写在前面
本文主要内容包括,什么是MP4、MP4文件的基本结构、Box的基本结构、常见且重要的box介绍、普通MP4与fMP4的区别、如何通过代码解析MP4文件 等。
写作背景:最近经常回答团队小伙伴关于直播 & 短视频的问题,比如 “flv.js的实现原理”、“为什么设计同学给的mp4文件浏览器里播放不了、但本地可以正常播放”、“MP4兼容性很好,可不可以用来做直播” 等。
在解答的过程中,发现经常涉及 MP4 协议的介绍。之前这块有简单了解过并做了笔记,这里稍微整理一下,顺便作为团队参考文档,如有错漏,敬请指出。
什么是MP4
首先,介绍下封装格式。多媒体封装格式(也叫容器格式),是指按照一定的规则,将视频数据、音频数据等,放到一个文件中。常见的 MKV、AVI 以及本文介绍的 MP4 等,都是封装格式。
MP4是最常见的封装格式之一,因为其跨平台的特性而得到广泛应用。MP4文件的后缀为.mp4,基本上主流的播放器、浏览器都支持MP4格式。
对从事直播、音视频相关工作的同学,很有必要了解MP4格式,下面简单介绍下。
MP4文件格式概览
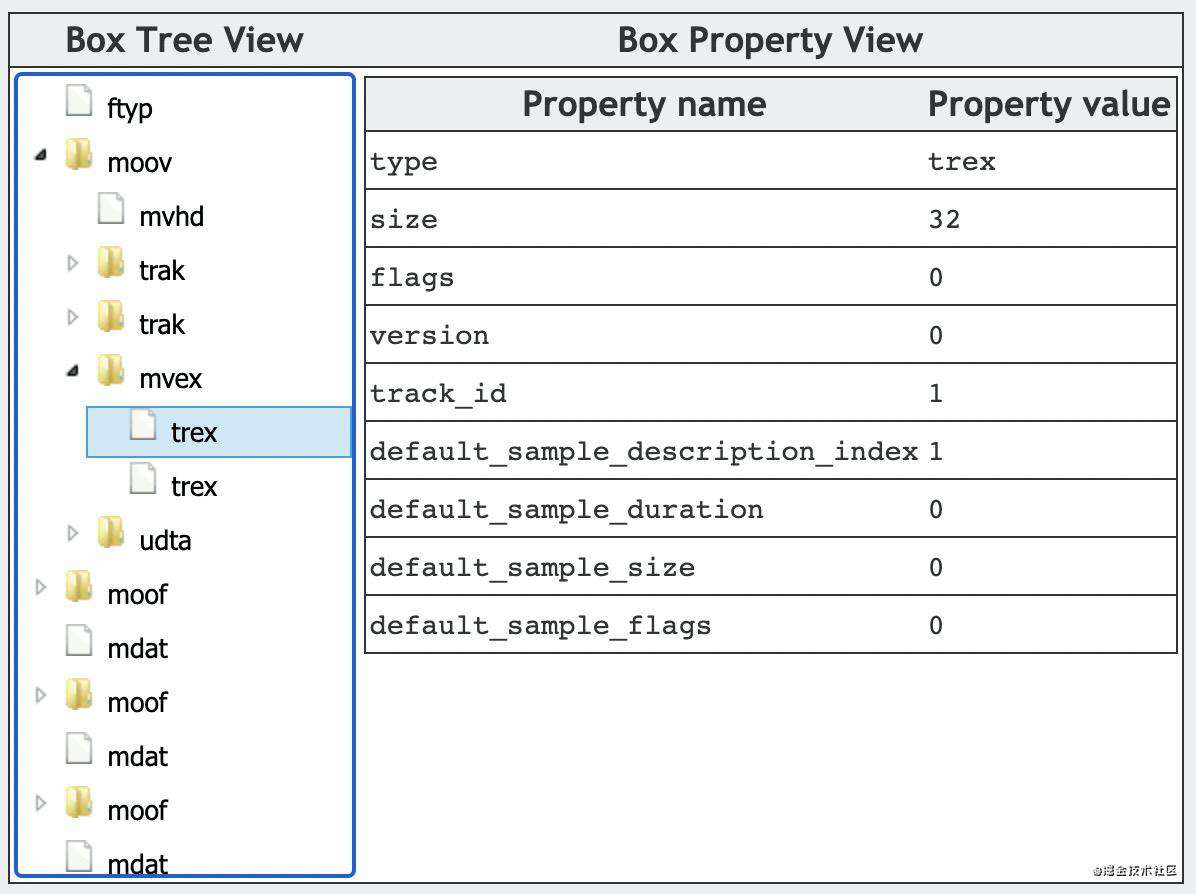
MP4文件由多个box组成,每个box存储不同的信息,且box之间是树状结构,如下图所示。
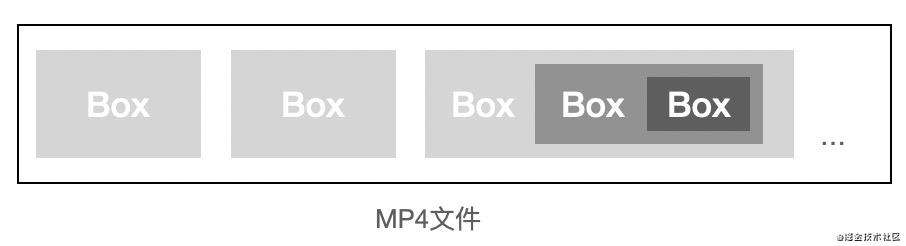
box类型有很多,下面是3个比较重要的顶层box:
- ftyp:File Type Box,描述文件遵从的MP4规范与版本;
- moov:Movie Box,媒体的metadata信息,有且仅有一个。
- mdat:Media Data Box,存放实际的媒体数据,一般有多个;
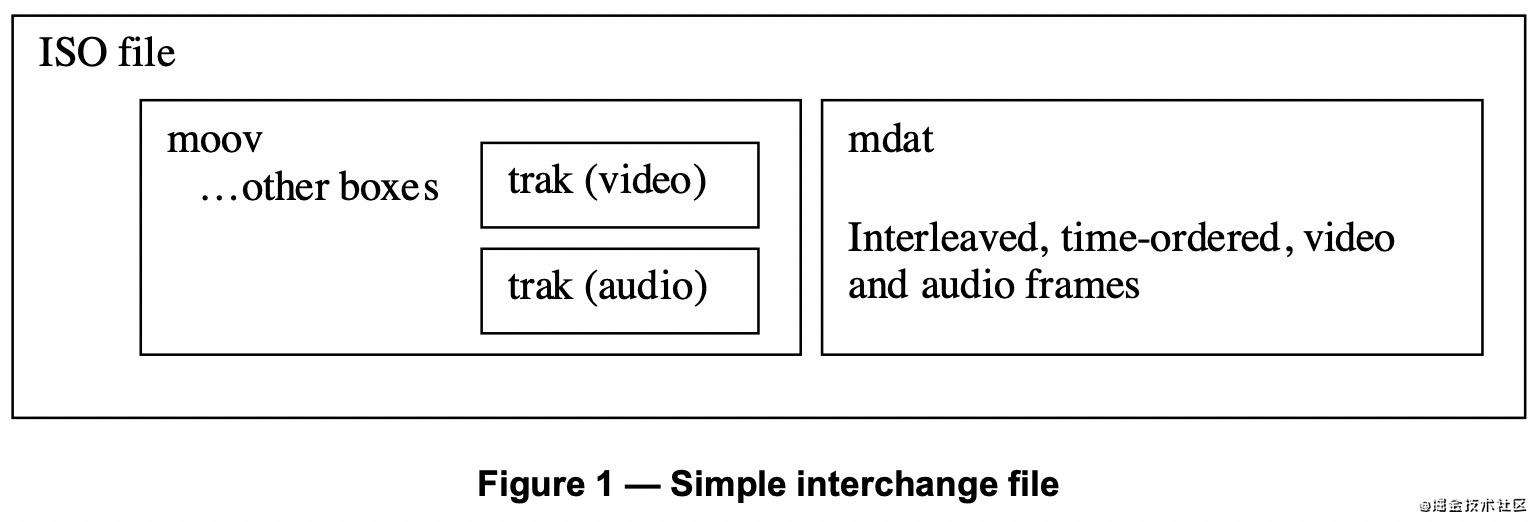
虽然box类型有很多,但基本结构都是一样的。下一节会先介绍box的结构,然后再对常见的box进行进一步讲解。
下表是常见的box,稍微看下有个大致的印象就好,然后直接跳到下一节。
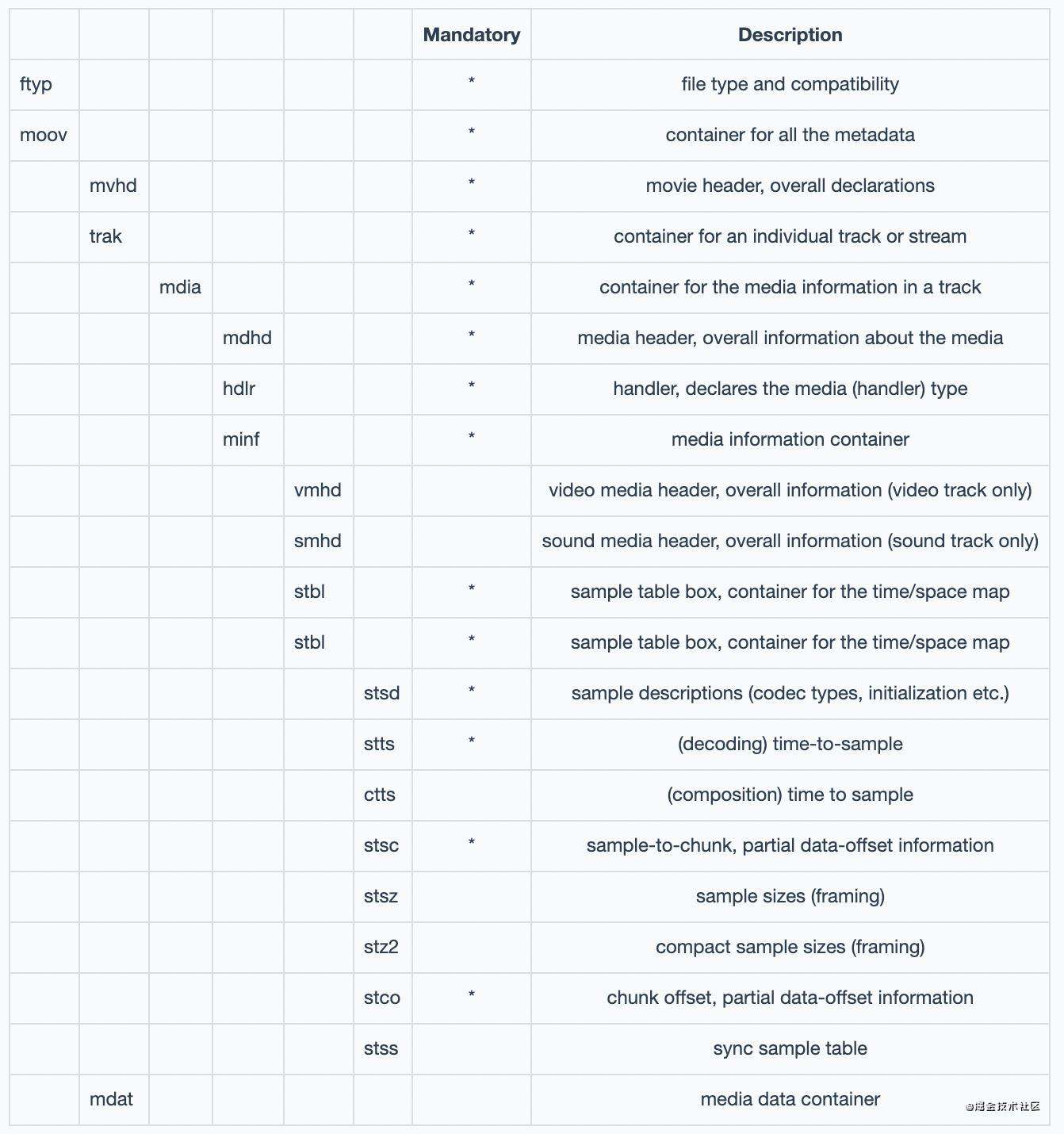
MP4 Box简介
1个box由两部分组成:box header、box body。
- box header:box的元数据,比如box type、box size。
- box body:box的数据部分,实际存储的内容跟box类型有关,比如mdat中body部分存储的媒体数据。
box header中,只有type、size是必选字段。当size==0时,存在largesize字段。在部分box中,还存在version、flags字段,这样的box叫做Full Box。当box body中嵌套其他box时,这样的box叫做container box。
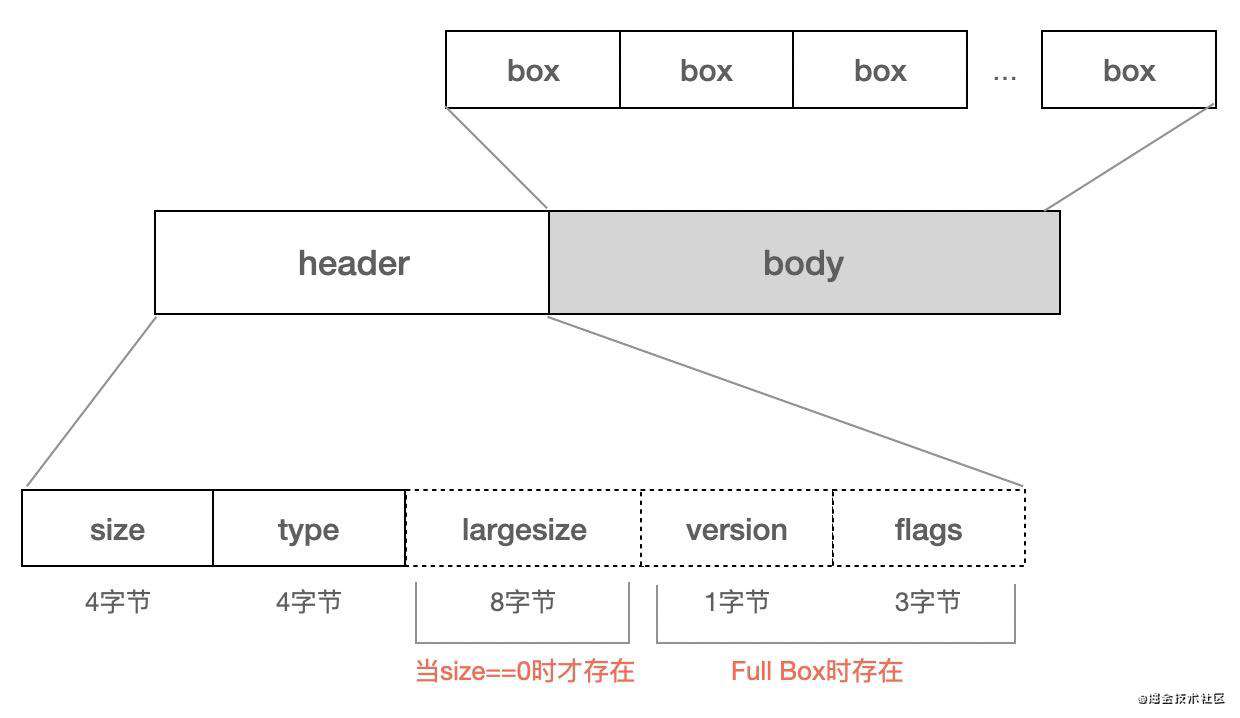
Box Header
字段定义如下:
- type:box类型,包括 “预定义类型”、“自定义扩展类型”,占4个字节;
- 预定义类型:比如ftyp、moov、mdat等预定义好的类型;
- 自定义扩展类型:如果type==uuid,则表示是自定义扩展类型。size(或largesize)随后的16字节,为自定义类型的值(extended_type)
- size:包含box header在内的整个box的大小,单位是字节。当size为0或1时,需要特殊处理:
- size等于0:box的大小由后续的largesize确定(一般只有装载媒体数据的mdat box会用到largesize);
- size等于1:当前box为文件的最后一个box,通常包含在mdat box中;
- largesize:box的大小,占8个字节;
- extended_type:自定义扩展类型,占16个字节;
Box的伪代码如下:
aligned(8) class Box (unsigned int(32) boxtype, optional unsigned int(8)[16] extended_type) {
unsigned int(32) size;
unsigned int(32) type = boxtype;
if (size==1) {
unsigned int(64) largesize;
} else if (size==0) {
// box extends to end of file
}
if (boxtype==‘uuid’) {
unsigned int(8)[16] usertype = extended_type;
}
}
Box Body
box数据体,不同box包含的内容不同,需要参考具体box的定义。有的 box body 很简单,比如 ftyp。有的 box 比较复杂,可能嵌套了其他box,比如moov。
Box vs FullBox
在Box的基础上,扩展出了FullBox类型。相比Box,FullBox 多了 version、flags 字段。
- version:当前box的版本,为扩展做准备,占1个字节;
- flags:标志位,占24位,含义由具体的box自己定义;
FullBox 伪代码如下:
aligned(8) class FullBox(unsigned int(32) boxtype, unsigned int(8) v, bit(24) f) extends Box(boxtype) {
unsigned int(8) version = v;
bit(24) flags = f;
}
FullBox主要在moov中的box用到,比如 moov.mvhd,后面会介绍到。
aligned(8) class MovieHeaderBox extends FullBox(‘mvhd’, version, 0) {
// 字段略...
}
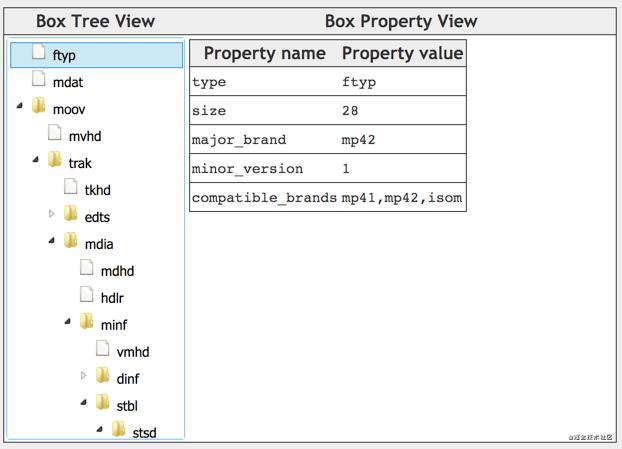
ftyp(File Type Box)
ftyp用来指出当前文件遵循的规范,在介绍ftyp的细节前,先科普下isom。
什么是isom
isom(ISO Base Media file)是在 MPEG-4 Part 12 中定义的一种基础文件格式,MP4、3gp、QT 等常见的封装格式,都是基于这种基础文件格式衍生的。
MP4 文件可能遵循的规范有mp41、mp42,而mp41、mp42又是基于isom衍生出来的。
ftyp定义
ftyp 定义如下:
aligned(8) class FileTypeBox extends Box(‘ftyp’) {
unsigned int(32) major_brand;
unsigned int(32) minor_version;
unsigned int(32) compatible_brands[]; // to end of the box
}
下面是是 brand 的描述,其实就是具体封装格式对应的代码,用4个字节的编码来表示,比如 mp41。
ftyp 的几个字段的含义:
- major_brand:比如常见的 isom、mp41、mp42、avc1、qt等。它表示“最好”基于哪种格式来解析当前的文件。举例,major_brand 是 A,compatible_brands 是 A1,当解码器同时支持 A、A1 规范时,最好使用A规范来解码当前媒体文件,如果不支持A规范,但支持A1规范,那么,可以使用A1规范来解码;
- minor_version:提供 major_brand 的说明信息,比如版本号,不得用来判断媒体文件是否符合某个标准/规范;
- compatible_brands:文件兼容的brand列表。比如 mp41 的兼容 brand 为 isom。通过兼容列表里的 brand 规范,可以将文件 部分(或全部)解码出来;
下面是常见的几种brand,以及对应的文件扩展名、mime type,更多brand可以参考 这里 。
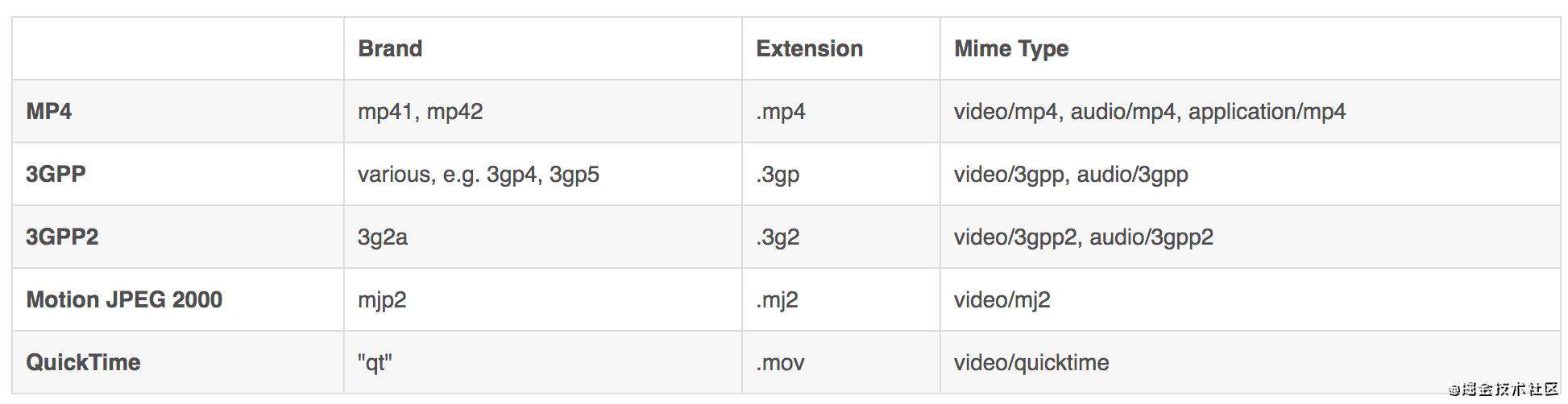
下面是实际例子的截图,不赘述。
关于AVC/AVC1
在讨论 MP4 规范时,提到AVC,有的时候指的是“AVC文件格式”,有的时候指的是"AVC压缩标准(H.264)",这里简单做下区分。
- AVC文件格式:基于 ISO基础文件格式 衍生的,使用的是AVC压缩标准,可以认为是MP4的扩展格式,对应的brand 通常是 avc1,在MPEG-4 PART 15 中定义。
- AVC压缩标准(H.264):在MPEG-4 Part 10中定义。
- ISO基础文件格式(Base Media File Format) 在 MPEG-4 Part 12 中定义。
moov(Movie Box)
Movie Box,存储 mp4 的 metadata,一般位于mp4文件的开头。
aligned(8) class MovieBox extends Box(‘moov’){ }
moov中,最重要的两个box是 mvhd 和 trak:
- mvhd:Movie Header Box,mp4文件的整体信息,比如创建时间、文件时长等;
- trak:Track Box,一个mp4可以包含一个或多个轨道(比如视频轨道、音频轨道),轨道相关的信息就在trak里。trak是container box,至少包含两个box,tkhd、mdia;
mvhd(Movie Header Box)
MP4文件的整体信息,跟具体的视频流、音频流无关,比如创建时间、文件时长等。
定义如下:
aligned(8) class MovieHeaderBox extends FullBox(‘mvhd’, version, 0) { if (version==1) {
unsigned int(64) creation_time;
unsigned int(64) modification_time;
unsigned int(32) timescale;
unsigned int(64) duration;
} else { // version==0
unsigned int(32) creation_time;
unsigned int(32) modification_time;
unsigned int(32) timescale;
unsigned int(32) duration;
}
template int(32) rate = 0x00010000; // typically 1.0
template int(16) volume = 0x0100; // typically, full volume const bit(16) reserved = 0;
const unsigned int(32)[2] reserved = 0;
template int(32)[9] matrix =
{ 0x00010000,0,0,0,0x00010000,0,0,0,0x40000000 };
// Unity matrix
bit(32)[6] pre_defined = 0;
unsigned int(32) next_track_ID;
}
字段含义如下:
- creation_time:文件创建时间;
- modification_time:文件修改时间;
- timescale:一秒包含的时间单位(整数)。举个例子,如果timescale等于1000,那么,一秒包含1000个时间单位(后面track等的时间,都要用这个来换算,比如track的duration为10,000,那么,track的实际时长为10,000/1000=10s);
- duration:影片时长(整数),根据文件中的track的信息推导出来,等于时间最长的track的duration;
- rate:推荐的播放速率,32位整数,高16位、低16位分别代表整数部分、小数部分([16.16]),举例 0x0001 0000 代表1.0,正常播放速度;
- volume:播放音量,16位整数,高8位、低8位分别代表整数部分、小数部分([8.8]),举例 0x01 00 表示 1.0,即最大音量;
- matrix:视频的转换矩阵,一般可以忽略不计;
- next_track_ID:32位整数,非0,一般可以忽略不计。当要添加一个新的track到这个影片时,可以使用的track id,必须比当前已经使用的track id要大。也就是说,添加新的track时,需要遍历所有track,确认可用的track id;
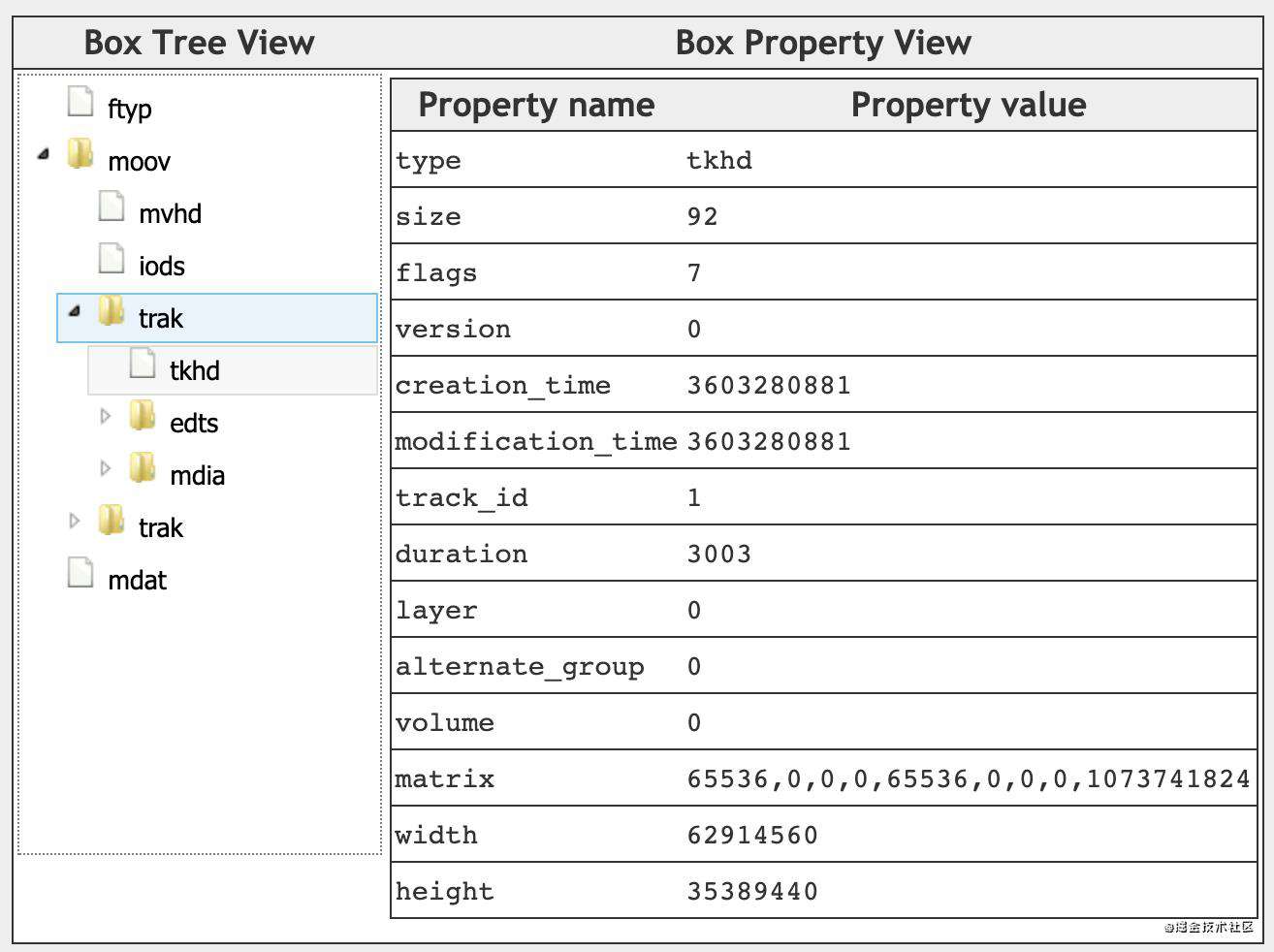
tkhd(Track Box)
单个 track 的 metadata,包含如下字段:
- version:tkhd box的版本;
- flags:按位或操作获得,默认值是7(0x000001 | 0x000002 | 0x000004),表示这个track是启用的、用于播放的 且 用于预览的。
- Track_enabled:值为0x000001,表示这个track是启用的,当值为0x000000,表示这个track没有启用;
- Track_in_movie:值为0x000002,表示当前track在播放时会用到;
- Track_in_preview:值为0x000004,表示当前track用于预览模式;
- creation_time:当前track的创建时间;
- modification_time:当前track的最近修改时间;
- track_ID:当前track的唯一标识,不能为0,不能重复;
- duration:当前track的完整时长(需要除以timescale得到具体秒数);
- layer:视频轨道的叠加顺序,数字越小越靠近观看者,比如1比2靠上,0比1靠上;
- alternate_group:当前track的分组ID,alternate_group值相同的track在同一个分组里面。同个分组里的track,同一时间只能有一个track处于播放状态。当alternate_group为0时,表示当前track没有跟其他track处于同个分组。一个分组里面,也可以只有一个track;
- volume:audio track的音量,介于0.0~1.0之间;
- matrix:视频的变换矩阵;
- width、height:视频的宽高;
定义如下:
aligned(8) class TrackHeaderBox
extends FullBox(‘tkhd’, version, flags){
if (version==1) {
unsigned int(64) creation_time;
unsigned int(64) modification_time;
unsigned int(32) track_ID;
const unsigned int(32) reserved = 0;
unsigned int(64) duration;
} else { // version==0
unsigned int(32) creation_time;
unsigned int(32) modification_time;
unsigned int(32) track_ID;
const unsigned int(32) reserved = 0;
unsigned int(32) duration;
}
const unsigned int(32)[2] reserved = 0;
template int(16) layer = 0;
template int(16) alternate_group = 0;
template int(16) volume = {if track_is_audio 0x0100 else 0}; const unsigned int(16) reserved = 0;
template int(32)[9] matrix= { 0x00010000,0,0,0,0x00010000,0,0,0,0x40000000 }; // unity matrix
unsigned int(32) width;
unsigned int(32) height;
}
例子如下:
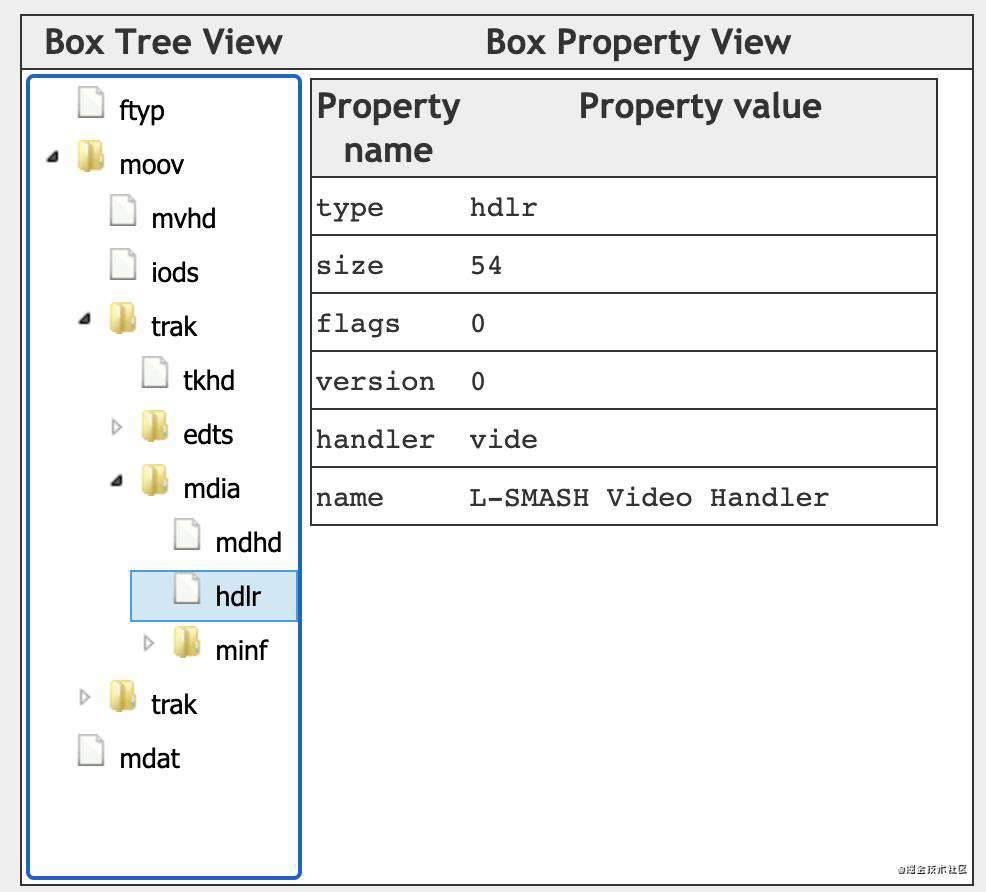
hdlr(Handler Reference Box)
声明当前track的类型,以及对应的处理器(handler)。
handler_type的取值包括:
- vide(0x76 69 64 65),video track;
- soun(0x73 6f 75 6e),audio track;
- hint(0x68 69 6e 74),hint track;
name为utf8字符串,对handler进行描述,比如 L-SMASH Video Handler(参考 这里)。
aligned(8) class HandlerBox extends FullBox(‘hdlr’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) pre_defined = 0;
unsigned int(32) handler_type;
const unsigned int(32)[3] reserved = 0;
string name;
}
stbl(Sample Table Box)
MP4文件的媒体数据部分在mdat box里,而stbl则包含了这些媒体数据的索引以及时间信息,了解stbl对解码、渲染MP4文件很关键。
在MP4文件中,媒体数据被分成多个chunk,每个chunk可包含多个sample,而sample则由帧组成(通常1个sample对应1个帧),关系如下:

stbl中比较关键的box包含stsd、stco、stsc、stsz、stts、stss、ctts。下面先来个概要的介绍,然后再逐个讲解细节。
stco / stsc / stsz / stts / stss / ctts / stsd 概述
下面是这几个box概要的介绍:
- stsd:给出视频、音频的编码、宽高、音量等信息,以及每个sample中包含多少个frame;
- stco:thunk在文件中的偏移;
- stsc:每个thunk中包含几个sample;
- stsz:每个sample的size(单位是字节);
- stts:每个sample的时长;
- stss:哪些sample是关键帧;
- ctts:帧解码到渲染的时间差值,通常用在B帧的场景;
stsd(Sample Description Box)
stsd给出sample的描述信息,这里面包含了在解码阶段需要用到的任意初始化信息,比如 编码 等。对于视频、音频来说,所需要的初始化信息不同,这里以视频为例。
伪代码如下:
aligned(8) abstract class SampleEntry (unsigned int(32) format) extends Box(format){
const unsigned int(8)[6] reserved = 0;
unsigned int(16) data_reference_index;
}
// Visual Sequences
class VisualSampleEntry(codingname) extends SampleEntry (codingname){
unsigned int(16) pre_defined = 0;
const unsigned int(16) reserved = 0;
unsigned int(32)[3] pre_defined = 0;
unsigned int(16) width;
unsigned int(16) height;
template unsigned int(32) horizresolution = 0x00480000; // 72 dpi
template unsigned int(32) vertresolution = 0x00480000; // 72 dpi
const unsigned int(32) reserved = 0;
template unsigned int(16) frame_count = 1;
string[32] compressorname;
template unsigned int(16) depth = 0x0018;
int(16) pre_defined = -1;
}
// AudioSampleEntry、HintSampleEntry 定义略过
aligned(8) class SampleDescriptionBox (unsigned int(32) handler_type) extends FullBox('stsd', 0, 0){
int i ;
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
for (i = 1 ; i u entry_count ; i++) {
switch (handler_type){
case ‘soun’: // for audio tracks
AudioSampleEntry();
break;
case ‘vide’: // for video tracks
VisualSampleEntry();
break;
case ‘hint’: // Hint track
HintSampleEntry();
break;
}
}
}
在SampleDescriptionBox 中,handler_type 参数 为 track 的类型(soun、vide、hint),entry_count 变量代表当前box中 smaple description 的条目数。
针对不同的handler_type,SampleDescriptionBox 后续应用不同的 SampleEntry 类型,比如video track为VisualSampleEntry。
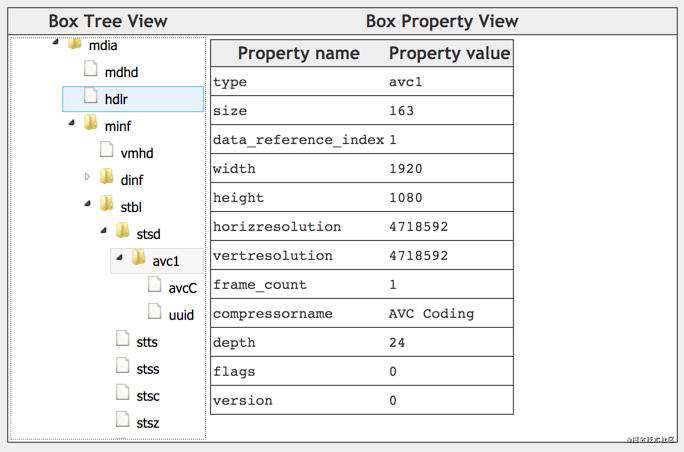
VisualSampleEntry包含如下字段:
- data_reference_index:当MP4文件的数据部分,可以被分割成多个片段,每一段对应一个索引,并分别通过URL地址来获取,此时,data_reference_index 指向对应的片段(比较少用到);
- width、height:视频的宽高,单位是像素;
- horizresolution、vertresolution:水平、垂直方向的分辨率(像素/英寸),16.16定点数,默认是0x00480000(72dpi);
- frame_count:一个sample中包含多少个frame,对video track来说,默认是1;
- compressorname:仅供参考的名字,通常用于展示,占32个字节,比如 AVC Coding。第一个字节,表示这个名字实际要占用N个字节的长度。第2到第N+1个字节,存储这个名字。第N+2到32个字节为填充字节。compressorname 可以设置为0;
- depth:位图的深度信息,比如 0x0018(24),表示不带alpha通道的图片;
例子如下:
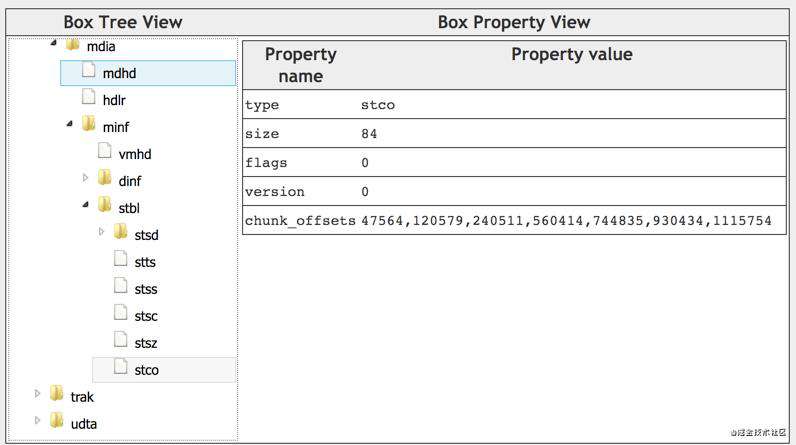
stco(Chunk Offset Box)
chunk在文件中的偏移量。针对小文件、大文件,有两种不同的box类型,分别是stco、co64,它们的结构是一样的,只是字段长度不同。
chunk_offset 指的是在文件本身中的 offset,而不是某个box内部的偏移。
在构建mp4文件的时候,需要特别注意 moov 所处的位置,它对于chunk_offset 的值是有影响的。有一些MP4文件的 moov 在文件末尾,为了优化首帧速度,需要将 moov 移到文件前面,此时,需要对 chunk_offset 进行改写。
stco 定义如下:
# Box Type: ‘stco’, ‘co64’
# Container: Sample Table Box (‘stbl’) Mandatory: Yes
# Quantity: Exactly one variant must be present
aligned(8) class ChunkOffsetBox
extends FullBox(‘stco’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
for (i=1; i u entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) chunk_offset;
}
}
aligned(8) class ChunkLargeOffsetBox
extends FullBox(‘co64’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
for (i=1; i u entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(64) chunk_offset;
}
}
如下例子所示,第一个chunk的offset是47564,第二个chunk的偏移是120579,其他类似。
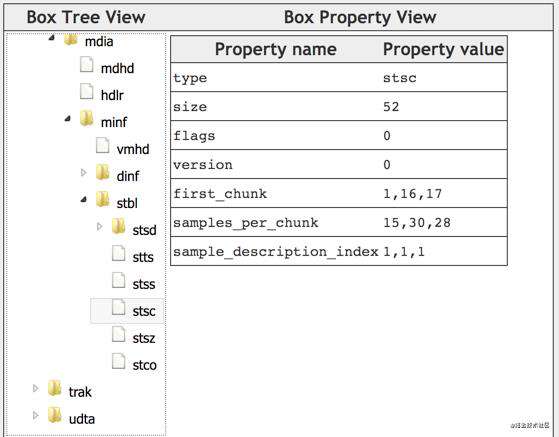
stsc(Sample To Chunk Box)
sample 以 chunk 为单位分成多个组。chunk的size可以是不同的,chunk里面的sample的size也可以是不同的。
- entry_count:有多少个表项(每个表项,包含first_chunk、samples_per_chunk、sample_description_index信息);
- first_chunk:当前表项中,对应的第一个chunk的序号;
- samples_per_chunk:每个chunk包含的sample数;
- sample_description_index:指向 stsd 中 sample description 的索引值(参考stsd小节);
aligned(8) class SampleToChunkBox
extends FullBox(‘stsc’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
for (i=1; i u entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) first_chunk;
unsigned int(32) samples_per_chunk;
unsigned int(32) sample_description_index;
}
}
前面描述比较抽象,这里看个例子,这里表示的是:
- 序号1~15的chunk,每个chunk包含15个sample;
- 序号16的chunk,包含30个sample;
- 序号17以及之后的chunk,每个chunk包含28个sample;
- 以上所有chunk中的sample,对应的sample description的索引都是1;
| first_chunk | samples_per_chunk | sample_description_index | 1 | 15 | 1 | 16 | 30 | 1 | 17 | 28 | 1 |
|---|
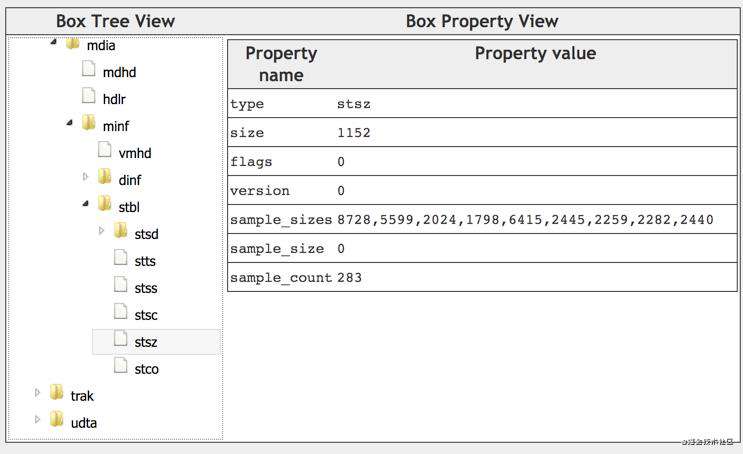
stsz(Sample Size Boxes)
每个sample的大小(字节),根据 sample_size 字段,可以知道当前track包含了多少个sample(或帧)。
有两种不同的box类型,stsz、stz2。
stsz:
- sample_size:默认的sample大小(单位是byte),通常为0。如果sample_size不为0,那么,所有的sample都是同样的大小。如果sample_size为0,那么,sample的大小可能不一样。
- sample_count:当前track里面的sample数目。如果 sample_size==0,那么,sample_count 等于下面entry的条目;
- entry_size:单个sample的大小(如果sample_size==0的话);
aligned(8) class SampleSizeBox extends FullBox(‘stsz’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) sample_size;
unsigned int(32) sample_count;
if (sample_size==0) {
for (i=1; i u sample_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) entry_size;
}
}
}
stz2:
- field_size:entry表中,每个entry_size占据的位数(bit),可选的值为4、8、16。4比较特殊,当field_size等于4时,一个字节上包含两个entry,高4位为entry[i],低4位为entry[i+1];
- sample_count:等于下面entry的条目;
- entry_size:sample的大小。
aligned(8) class CompactSampleSizeBox extends FullBox(‘stz2’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(24) reserved = 0;
unisgned int(8) field_size;
unsigned int(32) sample_count;
for (i=1; i u sample_count; i++) {
unsigned int(field_size) entry_size;
}
}
例子如下:
stts(Decoding Time to Sample Box)
stts包含了DTS到sample number的映射表,主要用来推导每个帧的时长。
aligned(8) class TimeToSampleBox extends FullBox(’stts’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
int i;
for (i=0; i < entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) sample_count;
unsigned int(32) sample_delta;
}
}
- entry_count:stts 中包含的entry条目数;
- sample_count:单个entry中,具有相同时长(duration 或 sample_delta)的连续sample的个数。
- sample_delta:sample的时长(以timescale为计量)
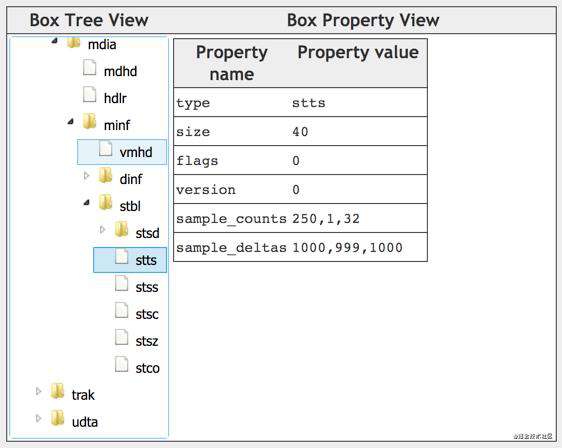
还是看例子,如下图,entry_count为3,前250个sample的时长为1000,第251个sample时长为999,第252~283个sample的时长为1000。
stss(Sync Sample Box)
mp4文件中,关键帧所在的sample序号。如果没有stss的话,所有的sample中都是关键帧。
- entry_count:entry的条目数,可以认为是关键帧的数目;
- sample_number:关键帧对应的sample的序号;(从1开始计算)
aligned(8) class SyncSampleBox
extends FullBox(‘stss’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
int i;
for (i=0; i < entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) sample_number;
}
}
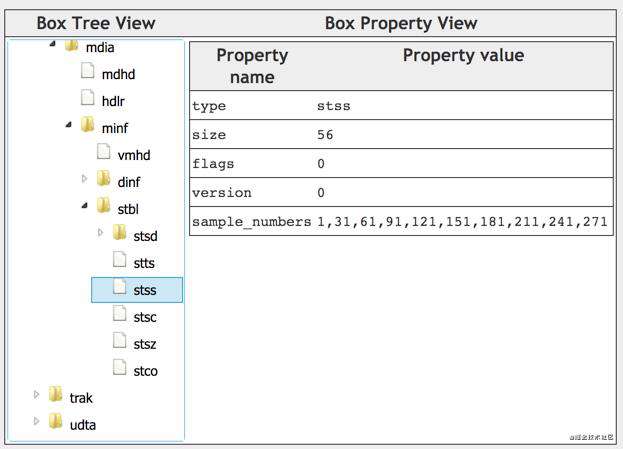
例子如下,第1、31、61、91、121...271个sample是关键帧。
ctts(Composition Time to Sample Box)
从解码(dts)到渲染(pts)之间的差值。
对于只有I帧、P帧的视频来说,解码顺序、渲染顺序是一致的,此时,ctts没必要存在。
对于存在B帧的视频来说,ctts就需要存在了。当PTS、DTS不相等时,就需要ctts了,公式为 CT(n) = DT(n) + CTTS(n) 。
aligned(8) class CompositionOffsetBox extends FullBox(‘ctts’, version = 0, 0) { unsigned int(32) entry_count;
int i;
for (i=0; i < entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) sample_count;
unsigned int(32) sample_offset;
}
}
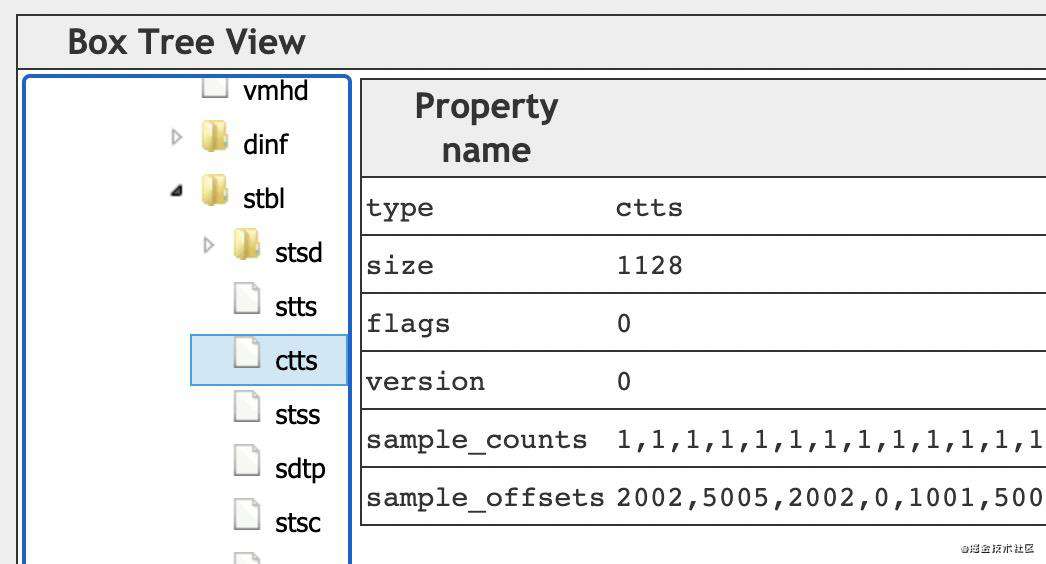
例子如下,不赘述:
fMP4(Fragmented mp4)
fMP4 跟普通 mp4 基本文件结构是一样的。普通mp4用于点播场景,fmp4通常用于直播场景。
它们有以下差别:
- 普通mp4的时长、内容通常是固定的。fMP4 时长、内容通常不固定,可以边生成边播放;
- 普通mp4完整的metadata都在moov里,需要加载完moov box后,才能对mdat中的媒体数据进行解码渲染;
- fMP4中,媒体数据的metadata在moof box中,moof 跟 mdat (通常)结对出现。moof 中包含了sample duration、sample size等信息,因此,fMP4可以边生成边播放;
举例来说,普通mp4、fMP4顶层box结构可能如下。以下是通过笔者编写的MP4解析小工具打印出来,代码在文末给出。
// 普通mp4
ftyp size=32(8+24) curTotalSize=32
moov size=4238(8+4230) curTotalSize=4270
mdat size=1124105(8+1124097) curTotalSize=1128375
// fmp4
ftyp size=36(8+28) curTotalSize=36
moov size=1227(8+1219) curTotalSize=1263
moof size=1252(8+1244) curTotalSize=2515
mdat size=65895(8+65887) curTotalSize=68410
moof size=612(8+604) curTotalSize=69022
mdat size=100386(8+100378) curTotalSize=169408
怎么判断mp4文件是普通mp4,还是fMP4呢?一般可以看下是否存在存在mvex(Movie Extends Box)。
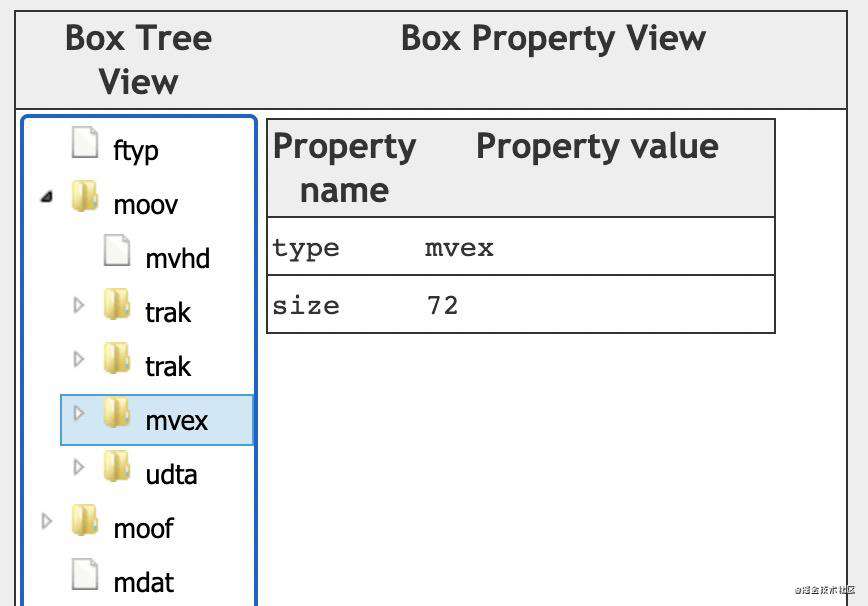
mvex(Movie Extends Box)
当存在mvex时,表示当前文件是fmp4(非严谨)。此时,sample相关的metadata不在moov里,需要通过解析moof box来获得。
伪代码如下:
aligned(8) class MovieExtendsBox extends Box(‘mvex’){ }
mehd(Movie Extends Header Box)
mehd是可选的,用来声明影片的完整时长(fragment_duration)。如果不存在,则需要遍历所有的fragment,来获得完整的时长。对于fmp4的场景,fragment_duration一般没办法提前预知。
aligned(8) class MovieExtendsHeaderBox extends FullBox(‘mehd’, version, 0) {
if (version==1) {
unsigned int(64) fragment_duration;
} else { // version==0
unsigned int(32) fragment_duration;
}
}
trex(Track Extends Box)
用来给 fMP4 的 sample 设置各种默认值,比如时长、大小等。
aligned(8) class TrackExtendsBox extends FullBox(‘trex’, 0, 0){
unsigned int(32) track_ID;
unsigned int(32) default_sample_description_index;
unsigned int(32) default_sample_duration;
unsigned int(32) default_sample_size;
unsigned int(32) default_sample_flags
}
字段含义如下:
- track_id:对应的 track 的 ID,比如video track、audio track 的ID;
- default_sample_description_index:sample description 的默认 index(指向stsd);
- default_sample_duration:sample 默认时长,一般为0;
- default_sample_size:sample 默认大小,一般为0;
- default_sample_flags:sample 的默认flag,一般为0;
default_sample_flags 占4个字节,比较复杂,结构如下:
- reserved:4 bits,保留位;
- is_leading:2 bits,是否 leading sample,可能的取值包括:
- 0:当前 sample 不确定是否 leading sample;(一般设为这个值)
- 1:当前 sample 是 leading sample,并依赖于 referenced I frame 前面的 sample,因此无法被解码;
- 2:当前 sample 不是 leading sample;
- 3:当前 sample 是 leading sample,不依赖于 referenced I frame 前面的 sample,因此可以被解码;
- sample_depends_on:2 bits,是否依赖其他sample,可能的取值包括:
- 0:不清楚是否依赖其他sample;
- 1:依赖其他sample(不是I帧);
- 2:不依赖其他sample(I帧);
- 3:保留值;
- sample_is_depended_on:2 bits,是否被其他sample依赖,可能的取值包括:
- 0:不清楚是否有其他sample依赖当前sample;
- 1:其他sample可能依赖当前sample;
- 2:其他sample不依赖当前sample;
- 3:保留值;
- sample_has_redundancy:2 bits,是否有冗余编码,可能的取值包括:
- 0:不清楚是否存在冗余编码;
- 1:存在冗余编码;
- 2:不存在冗余编码;
- 3:保留值;
- sample_padding_value:3 bits,填充值;
- sample_is_non_sync_sample:1 bits,不是关键帧;
- sample_degradation_priority:16 bits,降级处理的优先级(一般针对如流传过程中出现的问题);
例子如下:
关于 is_leading
is_leading 不是特别好解释,这里贴上原文,方便大家理解。
为方便讲解,下面的 leading frame 对应 leading sample,referenced frame 对应 referenced samle。
以 H264编码 为例,H264 中存在 I帧、P帧、B帧。由于 B帧 的存在,视频帧的 解码顺序、渲染顺序 可能不一致。
mp4文件的特点之一,就是支持随机位置播放。比如,在视频网站上,可以拖动进度条快进。
很多时候,进度条定位的那个时刻,对应的不一定是 I帧。为了能够顺利播放,需要往前查找最近的一个 I帧,如果可能的话,从最近的 I帧 开始解码播放(也就是说,不一定能从前面最近的I帧播放)。
将上面描述的此刻定位到的帧,称作 leading frame。leading frame 前面最近的一个 I 帧,叫做 referenced frame。
回顾下 is_leading 为 1 或 3 的情况,同样都是 leading frame,什么时候可以解码(decodable),什么时候不能解码(not decodable)?
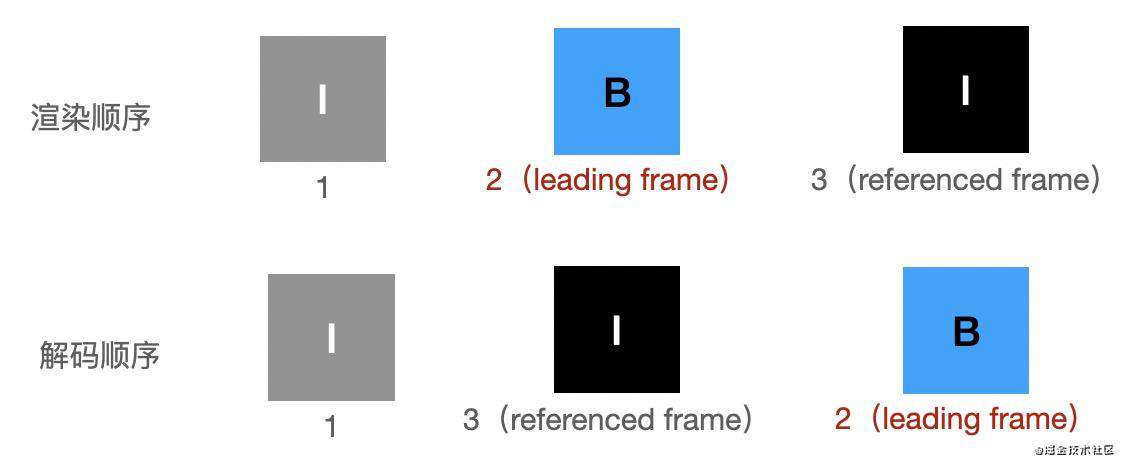
1、is_leading 为 1 的例子: 如下所示,帧2(leading frame) 解码依赖 帧1、帧3(referenced frame)。在视频流里,从 帧2 往前查找,最近的 I帧 是 帧3。哪怕已经解码了 帧3,帧2 也解不出来。
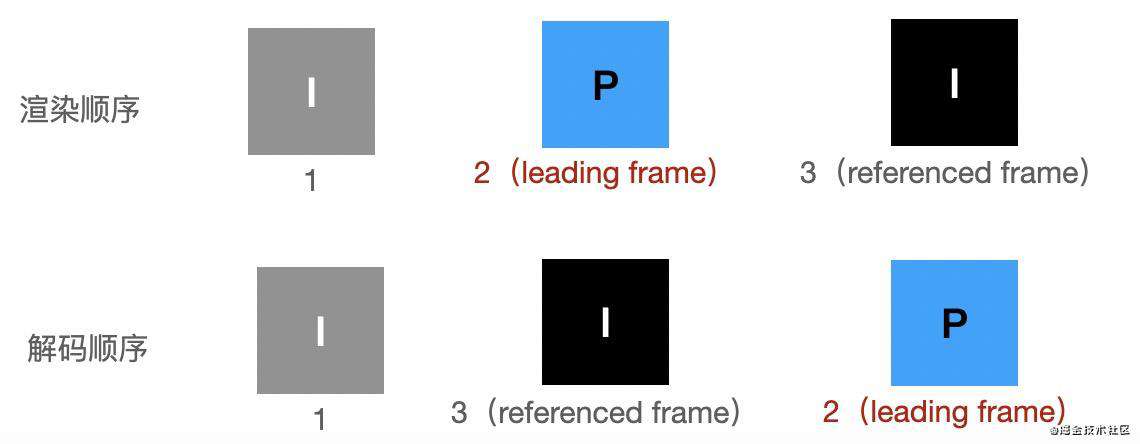
2、is_leading 为 3 的例子: 如下所示,此时,帧2(leading frame)可以解码出来。
moof(Movie Fragment Box)
moof是个container box,相关 metadata 在内嵌box里,比如 mfhd、 tfhd、trun 等。
伪代码如下:
aligned(8) class MovieFragmentBox extends Box(‘moof’){ }
mfhd(Movie Fragment Header Box)
结构比较简单,sequence_number 为 movie fragment 的序列号。根据 movie fragment 产生的顺序,从1开始递增。
aligned(8) class MovieFragmentHeaderBox extends FullBox(‘mfhd’, 0, 0){
unsigned int(32) sequence_number;
}
traf(Track Fragment Box)
aligned(8) class TrackFragmentBox extends Box(‘traf’){ }
对 fmp4 来说,数据被氛围多个 movie fragment。一个 movie fragment 可包含多个track fragment(每个 track 包含0或多个 track fragment)。每个 track fragment 中,可以包含多个该 track 的 sample。
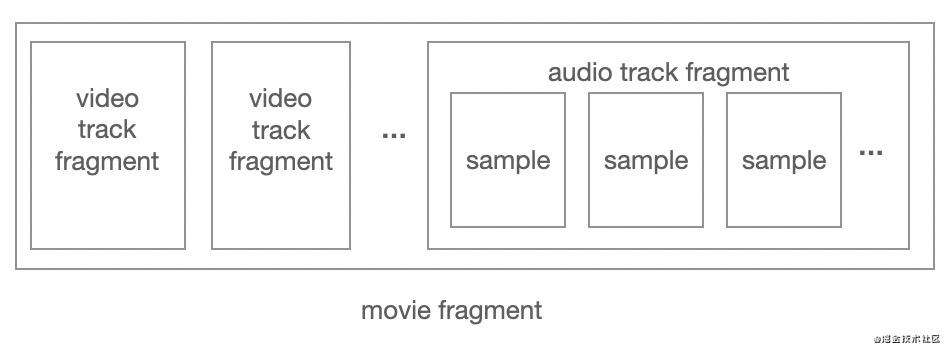
tfhd(Track Fragment Header Box)
tfhd 用来设置 track fragment 中 的 sample 的 metadata 的默认值。
伪代码如下,除了 track_ID,其他都是 可选字段。
aligned(8) class TrackFragmentHeaderBox extends FullBox(‘tfhd’, 0, tf_flags){
unsigned int(32) track_ID;
// all the following are optional fields
unsigned int(64) base_data_offset;
unsigned int(32) sample_description_index;
unsigned int(32) default_sample_duration;
unsigned int(32) default_sample_size;
unsigned int(32) default_sample_flags
}
sample_description_index、default_sample_duration、default_sample_size 没什么好讲的,这里只讲解下 tf_flags、base_data_offset。
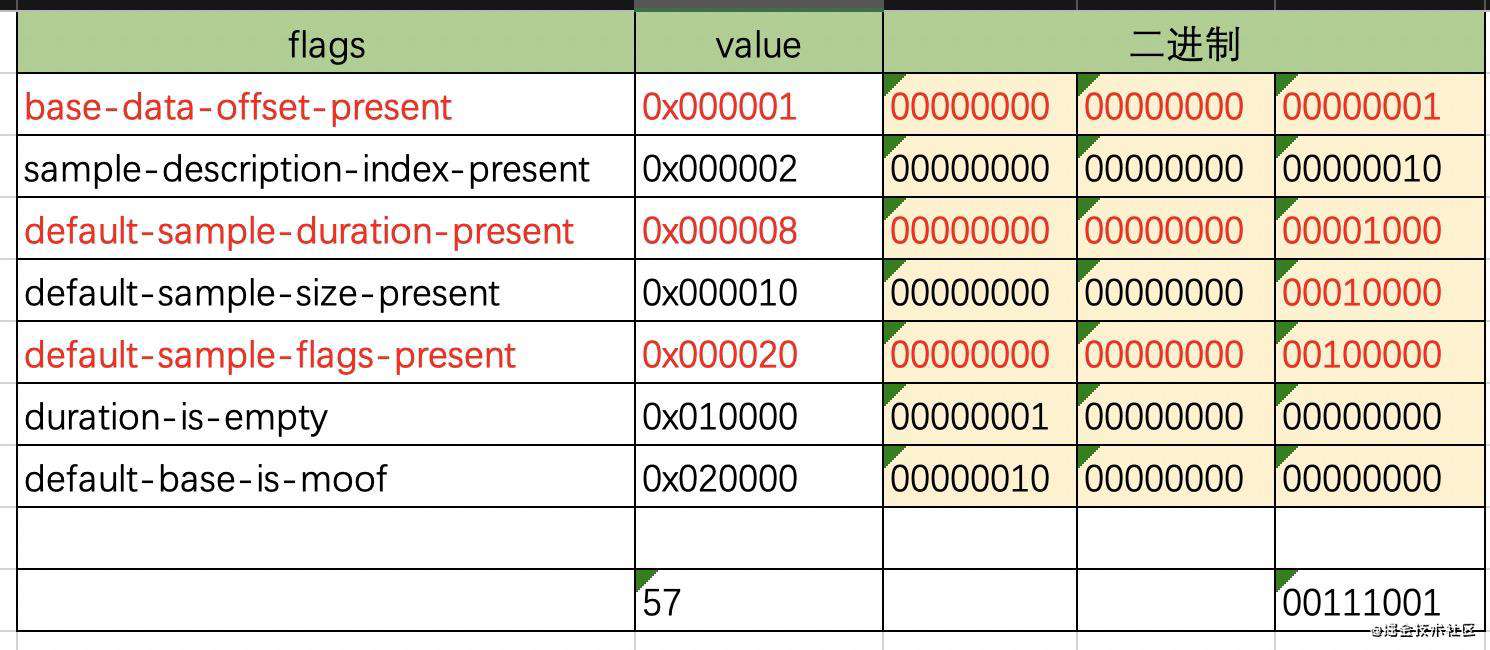
首先是 tf_flags,不同 flag 的值如下(同样是求按位求或) :
- 0x000001 base‐data‐offset‐present:存在 base_data_offset 字段,表示 数据位置 相对于整个文件的 基础偏移量。
- 0x000002 sample‐description‐index‐present:存在 sample_description_index 字段;
- 0x000008 default‐sample‐duration‐present:存在 default_sample_duration 字段;
- 0x000010 default‐sample‐size‐present:存在 default_sample_size 字段;
- 0x000020 default‐sample‐flags‐present:存在 default_sample_flags 字段;
- 0x010000 duration‐is‐empty:表示当前时间段不存在sample,default_sample_duration 如果存在则为0 ,;
- 0x020000 default‐base‐is‐moof:如果 base‐data‐offset‐present 为1,则忽略这个flag。如果 base‐data‐offset‐present 为0,则当前 track fragment 的 base_data_offset 是从 moof 的第一个字节开始计算;
sample 位置计算公式为 base_data_offset + data_offset,其中,data_offset 每个 sample 单独定义。如果未显式提供 base_data_offset,则 sample 的位置的通常是基于 moof 的相对位置。
举个例子,比如 tf_flags 等于 57,表示 存在 base_data_offset、default_sample_duration、default_sample_flags。
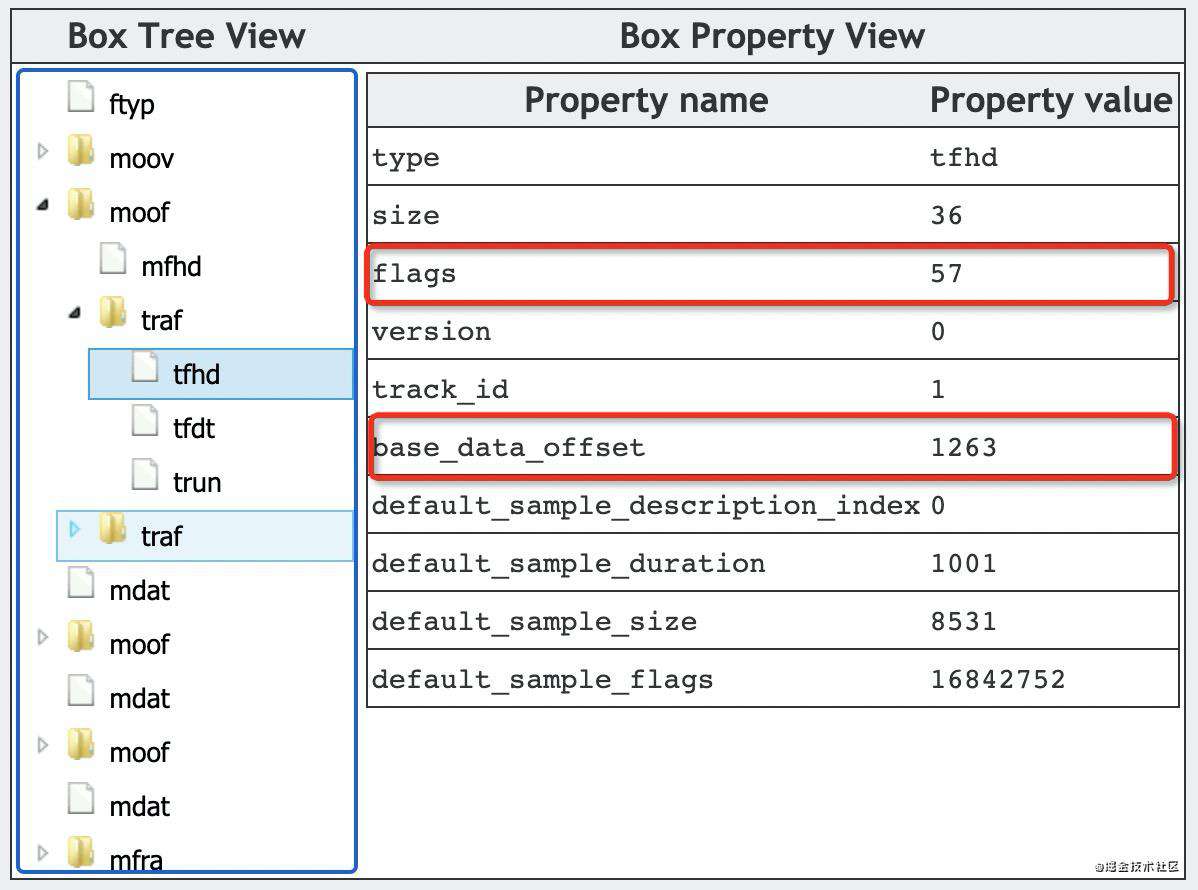
base_data_offset 为 1263 (ftyp、moov 的size 之和为 1263)。
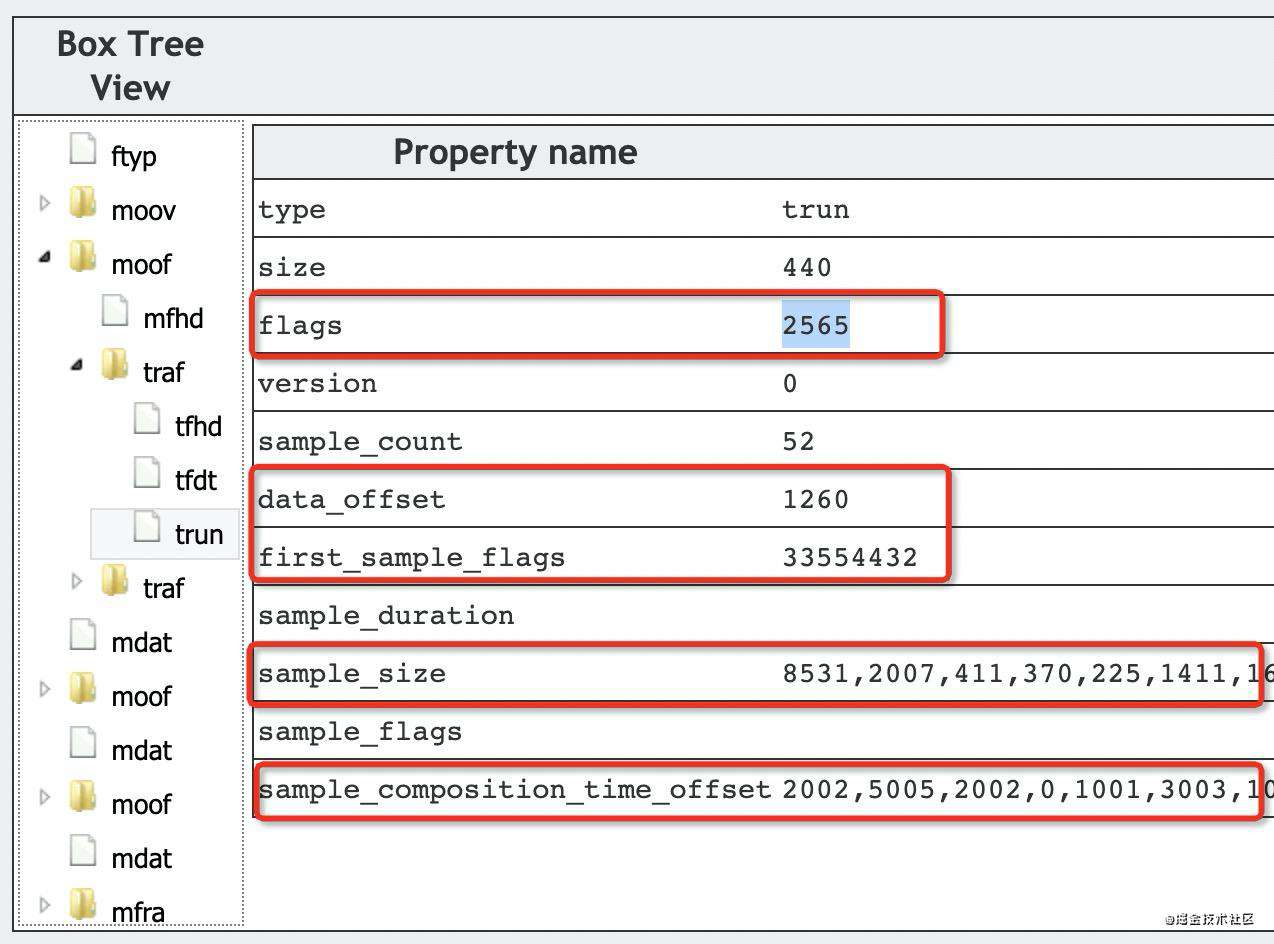
trun(Track Fragment Run Box)
trun 伪代码如下:
aligned(8) class TrackRunBox extends FullBox(‘trun’, version, tr_flags) {
unsigned int(32) sample_count;
// the following are optional fields
signed int(32) data_offset;
unsigned int(32) first_sample_flags;
// all fields in the following array are optional
{
unsigned int(32) sample_duration;
unsigned int(32) sample_size;
unsigned int(32) sample_flags
if (version == 0)
{ unsigned int(32) sample_composition_time_offset; }
else
{ signed int(32) sample_composition_time_offset; }
}[ sample_count ]
}
前面听过,track run 表示一组连续的 sample,其中:
- sample_count:sample 的数目;
- data_offset:数据部分的偏移量;
- first_sample_flags:可选,针对当前 track run中 第一个 sample 的设置;
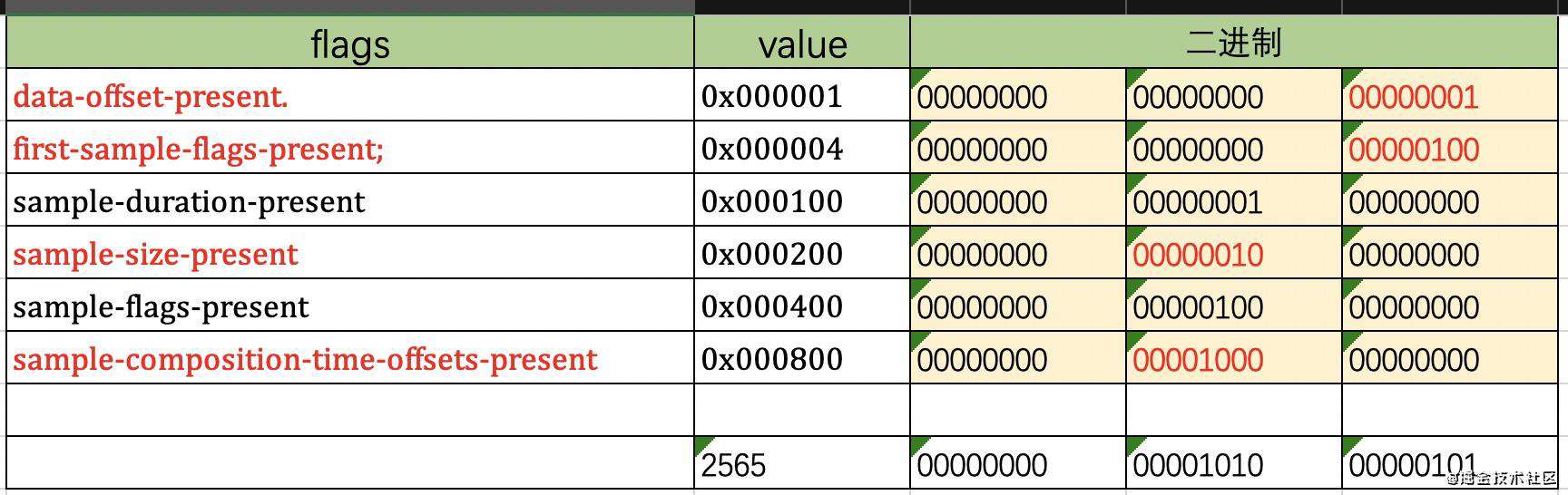
tr_flags 如下,大同小异:
-
0x000001 data‐offset‐present:存在 data_offset 字段;
-
0x000004 first‐sample‐flags‐present:存在 first_sample_flags 字段,这个字段的值,只会覆盖第一个 sample 的flag设置;当 first_sample_flags 存在时,sample_flags 则不存在;
-
0x000100 sample‐duration‐present:每个 sample 都有自己的 sample_duration,否则使用默认值;
-
0x000200 sample‐size‐present:每个 sample 都有自己的 sample_size,否则使用默认值;
-
0x000400 sample‐flags‐present:每个 sample 都有自己的 sample_flags,否则使用默认值;
-
0x000800 sample‐composition‐time‐offsets‐present:每个 sample 都有自己的 sample_composition_time_offset;
-
0x000004 first‐sample‐flags‐present,覆盖第一个sample的设置,这样就可以把一组sample中的第一个帧设置为关键帧,其他的设置为非关键帧;
举例如下,tr_flags 为 2565。此时,存在 data_offset 、first_sample_flags、sample_size、sample_composition_time_offset。
编程实践:解析MP4文件结构
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要coding。根据 mp4 文件规范,可以写个简易的 mp4 文件解析工具,比如前文对比 普通mp4、fMP4 的 box 结构,就是笔者自己写的分析脚本。
核心代码如下,完整代码有点长,可以在 笔者的github 上找到。
class Box {
constructor(boxType, extendedType, buffer) {
this.type = boxType; // 必选,字符串,4个字节,box类型
this.size = 0; // 必选,整数,4个字节,box的大小,单位是字节
this.headerSize = 8; //
this.boxes = [];
// this.largeSize = 0; // 可选,8个字节
// this.extendedType = extendedType || boxType; // 可选,16个字节
this._initialize(buffer);
}
_initialize(buffer) {
this.size = buffer.readUInt32BE(0); // 4个字节
this.type = buffer.slice(4, 8).toString(); // 4个字节
let offset = 8;
if (this.size === 1) {
this.size = buffer.readUIntBE(8, 8); // 8个字节,largeSize
this.headerSize += 8;
offset = 16;
} else if (this.size === 1) {
// last box
}
if (this.type === 'uuid') {
this.type = buffer.slice(offset, 16); // 16个字节
this.headerSize += 16;
}
}
setInnerBoxes(buffer, offset = 0) {
const innerBoxes = getInnerBoxes(buffer.slice(this.headerSize + offset, this.size));
innerBoxes.forEach(item => {
let { type, buffer } = item;
type = type.trim(); // 备注,有些box类型不一定四个字母,比如 url、urn
if (this[type]) {
const box = this[type](buffer);
this.boxes.push(box);
} else {
this.boxes.push('TODO 待实现');
// console.log(`unknowed type: ${type}`);
}
});
}
}
class FullBox extends Box {
constructor(boxType, buffer) {
super(boxType, '', buffer);
const headerSize = this.headerSize;
this.version = buffer.readUInt8(headerSize); // 必选,1个字节
this.flags = buffer.readUIntBE(headerSize + 1, 3); // 必选,3个字节
this.headerSize = headerSize + 4;
}
}
// FileTypeBox、MovieBox、MediaDataBox、MovieFragmentBox 代码有点长这里就不贴了
class Movie {
constructor(buffer) {
this.boxes = [];
this.bytesConsumed = 0;
const innerBoxes = getInnerBoxes(buffer);
innerBoxes.forEach(item => {
const { type, buffer, size } = item;
if (this[type]) {
const box = this[type](buffer);
this.boxes.push(box);
} else {
// 自定义 box 类型
}
this.bytesConsumed += size;
});
}
ftyp(buffer) {
return new FileTypeBox(buffer);
}
moov(buffer) {
return new MovieBox(buffer);
}
mdat(buffer) {
return new MediaDataBox(buffer);
}
moof(buffer) {
return new MovieFragmentBox(buffer);
}
}
function getInnerBoxes(buffer) {
let boxes = [];
let offset = 0;
let totalByteLen = buffer.byteLength;
do {
let box = getBox(buffer, offset);
boxes.push(box);
offset += box.size;
} while(offset < totalByteLen);
return boxes;
}
function getBox(buffer, offset = 0) {
let size = buffer.readUInt32BE(offset); // 4个字节
let type = buffer.slice(offset + 4, offset + 8).toString(); // 4个字节
if (size === 1) {
size = buffer.readUIntBE(offset + 8, 8); // 8个字节,largeSize
} else if (size === 0) {
// last box
}
let boxBuffer = buffer.slice(offset, offset + size);
return {
size,
type,
buffer: boxBuffer
};
}
写在后面
受限于时间,同时为了方便讲解,部分内容可能不是很严谨,如有错漏,敬请指出。如有问题,也欢迎随时交流。
相关链接
ISO/IEC 14496-12:2015 Information technology — Coding of audio-visual objects — Part 12: ISO base media file format www.iso.org/standard/68…
Introduction to QuickTime File Format Specification developer.apple.com/library/arc…
AVC_(file_format) fileformats.archiveteam.org/wiki/AVC_(f…
AV1 Codec ISO Media File Format Binding aomediacodec.github.io/av1-isobmff…
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!