如何编写前端测试一直是想了解的领域,之对jest测试的认知一直停留在expect和toBe的高度。这次将学习Jest+Enzyme如何对React项目进行测试。
环境搭建
准备react项目
通过create-react-app搭建一个基本react项目供测试使用。我使用的项目是学习技术胖的React学习路线搭建的项目。
搭建测试环境
安装依赖:
npm install jest --save-dev
npm install enzyme --save-dev
npm install enzyme-to-json --save-dev
npm install enzyme-adapter-react-16
配置packang.json:
"scripts": {
"test": "jest"
}
Jest配置文件
生成jest配置文件
npx jest --init
在新生成的jest配置文件jest.config.js中进行配置:
rootDir: './',
setupFiles: [
"<rootDir>/test/setup.js"
],
moduleFileExtensions: [
"js",
"jsx",
"ts",
"tsx",
"json",
"node"
],
setup.js文件
import Enzyme from 'enzyme';
import Adapter from 'enzyme-adapter-react-16';
Enzyme.configure({ adapter: new Adapter() });
在测试中可定会使用使用es6的import和export,所以需要通过babel来进行将es6模块转换成commonJs模块。
npm install @babel/core @babel/preset-env
.babelrc文件
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react"]
}
编写测试
待测试的组件:
// App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>hello World</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
测试代码:
//app.test.js
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('h1').text()).toBe('hello World')
})
})
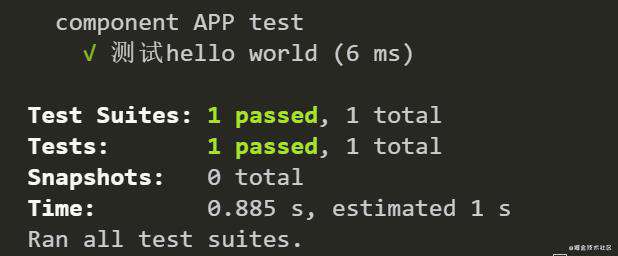
执行npm test产看运行结果如下:
Enzymejs
我所理解Enzyme的作用就是将要测试的组件进行渲染,使用户可以在测试环境中对UI渲染情况、DOM事件等进行测试。
参考文献
官方文档
常用API
.at(index)
可以理解为根据索引返回节点。嵌套的也在内。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>hello</h1>
<h1>World</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
console.log(app.find('h1').at(0))
console.log(app.find('h1').at(1))
expect(app.find('h1').at(0).text()).toBe('hello')
expect(app.find('h1').at(1).text()).toBe('World')
})
})
返回值:
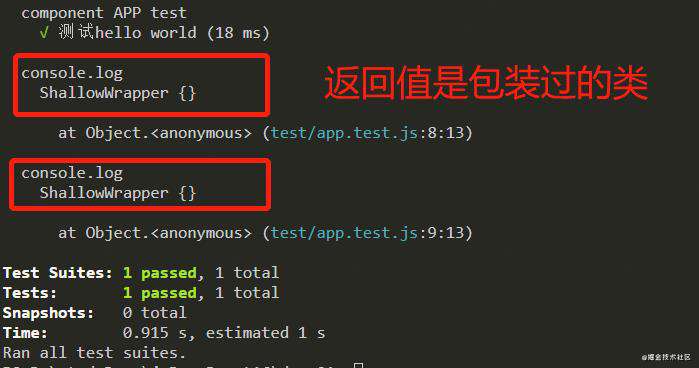
再举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>hello</h1>
<h1>World</h1>
// ********change start******
<div>
<h1>!!</h1>
</div>
// ********change end******
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('h1').at(0).text()).toBe('hello')
expect(app.find('h1').at(1).text()).toBe('World')
// **********change start*********
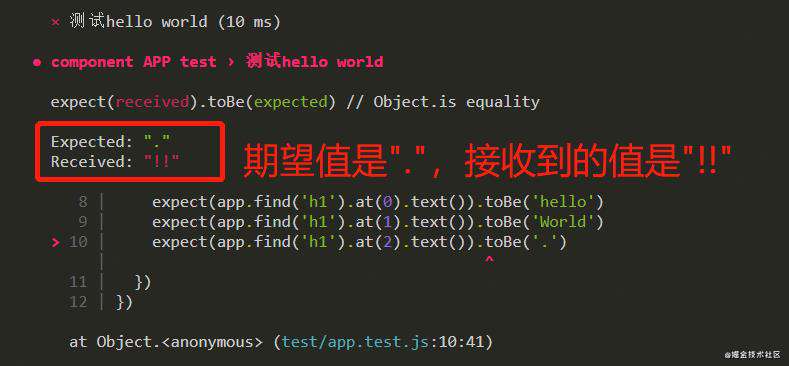
expect(app.find('h1').at(2).text()).toBe('.')
// **********change end*********
})
})
测试结果:
.childAt(index)
返回具有指定索引的子元素到新的wrapper。
举个?
// 待测试的组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>hello</h1>
<h1>World</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
// 注意是查找的div 不是h1
expect(app.find('div').childAt(0).text()).toBe('hello')
expect(app.find('div').childAt(1).text()).toBe('World')
})
})
测试结果
再举个?
测试代码不变,将待测试组件变成如下结构:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>hello</h1>
<h1>World</h1>
// change start------------
<div>
<h1>!!</h1>
</div>
// change end--------------
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
测试结果
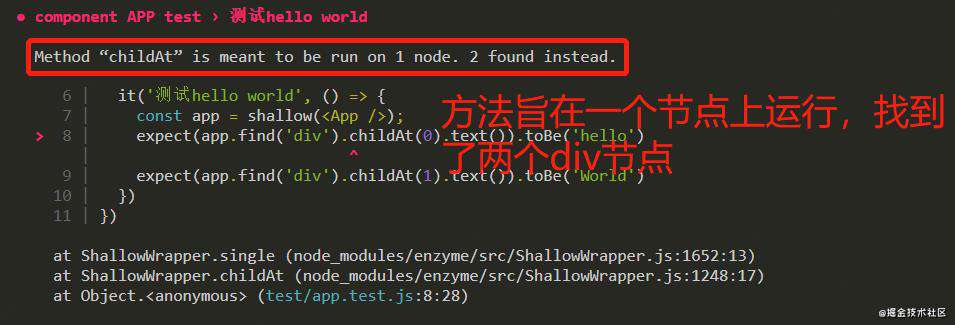
总结:要根据独一无二的条件(比如只有一个div)进行find的结果才可使用childAt。
.find(selector)
根据选择器,找到渲染树中的节点。
selector 参数:
- 标签:
find('tag') - 类名:
find('.className') - id:
.find('#id') - 组合:
.find('tag.className') - 构造函数:
.find(Foo) - 组件显示名字:
.find('Foo') - 对象属性选择器:
.find({ prop: 'value' })
举一堆???????
// MyCom组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class MyCom extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>xixi</h1>
)
}
}
export default MyCom;
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import MyCom from '../src/MyCom';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('span').at(1).text()).toBe('haha')
expect(app.find('.helloClass').text()).toBe('hello')
expect(app.find('#worldID').text()).toBe('World')
expect(app.find('span.spanClass').text()).toBe('ya')
expect(app.find('MyCom').text()).toBe('<MyCom />') // 不能匹配到xixi,子组件不渲染
expect(app.find(MyCom).text()).toBe('<MyCom />')
expect(app.find({ fo: 'heheKey' }).text()).toBe('hehe')
})
})
findWhere(predicate)
找到渲染树中里被的断言函数(predicate)返回true的节点。断言函数返回不布尔值。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 className='helloClass1'>helloyaya</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import MyCom from '../src/MyCom';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
const wrapper = app.findWhere(n => n.text().indexOf('hello') > -1);
expect(wrapper.find('.helloClass').text()).toBe('hello')
expect(wrapper.find('.helloClass1').text()).toBe('helloyaya')
})
})
// 测试通过!!!
我所理解的这个api类似于数组中的filter,满足条件的节点被过滤出来,组成到新的Wrapper中被返回。在返回的Wrapper中我们可以再进行find操作。
.filter(selector)
将与提供的选择器匹配的节点包装成wrapper返回。
举个?
// 待测试的组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('h1').filter('.helloClass').text()).toBe('hello');
expect(app.find('h1').filter('#worldID').text()).toBe('World');
})
})
// 测试通过
总结:从已经查找的节点中过滤出满足条件的节点
.filterWhere(predicate)
返回满足断言函数的节点。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('h1').filterWhere(n => n.text() === 'hello').text()).toBe('hello');
const wrapper = app.find('span').filterWhere(n => n.text().indexOf('h') > -1);
expect(wrapper.at(0).text()).toBe('haha');
expect(wrapper.at(1).text()).toBe('hehe');
})
})
// 测试通过
.contains(nodeOrNodes)
返回布尔值,表示给定的节点(nodeOrNodes)是否存在于渲染树中。可以检测props以及相应的值。也就是说,如果预期元素与包装器的元素有相同的props并且共享相同的值就返回true。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.contains(<h1>hello</h1>)).toEqual(false);
expect(app.contains(<h1 className={'a'}>hello</h1>)).toEqual(false);
expect(app.contains(<h1 className={'helloClass'}>Hello</h1>)).toEqual(false);
expect(app.contains(<h1 className={'helloClass'}>hello</h1>)).toEqual(true);
expect(app.contains(<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>)).toEqual(true);
expect(app.contains([
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>,
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
])).toEqual(true)
expect(app.contains([
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>,
<span>haha</span>
])).toEqual(false)
})
})
总结:严格匹配,不能差一丝一毫,多个节点必须相邻,否则不成功。
.containsMatchingElement(node)
返回浅渲染树中是否存在给定node节点的布尔值。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass' data-fo="foo">hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.containsMatchingElement(<h1>hello</h1>)).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsMatchingElement(<h1 className='helloClass' >hello</h1>)).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsMatchingElement(<h1 data-fo='foo'>hello</h1>)).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsMatchingElement(<h1 data-fo='foo-data'>hello</h1>)).toEqual(false);
expect(app.containsMatchingElement(<h1 data-fo='foo' />)).toEqual(false);
})
})
总结下来就是:可少不可多。props和值完全对用即可,不像contains那样严格。
.containsAllMatchingElements(nodes)
给定所有元素是否都存在于浅渲染树中。遵循containsMatchingElement匹配原则。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.containsAllMatchingElements([
<h1>hello</h1>,
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
])).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsAllMatchingElements([
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>,
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
])).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsAllMatchingElements([
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>,
<span>haha</span>
])).toEqual(true);
})
})
// 测试通过
.containsAnyMatchingElements(nodes)
给定节点(nodes)中有一个匹配就返回true。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.containsAnyMatchingElements([
<h1>hello</h1>,
<h1 id="worldIDDDD">World</h1>
])).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsAnyMatchingElements([
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>,
<h1 id="worldIDDDD">World</h1>
])).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsAnyMatchingElements([
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>,
<span>haha</span>
])).toEqual(true);
expect(app.containsAnyMatchingElements([
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>,
<span className='span'>haha</span>
])).toEqual(true);
})
})
contains总结:匹配规则越来越简单
| 标题 | 匹配规则 | 检测节点个数 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| contains | 严格匹配 | 单个或者多个(多个节点相邻才可以匹配成功) | containsMatchingElement | 最短匹配 | 单个 | containsAllMatchingElements | 最短匹配 | 多个(多个节点可以不相邻) | containsAnyMatchingElements | 最短匹配 | 多个(多个可以不相邻,多个节点一个满足就返回true) |
.equals(node)
返回布尔值:表示当前渲染树的根节点是否和传入的相同,忽略未定义的属性。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
{/* <h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom /> */}
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.equals(<div><h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1></div>)).toEqual(true)
expect(app.equals(<div><h1>hello</h1></div>)).toEqual(false)
expect(app.equals(<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>)).toEqual(false)
expect(app.equals(<div></div>)).toEqual(false)
})
})
注意:当组件中注释部分解注释的时候测试不通过
.matchesElement(node) => Boolean
当前node是存在当前浅渲染树中。
举个?
// 待测试的组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
{/* <h1 id="worldID">World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom /> */}
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.matchesElement(<div><h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1></div>)).toEqual(true)
expect(app.matchesElement(<div><h1>hello</h1></div>)).toEqual(true)
expect(app.matchesElement(<h1>hello</h1>)).toEqual(false)
expect(app.matchesElement(<div></div>)).toEqual(false)
})
})
注意:当组件注释部分解注释时,测试不通过
| 标题 | 匹配规则 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| equals | 严格匹配 | matchesElement | 最短匹配 |
但是二者对与嵌套来说都是严格匹配。
.hasClass(className) => Boolean
是否有这个className
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID" className='worldClass'>World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('h1').at(0).hasClass('helloClass')).toEqual(true);
expect(app.find('#worldID').hasClass('worldClass')).toEqual(true);
})
})
.is(selector) => Boolean
返回单个包装节点是否与提供的选择器匹配。它必须是单节点包装器。
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.is('.helloClass')).toEqual(true);
expect(app.is('h1')).toEqual(true);
})
})
再举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.is('.helloClass')).toEqual(false);
expect(app.is('h1')).toEqual(false);
expect(app.is('div')).toEqual(true);
})
})
.exists() => Boolean
当前节点是否存在
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID" className='worldClass'>World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.exists('.helloClass')).toEqual(true);
expect(app.find('#worldID').exists()).toEqual(true);
})
})
.not(selector) => ShallowWrapper
删除当前wrapper中与所提供的选择器匹配的节点。 (与 .filter()作用相反)
举个?
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID" className='worldClass'>World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
//测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('h1').not('.helloClass').text()).toBe('World')
})
})
.children() => ShallowWrapper
获取当前 wrapper 中所有子节点的 wrapper.
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID" className='worldClass'>World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('div').children()).toHaveLength(6)
expect(app.find('h1').children()).toHaveLength(2)
expect(app.find('h1').children().at(0).text()).toBe('hello')
expect(app.find('h1').children().at(1).text()).toBe('World')
})
})
.childAt(index) => ShallowWrapper
返回具有指定索引的子元素的 wrapper
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 className='helloClass'>hello</h1>
<h1 id="worldID" className='worldClass'>World</h1>
<span className="spanClass">ya</span>
<span>haha</span>
<span fo="heheKey">hehe</span>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
//测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('div').childAt(0).text()).toBe('hello')
// expect(app.find('h1').childAt(1)).toBe('World')
//“childAt” is meant to be run on 1 node. 2 found instead.
})
})
.parents() => ShallowWrapper
获取当前节点的所有父级(祖先)
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span>xixi</span>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('p').parents()).toHaveLength(2)
expect(app.find('span').parents()).toHaveLength(1)
})
})
.parent() => ShallowWrapper
获取当前节点的直接父级
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span>xixi</span>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('p').parent()).toHaveLength(1)
expect(app.find('span').parent()).toHaveLength(1)
})
})
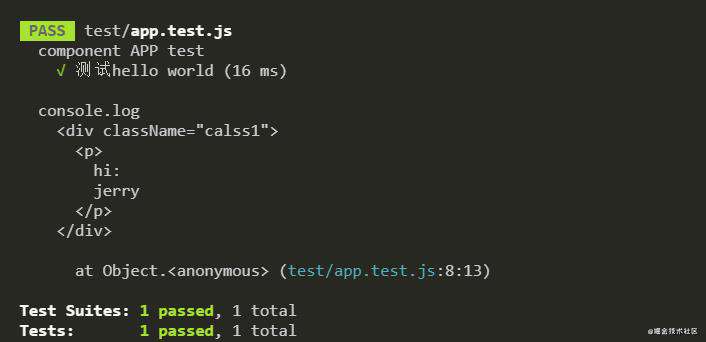
.closest(selector) => ShallowWrapper
从自身开始向上遍历,返回与当前选择器匹配的节点。必须是单节点包装器。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<span className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span>xixi</span>
{/* <p className='class2'>hehe</p> */}
</span>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('p').closest('.calss1').children().at(1).text()).toBe('xixi')
})
})
当组件中注释部分被解注释的时候,会报错:
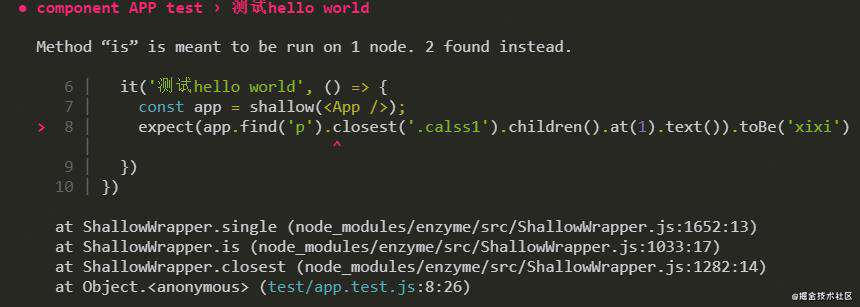
应该保证查找节点(p)是单一节点。
.shallow([options]) => ShallowWrapper
浅渲染当前组件,生成虚拟DOM。
.render() => CheerioWrapper
返回当前节点的子树的CheerioWrapper
.unmount() => ShallowWrapper
一种卸载组件的方法。这可用于模拟经历卸载/安装生命周期的组件。
.text() => String
返回当前渲染树中文本节点的字符串表示形式。
.html() => String
返回当前节点的静态HTML呈现
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<span className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</span>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
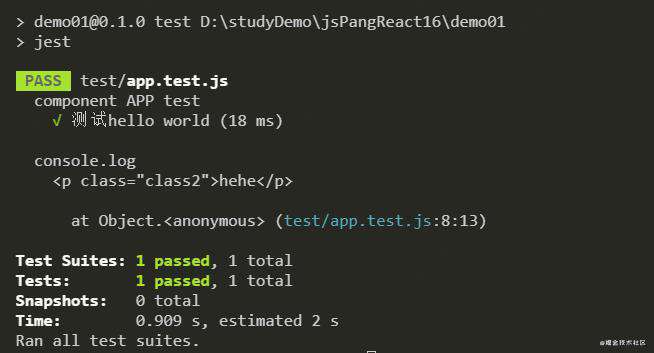
console.log(app.find('.class2').html())
})
})
测试结果:
.get(index) => ReactElement
返回给出索引的节点 ReactElement
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('div').children().get(1).props.foo).toBe('foo-data')
})
})
可用于测试props参数。
.at(index) => ShallowWrapper
根据索引返回节点。
???
// 待测试的组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('p')
.at(0)
.text()).toBe('haha')
})
})
// 测试通过
.first() => ShallowWrapper
返回当前第一个节点 wrapper
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('p')
.first()
.text()).toBe('haha')
})
})
.last() => ShallowWrapper
返回当前最后一个节点 wrapper
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find('p')
.last()
.text()).toBe('hehe')
})
})
.state([key]) => Any
返回根组件的状态,只能应用于跟组件,如果在find的某个节点上使用会报错。
ShallowWrapper::state() can only be called on the root
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: 'jerry',
age: 23
}
}
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
<span>enen</span>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.state('name')).toBe('jerry')
})
})
.context([key]) => Any
返回根组件的上下文环境
.props() => Object
返回当前节点的 props
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
<span>enen</span>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
console.log(app.find("span").at(1).props());
// { foo: 'foo-data', children: 'xixi' }
})
})
.prop(key) => Any
返回当前节点props的某个(key)属性的值
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1>
<p>haha</p>
<span>enen</span>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find("span").at(1).prop('foo')).toBe('foo-data');
})
})
.key() => String
返回当前节点的键(key)
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<h1 key='h1Key'>
<p>haha</p>
<span>enen</span>
</h1>
<span foo='foo-data'>xixi</span>
<p className='class2'>hehe</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.find("h1").key()).toBe('h1Key');
})
})
.simulate(event[, data]) => ShallowWrapper
模拟当前节点上的事件
???
当前存在如下组件:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
})
}
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>increase</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
我们需要测试的内容有:
- 点击
increase按钮触发点击事件---simulate - 测试点击事件后状态中
count是否增1
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.state("count")).toBe(0)
const btn = app.find('button');
btn.simulate('click');
expect(app.state('count')).toBe(1)
})
})
.setState(nextState) => ShallowWrapper
手动setState更新根组件状态
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
})
}
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>increase</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App />);
expect(app.state('count')).toBe(0);
app.setState({count:5})
expect(app.state('count')).toBe(5)
})
})
.setProps(nextProps) => ShallowWrapper
手动更新根组件的props
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<p>hi:{this.props.name}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
expect(app.find('p').text()).toBe('hi:jerry');
app.setProps({name:'tom'});
expect(app.find('p').text()).toBe('hi:tom')
})
})
.setContext(context) => ShallowWrapper
手动设置根组件的上下文
.instance() => ReactComponent
返回根组件的实例
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<p>hi:{this.props.name}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
console.log(app.instance())
})
})
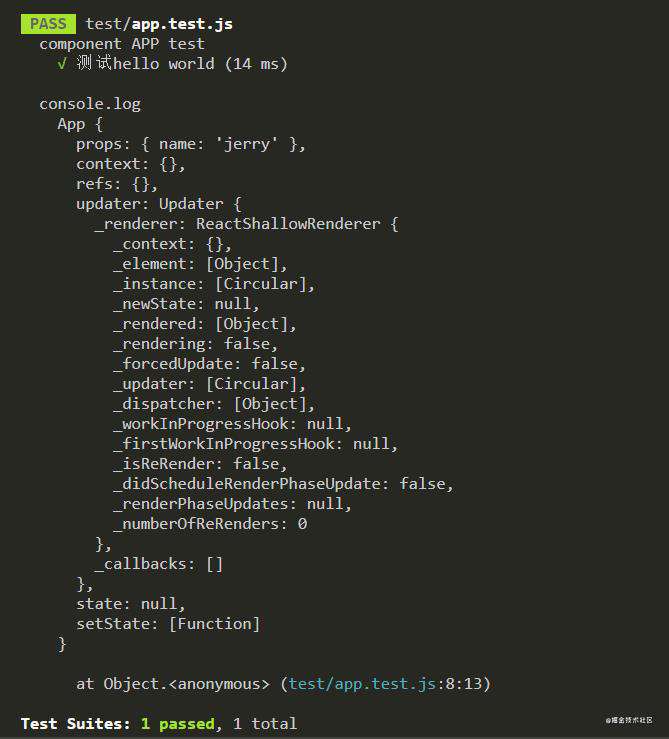
注意:只能在根实例的包装器实例上调用。 在 React 16 及更高版本中,instance() 为无状态功能组件返回 null。
.update() => ShallowWrapper
在根组件实例上调用.forceUpdate()
.debug() => String
返回当前浅渲染树的字符串表示形式,以便进行调试
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<p>hi:{this.props.name}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
console.log(app.debug())
})
})
.type() => String|Function
返回包装器的当前节点的类型。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<p>hi:{this.props.name}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试组件
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
expect(app.find('p').type()).toBe("p")
expect(app.find('div').type()).toBe('div')
})
})
.name() => String
返回当前节点的名称
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<p>hi:{this.props.name}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
expect(app.find('p').name()).toBe("p")
expect(app.find('div').name()).toBe('div')
})
})
.forEach(fn) => ShallowWrapper
迭代当前的每个节点并执行提供的函数
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo bax" />
<div className="foo bar" />
<div className="foo baz" />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.calss1').children();
wrappers.forEach(e=>{
expect(e.hasClass('foo')).toEqual(true);
})
})
})
.map(fn) => Array
将当前的节点数组映射到另一个数组
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo bax" >a</div>
<div className="foo bar" >b</div>
<div className="foo baz bar" >c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.calss1').children();
const map_wrappers = wrappers.map(e => e.hasClass('bar'));
expect(map_wrappers).toEqual([false, true, true]);
const text_wrappers = wrappers.map(e=>e.text());
expect(text_wrappers).toEqual(['a','b','c'])
})
})
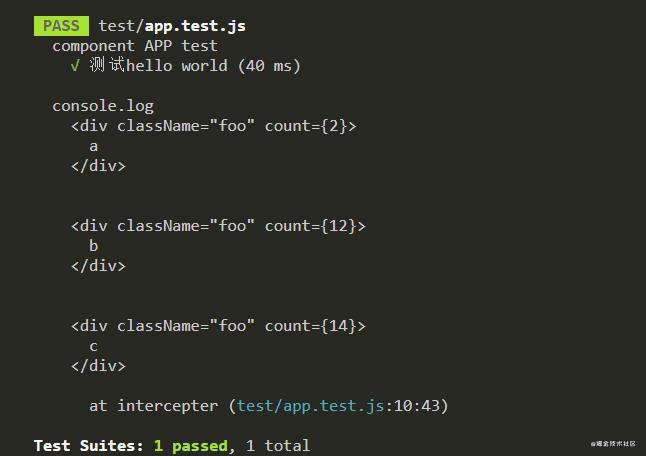
.reduce(fn[, initialValue]) => Any
将提供的减少函数应用于包装器中的每个节点以减少到单个值。每个节点作为一个 ShallowWrapper 传入,并从左到右进行处理。
- function:为集合中的每个节点运行的归约函数,具有以下参数:
- value:上次调用此函数返回的值
- node:正在处理的节点wrapper
- index:正在处理的节点索引
- initialValue:如果提供,这将作为第一个参数传入减少函数的第一次调用。 如果省略,将提供第一个节点,迭代将从集合中的第二个节点开始。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo" count={2}>a</div>
<div className="foo" count={12}>b</div>
<div className="foo" count={14}>c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.foo');
const totalCount = wrappers.reduce((count, n) => count + n.prop('count'), 0);
expect(totalCount).toEqual(28);
const totalCount1 = wrappers.reduce((count, n) => count + n.prop('count'));
expect(totalCount1).toEqual("[object Object]1214")
})
})
.reduceRight(fn[, initialValue]) => Any
将当前节点数组从右到左减少为一个值。reduce为从左到右,这个为从右到左。
.slice([begin[, end]]) => ShallowWrapper
根据Array的slice的规则返回具有原始包装器的节点的子集的新包装器。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo" count={2}>a</div>
<div className="foo" count={12}>b</div>
<div className="foo" count={14}>c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.foo');
const slice_wrapper = wrappers.slice(1,2);
const text = slice_wrapper.map(e=>e.text())
expect(text).toEqual(['b'])
})
})
.tap(intercepter) => Self
点击wrapper方法链。有助于调试。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo" count={2}>a</div>
<div className="foo" count={12}>b</div>
<div className="foo" count={14}>c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.foo');
const result= wrappers.tap(n=>console.log(n.debug())).map(n=>n.text());
expect(result).toEqual(['a','b','c'])
})
})
.some(selector) => Boolean
返回渲染树中是否有节点与提供的选择器匹配。
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo" id='aId' count={2}>a</div>
<div className="foo" count={12}>b</div>
<div className="foo" count={14}>c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.foo');
expect(wrappers.some('#aId')).toEqual(true)
})
})
.someWhere(predicate) => Boolean
返回渲染树中是否有节点与提供的断言函数匹配。个人理解是some的函数表现形式,比如需要处理再进行断言的时候可以通过这种方式。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo bar" count={2}>a</div>
<div className="foo" count={12}>b</div>
<div className="foo" count={14}>c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.foo');
expect(wrappers.someWhere(n => n.hasClass('bar'))).toEqual(true)
})
})
.every(selector) => Boolean
返回渲染树中是否所有节点与提供的选择器匹配。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo bar" count={2}>a</div>
<div className="foo boo" count={12}>b</div>
<div className="foo aoo" count={14}>c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.foo');
expect(wrappers.every('.bar')).toEqual(false);
expect(wrappers.every('.boo')).toEqual(false);
expect(wrappers.every('.foo')).toEqual(true);
})
})
.everyWhere(predicate) => Boolean
返回是否所有节点都满足所提供的断言函数。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo bar" count={2}>a</div>
<div className="foo boo" count={12}>b</div>
<div className="foo aoo" count={14}>c</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrappers = app.find('.foo');
expect(wrappers.everyWhere(n=>n.hasClass('bar'))).toEqual(false);
expect(wrappers.everyWhere(n=>n.hasClass('boo'))).toEqual(false);
expect(wrappers.everyWhere(n=>n.hasClass('foo'))).toEqual(true);
})
})
.dive([options]) => ShallowWrapper
浅渲染当前wrapper的一个非DOM子元素,并在结果周围返回一个wrapper,必须是单节点包装器。
???
// 待测试组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyCom from './MyCom'
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className='calss1'>
<div className="foo bar" count={2}>a</div>
<MyCom />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
// MyCom
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class MyCom extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>xixi</h1>
)
}
}
export default MyCom;
// 测试代码
import React from 'react';
import App from '../src/App';
import { shallow } from 'enzyme'
describe('component APP test', () => {
it('测试hello world', () => {
const app = shallow(<App name='jerry' />);
const wrapper = app.find('MyCom');
expect(wrapper.text()).toBe('<MyCom />');
// expect(wrapper.find('h1').text()).toBe('xixi')
// Method “text” is meant to be run on 1 node. 0 found instead.
expect(wrapper.dive().find('h1').text()).toBe('xixi')
})
})
只能在单个非 DOM 组件元素节点的包装器上调用,否则会抛出错误。 如果您必须对具有多个子节点的包装器进行浅包装,请使用 .shallow()。
我所理解就是shallow不能渲染出来子组件,所以就不能查找到子组件中的内容,通过dive()可以实现。
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 最常见的情况是下载不完整: 可对比下载完压缩包的与网盘上的容量,若小于网盘提示的容量则是这个原因。这是浏览器下载的bug,建议用百度网盘软件或迅雷下载。若排除这种情况,可在对应资源底部留言,或 联络我们.。
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 对于PPT,KEY,Mockups,APP,网页模版等类型的素材,文章内用于介绍的图片通常并不包含在对应可供下载素材包内。这些相关商业图片需另外购买,且本站不负责(也没有办法)找到出处。 同样地一些字体文件也是这种情况,但部分素材会在素材包内有一份字体下载链接清单。
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?
- 请QQ联系我们




发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!