionAnimation,
textDirection: textDirection,
transformHitTests: false,
child: SlideTransition(
position: _primaryPositionAnimation,
textDirection: textDirection,
child: DecoratedBoxTransition(
decoration: _primaryShadowAnimation,
child: child,
),
)
看到SlideTransition嵌套到一个child上是不是很疑惑?两个动画用在一个Widget上?
先解释下其他参数:
_secondaryPositionAnimation是从Offset.zero到Offset(-1.0/3.0, 0.0),正常情况下就是从右往左移动1/3的屏幕宽度。
final Animatable<Offset> _kMiddleLeftTween = Tween<Offset>(
begin: Offset.zero,
end: const Offset(-1.0/3.0, 0.0),
);
_primaryPositionAnimation是从Offset(1.0, 0.0)到Offset.zero,正常情况下就是从不可见的屏幕右边移动到屏幕最左边,然后占据整个屏幕宽度。
final Animatable<Offset> _kRightMiddleTween = Tween<Offset>(
begin: const Offset(1.0, 0.0),
end: Offset.zero,
);
我们接下来解释下pop一个Route时候的动画逻辑, Animation:0->1
- 新加的Route是被
_primaryPositionAnimation直接驱动的,也就是执行了从右到左的_kRightMiddleTween动画; _secondaryPositionAnimation只是被修改了值,我们前面TransitionRoute的介绍中提到过,新加入Route的animation赋值给了前一个Route的secondaryAnimation属性。_ModalScopeState中介绍过secondaryAnimation也能驱动Route的动画,也就是说前一个Route也能产生一个_kMiddleLeftTween动画;
概括:
新加的Route通过animation驱动从屏幕右边移动到左边的动画,animation赋值给了前一个Route的secondaryAnimation驱动前一个Route向左移动1/3个屏幕位置。
push的逻辑类似,只是一个反向的动画reverse。前一个Route在secondaryAnimation的驱动下右移了1/3屏幕宽度,当前的Route在animation驱动下移出屏幕。
我们可以点击Flutter DevTools的Slow Animations看看动画的慢放过程:

阶段总结
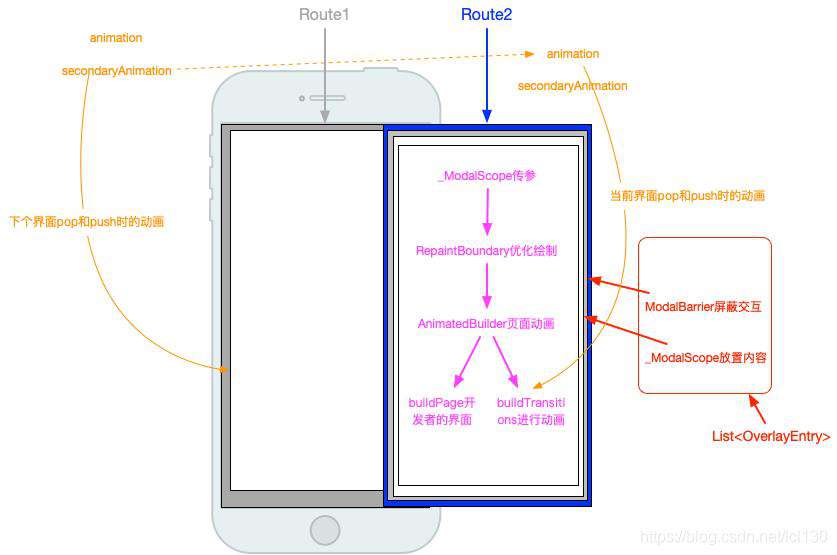
_RouteEntry
Navigator不是直接操作的Route,而是Route的封装类_RouteEntry。
_RouteEntry(
this.route,
{
required _RouteLifecycle initialState,
this.restorationInformation,
})
_RouteEntry除了持有route外,还持有一个_RouteLifecycle,即路由状态。
函数则主要是修改_RouteLifecycle状态的函数,譬如markForPush,markForAdd,markForPop,markForRemove,markForComplete等。此外还有_RouteLifecycle被标记后对Route进行操作函数,譬如handlePush,handleAdd,handlePop,remove等。
Navigator
Navigator({
Key? key,
this.pages = const <Page<dynamic>>[],
// ...
})
Navigator的构造方法中有一个关键的属性pages,Navigator会将传入的pages会转换成Routes对应的_RouteEntry数组。
我们接下来分析NavigatorState的重要代码。
class NavigatorState extends State<Navigator> with TickerProviderStateMixin, RestorationMixin {
List<_RouteEntry> _history = <_RouteEntry>[];
late GlobalKey<OverlayState> _overlayKey;
OverlayState? get overlay => _overlayKey.currentState;
final FocusScopeNode focusScopeNode = FocusScopeNode(debugLabel: 'Navigator Scope');
}
NavigatorState的核心方法是didUpdateWidget方法, 其调用了一个_updatePages()方法:
void didUpdateWidget(Navigator oldWidget) {
_updatePages();
}
_updatePages方法的主要作用是对pages进行diff比对,更新_history数组中每个_routeEntry的_RouteLifecycle, 最后调用_flushHistoryUpdates()方法。
void _flushHistoryUpdates({bool rearrangeOverlay = true}) {
final List<_RouteEntry> toBeDisposed = <_RouteEntry>[];
while (index >= 0) {
switch (entry!.currentState) {
case _RouteLifecycle.push:
case _RouteLifecycle.pushReplace:
case _RouteLifecycle.replace:
entry.handlePush(
navigator: this,
previous: previous?.route,
previousPresent: _getRouteBefore(index - 1, _RouteEntry.isPresentPredicate)?.route,
isNewFirst: next == null,
);
if (entry.currentState == _RouteLifecycle.idle) {
continue;
}
break;
// ...
}
index -= 1;
next = entry;
entry = previous;
previous = index > 0 ? _history[index - 1] : null;
}
_flushObserverNotifications();
_flushRouteAnnouncement();
for (final _RouteEntry entry in toBeDisposed) {
for (final OverlayEntry overlayEntry in entry.route.overlayEntries)
overlayEntry.remove();
entry.dispose();
}
if (rearrangeOverlay) {
overlay?.rearrange(_allRouteOverlayEntries);
}
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return HeroControllerScope.none(
child: Listener(
onPointerDown: _handlePointerDown,
onPointerUp: _handlePointerUpOrCancel,
onPointerCancel: _handlePointerUpOrCancel,
child: AbsorbPointer(
absorbing: false, // it's mutated directly by _cancelActivePointers above
child: FocusScope(
node: focusScopeNode,
autofocus: true,
child: UnmanagedRestorationScope(
bucket: bucket,
child: Overlay(
key: _overlayKey,
initialEntries: overlay == null ? _allRouteOverlayEntries.toList(growable: false) : const <OverlayEntry>[],
),
),
),
),
),
);
}
顺便提一下HeroControllerScope是负责进行Hero动画的的Widget,类似于Android中的共享元素动画。
阶段总结
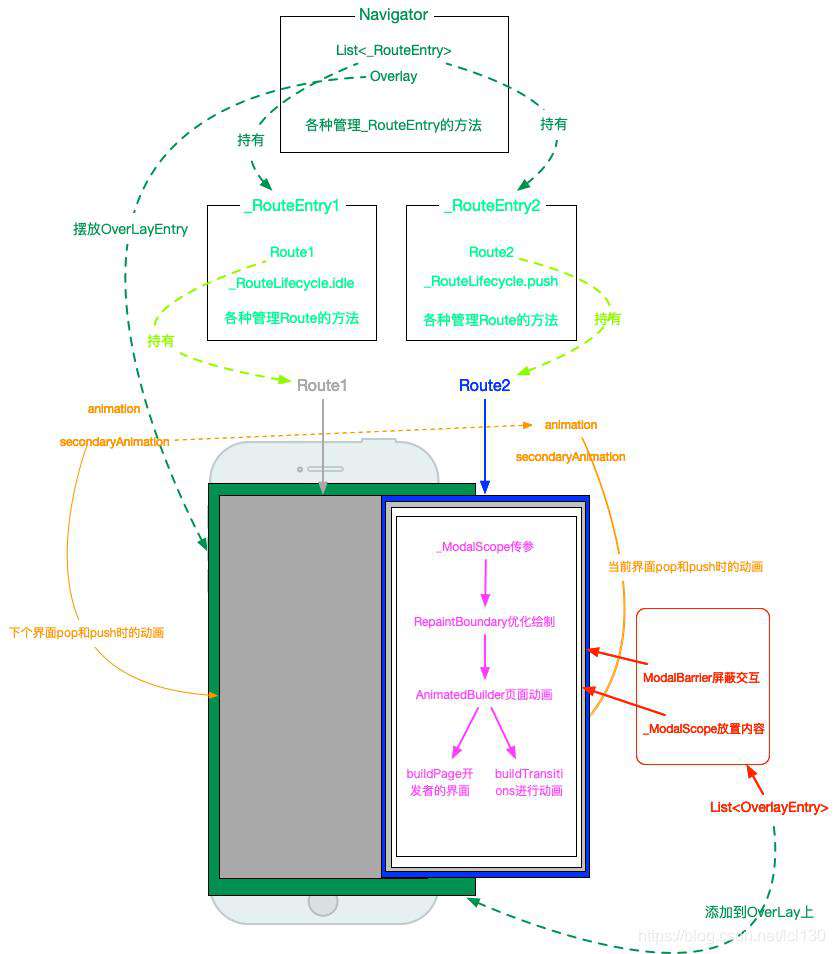
到目前为止,我们通过切换Navigator的page就能够实现路由切换了,是不是文章就结束了?没有,因为Navigator 2.0是为Flutter 2.0 的全平台而生的,目前还没有解决一些问题,例如编辑浏览器网址,网页返回,安卓物理键返回等功能。
Router
Router({
Key? key,
this.routeInformationProvider,
this.routeInformationParser,
required this.routerDelegate,
this.backButtonDispatcher,
})
final RouteInformationProvider? routeInformationProvider;
final RouteInformationParser<T>? routeInformationParser;
final RouterDelegate<T> routerDelegate;
final BackButtonDispatcher? backButtonDispatcher;
我们看到Router有四个属性,RouteInformationProvider路由信息提供者,RouteInformationParser路由信息解析者,RouterDelegate路由信息的处理代理,BackButtonDispatcher返回处理的分发者。他们四个协同作用,共同实现路由的功能。
RouteInformation
上面说的到路由信息就是指RouteInformation,包括路由的路径location和路由对应的状态state。这里所指的状态就是数据。
class RouteInformation {
final String? location;
final Object? state;
}
RouteInformationProvider
RouteInformationProvider只有一个抽象方法routerReportsNewRouteInformation,这个方法的作用是根据RouteInformation进行一些额外的操作。
abstract class RouteInformationProvider extends ValueListenable<RouteInformation?> {
void routerReportsNewRouteInformation(RouteInformation routeInformation) {}
}
系统默认使用的是PlatformRouteInformationProvider, 它的routerReportsNewRouteInformation方法中回调了系统路由的更新,例如浏览器就会在History栈中新增一条历史访问记录:
class PlatformRouteInformationProvider extends RouteInformationProvider with WidgetsBindingObserver, ChangeNotifier {
void routerReportsNewRouteInformation(RouteInformation routeInformation) {
SystemNavigator.routeInformationUpdated(
location: routeInformation.location!,
state: routeInformation.state,
);
_value = routeInformation;
}
}
RouteInformationParser
这个类的作用是对T页面模型和RouteInformation路由信息进行相互转换:
abstract class RouteInformationParser<T> {
Future<T> parseRouteInformation(RouteInformation routeInformation);
RouteInformation? restoreRouteInformation(T configuration) => null;
}
parseRouteInformation这个方法主要是解析初始路由的时候会使用到,例如 根据RouteInformation(location: "/")显示启动页面;
restoreRouteInformation这个方法就是根据T页面模型生成对应的RouteInformation。
RouterDelegate
RouterDelegate顾名思义就是代替Router工作的类,它包括根据T页面模型添加一个页面,pop一个页面,提供构建的内容等。
abstract class RouterDelegate<T> extends Listenable {
Future<void> setInitialRoutePath(T configuration) {
return setNewRoutePath(configuration);
}
Future<void> setNewRoutePath(T configuration);
Future<bool> popRoute();
T? get currentConfiguration => null;
Widget build(BuildContext context);
}
我们从源码角度看看RouteInformationProvider,RouteInformationParser和RouterDelegate他们三者在初始化路由是如何实现的:
class _RouterState<T> extends State<Router<T>> {
void initState() {
super.initState();
if (widget.routeInformationProvider != null) {
_processInitialRoute();
}
}
void _processInitialRoute() {
_currentRouteInformationParserTransaction = Object();
_currentRouterDelegateTransaction = Object();
_lastSeenLocation = widget.routeInformationProvider!.value!.location;
widget.routeInformationParser!
.parseRouteInformation(widget.routeInformationProvider!.value!)
.then<T>(_verifyRouteInformationParserStillCurrent(_currentRouteInformationParserTransaction, widget))
.then<void>(widget.routerDelegate.setInitialRoutePath)
.then<void>(_verifyRouterDelegatePushStillCurrent(_currentRouterDelegateTransaction, widget))
.then<void>(_rebuild);
}
}
在_processInitialRoute方法中我们看到了,routeInformationParser解析routeInformationProvider的value,然后routerDelegate根据这个解析的结果去调用setNewRoutePath设置路由。
routeInformationProvider -> routeInformationParser -> routerDelegate -> (setNewRoutePath)
RouterDelegate的覆写案例:
class MyRouterDelegate extends RouterDelegate<PageConfiguration>
with ChangeNotifier, PopNavigatorRouterDelegateMixin<PageConfiguration> {
final List<Page> _pages = [];
final AppState appState;
final GlobalKey<NavigatorState> navigatorKey;
ShoppingRouterDelegate(this.appState) : navigatorKey = GlobalKey() {
appState.addListener(() {
notifyListeners();
});
}
List<MaterialPage> get pages => List.unmodifiable(_pages);
Future<bool> popRoute() {
_removePage(_pages.last);
return Future.value(false);
}
Future<void> setNewRoutePath(PageConfiguration configuration) {
if (shouldAddPage) {
_pages.clear();
addPage(configuration);
}
return SynchronousFuture(null);
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Navigator(
key: navigatorKey,
onPopPage: _onPopPage,
pages: buildPages(),
);
}
}
MyRouterDelegate有_pages属性,这个属性作为Navigator的pages;appState是状态管理的数据,用这个数据去驱动MyRouterDelegate的观察者也就是Router即去重构,这样Navigator也就会重构了。popRoute将_pages的最后一个页面删掉,通知Router即去重构,更新Navigator;setNewRoutePath给_pages添加对应的Page,通知Router即去重构Navigator。
BackButtonDispatcher
BackButtonDispatcher主要就是解决安卓,网页等物理返回的事件。它有两个子类RootBackButtonDispatcher和ChildBackButtonDispatcher可以解决Navigator的嵌套问题。
BackButtonDispatcher的返回处理可以直接交给RouterDelegate去处理,例如下面的逻辑:
class MyBackButtonDispatcher extends RootBackButtonDispatcher {
final MyRouterDelegate _routerDelegate;
MyBackButtonDispatcher(this._routerDelegate)
: super();
// 3
@override
Future<bool> didPopRoute() {
return _routerDelegate.popRoute();
}
}
最后总结
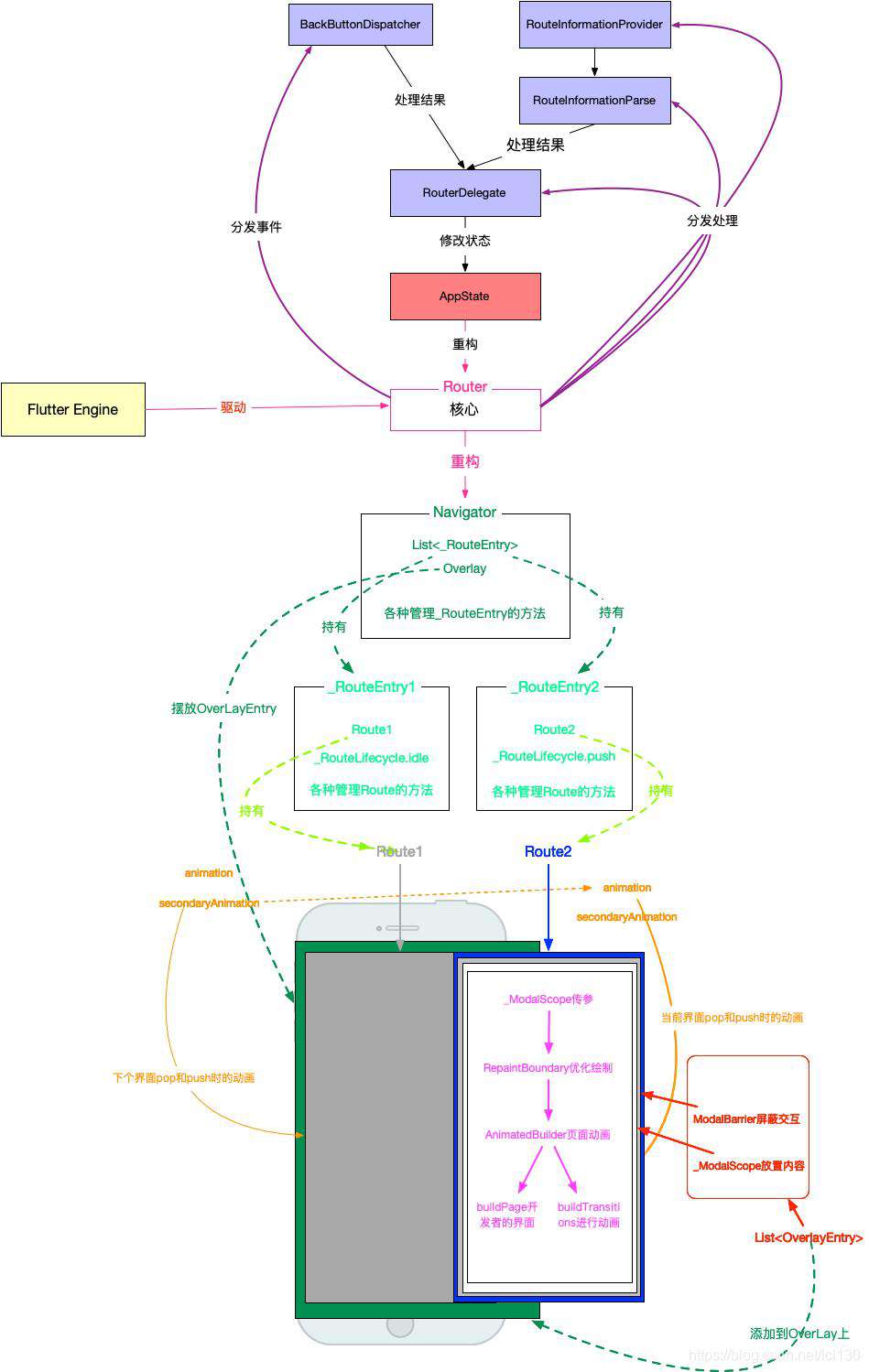
总结
Navigator 2.0的功能更加强大了,使用方式也变得更加Flutter了。但是变得更复杂了,这样对学习和使用成本造成了很大的困扰,这方面也是很多人认为Navigator 2.0是一个失败的改造的原因。
本文主要从源码角度分析了Navigator 2.0的实现逻辑,原理清楚后写代码应该还是很简单的。
如果你需要Demo,可以参阅下面两篇文章的代码,特别是第一篇文章的代码非常具有参考价值:
Flutter Navigator 2.0 and Deep Links
Learning Flutter’s new navigation and routing system
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!