大家好,我是前端图图。现在基本上每周都会更新一篇文章,也算是把自己学过的东西分享给大家。或者说算是一次复盘吧。下面废话不多说,这篇文章我们就来聊聊链表。
链表
链表数据结构
首先,数组在我们日常开发当中是最常用的一种数据结构。通过[]就可以访问元素,但是数组的缺点很明显。大小是固定的,从数组的头部或中间插入或者移除一个元素的成本是非常高的。为什么这么说呢?因为要移动元素。
链表是存储有序的元素集合,链表中的每个元素都有一个存储元素(也叫节点)本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的指针所组成。
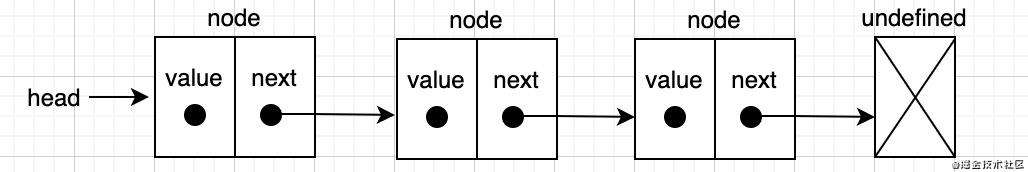
链表就像一辆火车,每节车皮就相当于链表的节点,而车皮之间的连接扣就是一个指针。
链表有一个好处是,添加或移除元素时不需要移动移动其他的元素。但是链表需要指针,所以实现链表时需要注意这一点。
单向链表
还是按照之前的惯例,用一个类来表示一个数据结构。
function equalFn(a, b) {
return a === b;
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.count = 0; // 存在链表中的节点总数
this.head = undefined; // 第一个元素的引用
this.equalFn = equalFn; // 比较函数
}
}
上面的代码中,count用来表示存储链表中的节点数量。head属性是保存第一个节点的引用。equalFn属性是一个函数,用作比较链表中的节点是否相等。
下面我们要创建的是Node类,也就是链表中的节点。
class Node {
constructor(ele) {
this.element = ele; // 链表节点的值
this.next = undefined; // 指向下一个元素的指针
}
}
Node类具有两个属性:element和next。
我们来看看单向链表具有哪些方法。
push(ele):向链表末尾添加一个节点。insert(ele, position):向链表特定的位置插入一个节点。getElementAt(index):获取链表中某个位置的节点,如果节点不存在,则返回undefined。remove(ele):移除链表中的节点。indexOf(ele):查看节点所在的位置,如果没找到则返回-1。removeAt(position):移除链表中特定位置的一个节点。isEmpty:查看链表是否为空,为空返回true,不为空false。size():返回链表中的节点个数。toString():返回整个链表节点拼接的字符串。
push方法
在向LinkedList对象末尾添加节点时,有两种场景:
- 链表为空时,表示添加的是第一个节点;
- 链表不为空时,向链表末尾追加节点;
push(ele) {
const node = new Node(ele);
// 当前节点
let current = "";
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
while (current.next != undefined) {
// 设置current为下一个元素进行迭代
current = current.next;
}
// current.next为undefined就表示已经是链表的末尾,然后把最后一个节点的指针属性设置为下一个元素
current.next = node;
}
this.count++;
}
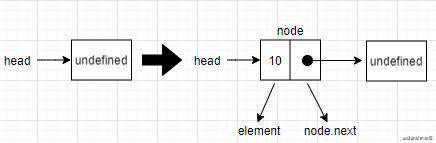
- 向链表中添加一个节点时,如果
head为undefined,那就证明是向链表添加第一个元素。
- 向一个非空的链表添加一个节点时,首先要找到最后一个节点。那么只能通过第一个节点的引用,循环访问链表,直到找到最后一个节点。
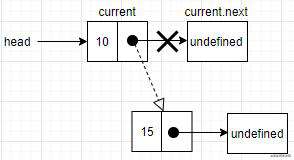
用循环的方式访问链表才能找到最后一个元素,所以就需要一个指向链表中当前节点的变量current。在循环访问的过程中,如果当前元素的指针为undefined,就说明到达链表的末尾了。然后用最后一个元素的指针指向想要添加到链表的节点。
const linked = new LinkedList();
linked.push(10);
linked.push(15);
linked.push(11);
console.log(linked.head);
// 通过浏览器控制台可以查看
// Node {
// element: 10,
// next: Node {
// element: 15,
// next: Node {
// element: 11,
// next: undefined
// }
// }
// }
removeAt方法
从链表中移除一个节点要实现的两种删除节点方法:
- 从特定位置移除一个节点。
- 根据元素的值移除元素(后面再说)。
从链表中移除节点存在两种场景:
- 移除第一个元素。
- 移除其他的元素。
下面是removeAt方法。
removeAt(index) {
// 验证index是否有效。
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
// 获取第一个节点
current = this.head;
// 删除第一个元素
if (index === 0) {
// 将第二个节点设置为第一个节点,从而实现了删除第一个节点的效果
this.head = current.next;
} else {
// 当前节点的前一个节点的引用
let prev = "";
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 把当前节点的上一个节点和当前节点的下一个节点连接起来,跳过当前节点,从而删除它
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
首先验证index是否有效,如果不是有效的位置就返回undefined。移除第一个元素时,就是将head指向链表中的第二个节点,用current变量保存链表中第一个节点。将head的值赋为current.next的值就会移除了第一个节点。
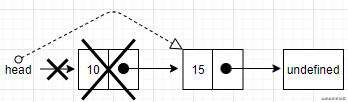
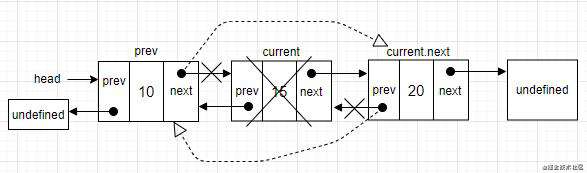
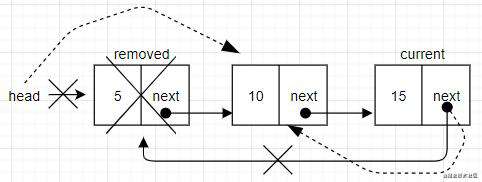
要移除链表中最后一个或者是中间某个节点。就要迭代链表的节点,直到找到目标位置。需要注意的是,current一直都引用着链表中的节点。这里还有一个变量prev,prev表示当前节点的前一个节点。在迭代找到目标位置后,current变量就是想要移除的节点。通过用当前节点的前一个节点和当前节点的下一个节点连接起来,实现移除节点的效果。看下面的图就很容易明白了。
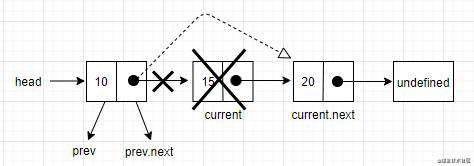
如果是最后一个元素,在跳出循环时,current变量就是链表中最后一个节点。current.next的值为undefined。由于还保留了对prev节点的引用,prev.next就指向了current。要移除current,就是把prev.next的值改成current.next的值。
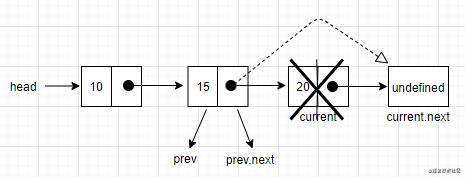
console.log(linked.removeAt(2)); // 11
如果理解了移除链表中的节点这个例子,后面的操作就很好理解了。
getElementAt方法
下面是getElementAt方法。
getElementAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
// 初始化node变量,从链表的第一个节点开始迭代
let node = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index && node != undefined; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
return undefined;
}
console.log(linked.getElementAt(1));
// Node {element: 15, next: undefined}
上面代码中,使用一个node变量,从第一个节点开始迭代整个链表。直到目标index。结束循环时,node变量就是index位置的节点引用。
大家可以看到getElementAt方法的部分逻辑和removeAt方法相似,我们可以改写一下removeAt方法。
removeAt(index) {
// 验证index是否有效。
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
// 获取第一个节点
let current = this.head;
// 删除第一个元素
if (index === 0) {
// 将第二个节点设置为第一个节点,从而实现了删除第一个节点的效果
this.head = current.next;
} else {
// 获取前一个节点
let prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
insert方法
下面来实现insert方法,该方法可以在任何位置插入一个节点。
insert(ele, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(ele);
if (index === 0) {
// 第一个节点的引用
const current = this.head;
node.next = current;
this.head = node;
} else {
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
const current = prev.next;
node.next = current;
prev.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
首先检查index是否有效,和removeAt类似。如果位置是有效的,就要处理不同的场景。
- 场景一:在链表第一个位置添加一个节点,
current是链表中第一个节点的引用,把node.next的值设为current。最后把head的引用改成node。
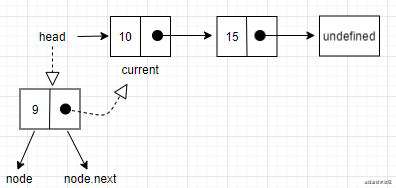
- 场景二:在链表中间或尾部添加一个节点。首先,迭代链表,找到目标位置。这时,会循环到
index - 1的位置,也就是添加新节点的前一个位置。当循环结束后,prev就是想要插入节点的位置的前一个节点,而current是想要插入节点的位置后面一个节点。在prev和current之间插入新元素,先把新节点和当前节点链接起来,然后需要改变prev和current之间的链接。还需要把prev.next指向node,用node取代掉current。
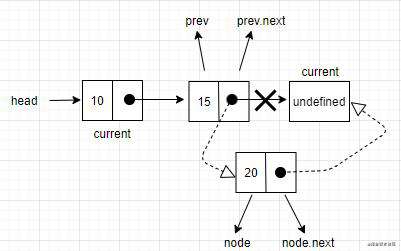
向最后一个位置添加一个节点,prev就是链表最后一个节点,current就是undefined。在这种情况下,nodex.next将指向current,而prev.next指向node。
向链表中间添加一个元素的过程如下。
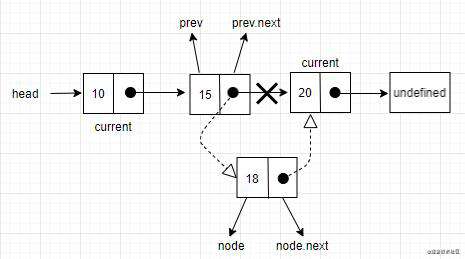 像这种情况,把新元素插入
像这种情况,把新元素插入prev和current元素之间。首先需要把node.next的值指向current,
然后把prev.next的值设置为node。
linked.insert(20, 2);
console.log(linked.head);
console.log(linked.getElementAt(2));
// Node {element: 20, next: undefined}
indexOf方法
indexOf方法接收一个节点的值,如果在链表中找到该节点,就返回节点的位置,否则返回-1。
indexOf(ele) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.count && current.next != undefined; i++) {
if (this.equalFn(ele, current.element)) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
同样的。首先,需要一个变量current来循环访问链表,它的值就是head。然后迭代元素,从head开始一直到链表的末尾为止。然后用equalFn判断相等函数。大家需要注意的是,equalFn函数只能运用在基本数据类型上。如果节点的值是一个引用类型的值,就需要自己写一个判断函数。如果当前位置的节点是我们要找的节点,就返回它的位置。如果没找到,则返回-1表示没找着。
remove方法
remove方法的实现就比较简单了,这里就使用reomoveAt和indexOf方法组合起来。
remove(ele) {
const index = this.indexOf(ele);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
isEmpty、size、getHead方法
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
isEmpty和size方法的实现和队列一样。而getHead方法只要返回头部的元素即可。
clear方法
clear方法只要把count和head的值设置成初始化时的值即可。
clear() {
this.count = 0;
this.head = undefined;
}
toString方法
toString方法就是把LinkedList对象
toString() {
if (this.head == undefined) {
return "";
}
let objString = `${this.head.element}`;
let current = this.head.next;
for (let i = 1; i < this.size() && current != undefined; i++) {
objString = `${objString} -> ${current.element}`;
current = current.next;
}
return objString;
}
toString方法和之前讲过的数据结构的toString方法都是大同小异的,这里就不做过多的讲解。
整体代码
function equalFn(a, b) {
return a === b;
}
class Node {
constructor(ele) {
this.element = ele; // 链表节点的值
this.next = undefined; // 指向下一个元素的指针
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.count = 0; // 存在链表中的元素总数
this.head = undefined; // 第一个元素的引用
this.equalFn = equalFn;
}
push(ele) {
const node = new Node(ele);
let current = "";
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
while (current.next != undefined) {
// 设置current为下一个元素进行迭代
current = current.next;
}
// current.next为undefined就表示已经是链表的末尾,然后把最后一个节点的指针属性设置为下一个元素
current.next = node;
}
this.count++;
}
removeAt(index) {
// 验证index是否有效。
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
// 获取第一个节点
let current = this.head;
// 删除第一个元素
if (index === 0) {
// 将第二个节点设置为第一个节点,从而实现了删除第一个节点的效果
this.head = current.next;
} else {
// 获取前一个节点
let prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
getElementAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
// 初始化node变量,从链表的第一个节点开始迭代
let node = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index && node != undefined; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
return undefined;
}
insert(ele, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(ele);
if (index === 0) {
// 第一个节点的引用
const current = this.head;
node.next = current;
this.head = node;
} else {
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
const current = prev.next;
node.next = current;
prev.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
indexOf(ele) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.count && current != undefined; i++) {
if (this.equalFn(ele, current.element)) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
remove(ele) {
const index = this.indexOf(ele);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
clear() {
this.count = 0;
this.head = undefined;
}
toString() {
if (this.head == undefined) {
return "";
}
let objString = `${this.head.element}`;
let current = this.head.next;
for (let i = 1; i < this.size() && current != undefined; i++) {
objString = `${objString} -> ${current.element}`;
current = current.next;
}
return objString;
}
}
const linked = new LinkedList();
console.log(linked.size()); // 0
linked.push(10);
linked.push(15);
linked.push(11);
console.log(linked.removeAt(2)); // 11
console.log(linked.getElementAt(1)); // 15
linked.insert(20, 2);
console.log(linked.getElementAt(2)); // 20
console.log(linked.getHead());
// Node {element: 10, next: Node}
linked.insert(9, 0);
console.log(linked.getElementAt(0)); // 9
console.log(linked.indexOf(9)); // 0
console.log(linked.indexOf(20)); // 3
console.log(linked.toString());
// 9 -> 10 -> 15 -> 20
console.log(linked.size()); // 4
console.log(linked.remove(9)); // 9
console.log(linked.toString());
// 10 -> 15 -> 20
linked.clear();
console.log(linked.isEmpty());
// true
双向链表
双向链表和单向链表的区别就在于,每个节点还具有一个指向上一个节点的指针。也就是说,第一个节点指向第二个节点,而第二个节点又指向第一个节点。看下面的图。
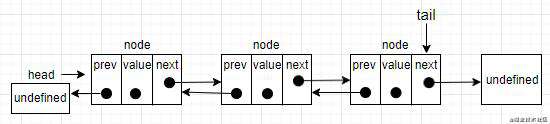
可以看到,双向链表的每个节点都多出一个指向上一个节点的指针(prev)。
下面我们来创建一个双向链表的类。
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalFn) {
super(equalFn);
this.tail = undefined; // 最后一个节点的引用
}
}
双向链表是一种特殊的链表,具有单向链表的属性。我们可以通过extends继承LinkedList类上的属性,并新增一个tail属性用来保存链表最后一个节点的引用。
class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(ele, next) {
super(ele, next);
this.prev = undefined; // 前一个元素的指针
}
}
DoublyNode是一个特殊节点,不仅继承了Node上的属性,还需要添加一个指向前一个节点的指针prev属性。
下面我们要重写几个方法。
insert方法
往双向链表中插入一个节点和单向链表类似。单向链表只需要控制next指针,而双向链表需要控制prev和next两个指针。下面将重写insert方法。
insert(ele, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new DoublyNode(ele);
let current = this.head;
// 场景一:插入第一个节点或从头部插入一个节点
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else if (index === this.count) {
// 场景二:从末尾添加一个节点
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
} else {
// 场景三:从双向链表中间插入节点
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
node.next = current;
prev.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = prev;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
上面的代码中,分别考虑了三种场景。
- 场景一:往双向链表中第一个位置插入一个节点,和单向链表里的操作差不多。主要区别在于需要给上一个节点的指针设一个值,
current.prev指针指向undefined变成指向新元素,node.prev指针已经是undefined,所以不需要做任何的操作。
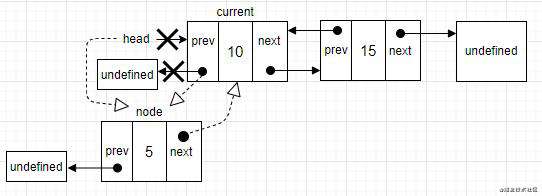
- 场景二:向双向链表尾部添加一个节点,就需要控制指向最后一个节点的指针。
current引用最后一个节点,然后建立连接。current.next指针指向node(node已经指向了undefined),node.prev指向current。最后更新tail。它原来指向current现在变成指向node。
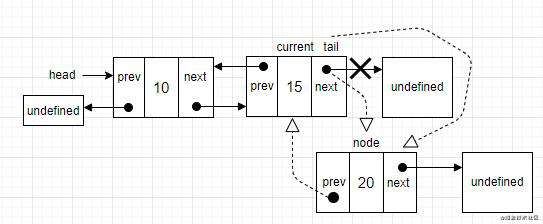
- 场景三:在双向链表中间插入一个节点,跟单向链表的做法一样。用
LinkedList继承下来的getElementAt方法,迭代双向链表,直到要找的位置。在prev和current之间插入节点。先把node.next指向current,而prev.next指向node。然后需要把它们都链接起来,current.prev指向node,node.prev指向prev。
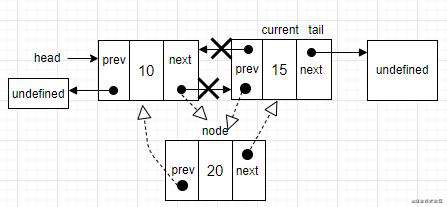
removeAt方法
从双向链表中删除一个节点和单向链表类似。区别在于,需要设置前一个位置的指针。
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
// 场景一:删除第一个节点
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
if (this.count === 1) {
this.tail = undefined;
} else {
this.head.prev = undefined;
}
} else if (index === this.count - 1) {
// 场景二:删除最后一个位置的节点
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = undefined;
} else {
// 场景三:删除中间一个节点
current = this.getElementAt(index);
const prev = current.prev;
prev.next = current.next;
current.prev.next = prev;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
同样是要处理三种不同的场景。
- 场景一:移除第一个节点。
current是双向链表中的第一个节点,它也是要删除的节点。需要做的是改变head的引用,将它从current改为下一个节点。还要更新current.next指向上一个节点的指针(第一个节点的prev指针是undefined)。因此,把head.prev的引用改成undefined(因为head也指向了双向链表中的新的第一个节点)。还需要控制tail的引用,可以检查双向链表中是否只有一个节点,如果只有一个节点就把tail设为undefined。
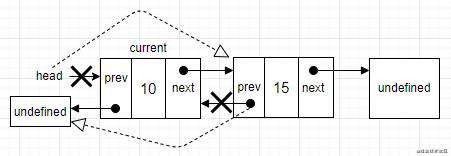
- 场景二:从最后一个位置删除节点。有了最后一个节点
tail,就不需要迭代双链表找到最后一个节点了。直接把tail的值赋给current。然后,把tail更新为双向链表的倒数第二个元素。然后再把next指针更新为undefined。
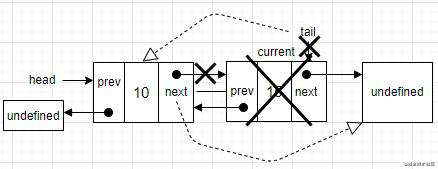
- 场景三:从双向链表中间删除一个节点。首先要迭代双向链表,找到该节点的位置。
current变量就是要删除的节点。通过prev.next指向current.next,直接跳过它。最后,current.prev.next指向prev。
整体代码
class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(ele, next) {
super(ele, next);
this.prev = undefined;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalFn) {
super(equalFn);
this.tail = undefined;
}
push(ele) {
const node = new DoublyNode(ele);
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node; // 新增
} else {
// 新增
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.count++;
}
insert(ele, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new DoublyNode(ele);
let current = this.head;
// 场景一:插入第一个节点或从头部插入一个节点
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else if (index === this.count) {
// 场景二:从末尾添加一个节点
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
} else {
// 场景三:从双向链表中间插入节点
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
node.next = current;
prev.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = prev;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
// 场景一:删除第一个节点
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
if (this.count === 1) {
this.tail = undefined;
} else {
this.head.prev = undefined;
}
} else if (index === this.count - 1) {
// 场景二:删除最后一个位置的节点
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = undefined;
} else {
// 场景三:删除中间一个节点
current = this.getElementAt(index);
const prev = current.prev;
prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = prev;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
indexOf(ele) {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current != undefined) {
if (this.equalFn(ele, current.element)) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
getTail() {
return this.tail;
}
clear() {
super.clear();
this.tail = undefined;
}
toString() {
if (this.head == undefined) {
return "";
}
let objString = `${this.head.element}`;
let current = this.head.next;
while (current != undefined) {
objString = `${objString} -> ${current.element}`;
current = current.next;
}
return objString;
}
inverseToString() {
if (this.tail == undefined) {
return "";
}
let objString = `${this.tail.element}`;
let prev = this.tail.prev;
while (prev != undefined) {
objString = `${objString} -> ${prev.element}`;
prev = prev.prev;
}
return objString;
}
}
const list = new DoublyLinkedList();
console.log(list.isEmpty()); // true
list.push(10);
list.push(11);
list.push(12);
console.log(list.size()); // 3
console.log(list.toString());
// 10 -> 11 -> 12
console.log(list.removeAt(list.size() - 1));
console.log(list.inverseToString());
// 11 -> 10
console.log(list.size());// 2
console.log(list.toString());
// 10 -> 11
双向链表的优点在于,从链表中的任何一个节点开始,都可以很方便地访问前面的节点和后面的节点。还可以从头部或尾部开始循环迭代。
缺点:增加了删除的难度,需要多分配一个指针存储空间。
循环链表
循环链表是单双链表的组合体。可单向引用,也可以双向引用。和双向链表的区别在于,最后一个节点指向下一个节点的的指针(tail.next)不是undefined,而是指向第一个节点head。
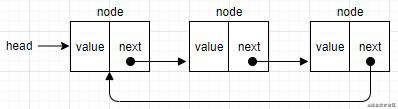
双向循环链表的tail.next指向head,而head.prev指向tail。
class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalFn) {
super(equalFn);
}
}
CircularLinkedList没有任何额外的属性,直接继承LinkedList类并覆盖要改写的方法就行了。
insert方法
向循环链表插入节点的逻辑跟单向链表插入元素的逻辑一样,主要区别在于把循环链表末尾的节点的next指针指向头部节点head。
insert(ele, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(ele);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
node.next = this.head;
} else {
node.next = current;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
this.head = node;
current.next = this.head;
}
} else {
// 和单向链表一样
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
node.next = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
下面来分析不同的场景。
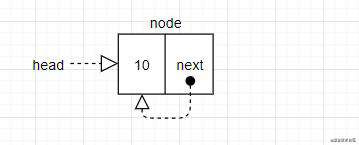
- 场景一:在循环链表第一个位置插入节点,如果循环链表为空,将
head的值赋为node,并把最后一个节点与head链接起来。而这个节点也就是node,同时也是head。
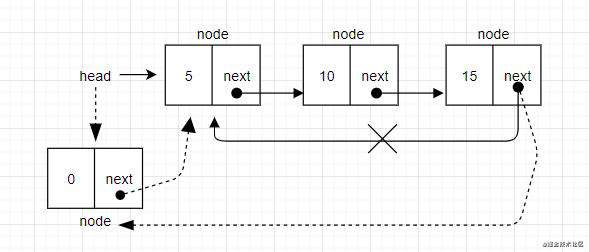
- 场景二:在一个非空循环链表的第一个位置插入节点。首先,需要把
node.next指向head(current变量)。然后用getElementAt方法并传入循环链表的长度作为参数,将头部节点更新为node节点,再把最后一个节点current指向新的头部节点。
如果在循环链表中间插入节点,代码和LinkedList中的一模一样,因为并没有对循环链表中的第一个和最后一个节点做修改。
removeAt方法
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.size() === 1) {
this.head = undefined;
} else {
// 新增
const removed = this.head;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
this.head = this.head.next;
current.next = this.head;
// 改变current引用,因为后面return的时候要用到该值并且表示移除了元素的值
current = removed;
}
} else {
// 不变
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
从循环链表中移除节点,只需要考虑第二种场景,也就是修改循环链表的head节点。
- 场景一:从只有一个节点的循环链表中删除元素,直接把
head的值改成undefined。 - 场景二:从一个非空链表中移除第一个元素,首先保存现在的
head节点引用,将从循环链表中移除。下面,获取循环链表中最后一个节点,它被存储在current变量中。接下来要做的是,开始链接新的节点的指向。首先,把head指向第二个节点,然后再把最后一个节点指向head。最后更新current变量的引用,因为还要返回删除的节点的值表示移除了节点。
整体代码
class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalFn) {
super(equalFn);
}
push(ele) {
const node = new Node(ele);
let current;
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.getElementAt(this.size() - 1);
current.next = node;
}
node.next = this.head;
this.count++;
}
insert(ele, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(ele);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == undefined) {
this.head = node;
node.next = this.head;
} else {
node.next = current;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
this.head = node;
current.next = this.head;
}
} else {
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
node.next = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.size() === 1) {
this.head = undefined;
} else {
const removed = this.head;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
this.head = this.head.next;
current.next = this.head;
// 改变current引用,return的时候要用到该值并且表示移除了该节点
current = removed;
}
} else {
// 不变
const prev = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
}
有序链表
有序链表指的是保持节点有序的链表结构。
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
};
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return 0;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
class SortedLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalFn) {
super(equalFn);
this.compareFn = defaultCompare;
}
}
SortedLinkedList类继承了LinkedList类中的所有属性和方法。但这个类比较特殊,需要一个比较节点的函数compareFn。如果节点有相同的,就返回0。如果第一个元素小于第二个元素就返回-1,否则返回1。
insert方法
insert(ele) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return super.insert(ele, 0);
}
const pos = this.getIndexNextSortedEle(ele);
return super.insert(ele, pos);
}
getIndexNextSortedEle(ele) {
let current = this.head;
let i = 0;
for (; i < this.size() && current; i++) {
const comp = this.compareFn(ele, current.element);
if (comp === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
return i;
}
在这个insert方法中,没有index参数。插入节点的位置是由内部控制的,因为是有序链表。如果有序链表为空,直接调用父类LinkedList上的insert方法并传入0作为index。如果不为空,就知道插入元素的正确位置并调用LinkedList类上的insert方法,传入该位置来保存链表的有序。
要获取插入节点的正确位置,这里创建了一个getIndexNextSortedEle方法。这个方法中,迭代整个有序链表直到找到插入节点的位置或迭代完所有的节点。在后者的场景中,返回的index是有序链表的长度(把节点插入末尾)。然后用compareFn比较传入构造函数的节点。当要插入的节点小于current的节点时,就找到插入节点的位置。
其他的方法直接调用LinkedList类中的方法即可。
整体代码
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
};
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return 0;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
class SortedLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalFn) {
super(equalFn);
this.compareFn = defaultCompare;
}
push(ele) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
super.push(ele);
} else {
const index = this.getIndexNextSortedEle(ele);
super.insert(ele, index);
}
}
insert(ele) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return super.insert(ele, 0);
}
const pos = this.getIndexNextSortedEle(ele);
return super.insert(ele, pos);
}
getIndexNextSortedEle(ele) {
let current = this.head;
let i = 0;
for (; i < this.size() && current; i++) {
const comp = this.compareFn(ele, current.element);
if (comp === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
return i;
}
}
const list = new SortedLinkedList();
list.push(10);
list.push(9);
list.insert(8);
console.log(list.toString());
// 8 -> 9 -> 10
配合其他数据结构
链表还可以用作内部数据结构来创建其他的数据结构。例如栈、队列和双端队列。
class StackLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.items = new DoublyLinkedList();
}
push(ele) {
this.items.push(ele);
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
const result = this.items.removeAt(this.size() - 1);
return result;
}
}
StackLinkedList类中,使用了双向链表存储数据。原因是,对于栈来说。可以从尾部添加元素,也可以从尾部删除元素。双向链表具有最后一个节点tail的引用。因此,不需要迭代整个双向链表节点就可以获取它。双向链表可以获取头部和尾部的节点,这样可以减少过程的消耗。
class StackLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.items = new DoublyLinkedList();
}
push(ele) {
this.items.push(ele);
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
const result = this.items.removeAt(this.size() - 1);
return result;
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
return this.items.getElementAt(this.size() - 1).element;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return this.items.size();
}
clear() {
this.items.clear();
}
toString() {
return this.items.toString();
}
}
const stackList = new StackLinkedList();
console.log(stackList.isEmpty());
stackList.push(10);
stackList.push(11);
console.log(stackList.toString());
// 10 -> 11
stackList.push(12);
console.log(stackList.toString());
// test.js:467 10 -> 11 -> 12
stackList.pop();
console.log(stackList.toString());
// 10 -> 11
console.log(stackList.peek()); // 11
实际上只是调用了双向链表里面的方法而已。
总结
链表和栈、队列相比,操作起来是要复杂得多的。因为要控制next和prev指针,所以大家在操作链表时要极其小心。在我看来,我会把链表想象成一条铁链。在操作链表的过程,把next和prev指针想象成铁链的扣子进行链接。这是我的想法?。
好啦!写作不易,如果喜欢的话,希望各位大佬给个赞!基本上每周都会更新一篇文章。如有哪里不对,欢迎各位大佬多多指点。
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?




发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!