“这是我参与更文挑战的第3天,活动详情查看: 更文挑战”
前言
Vue组件的生命周期分为创造、挂载、更新、销毁四大阶段,并在生命周期每个阶段的前后会触发各自的钩子函数,如:
- 组件创造前会执行
beforeCreate钩子函数; - 组件创造后
created钩子函数; - 组件挂载前
beforeMount钩子函数; - 组件挂载后
mounted钩子函数; - 组件更新前
beforeUpdate钩子函数; - 组件更新后
updated钩子函数; - 组件销毁前
beforeDestroy钩子函数; - 组件销毁后
destroyed钩子函数。
而React组件的生命周期分为挂载、更新、卸载阶段,学习生命周期最主要是弄清楚每个生命周期的阶段会触发那些钩子函数。先用一张图来展示React提供哪些生命周期钩子函数,不过该图展示的是React16.4版本后的生命周期钩子函数,且只能在类组件中使用,而函数组件中的生命周期钩子函数用React Hook来实现,在后续文章中介绍。
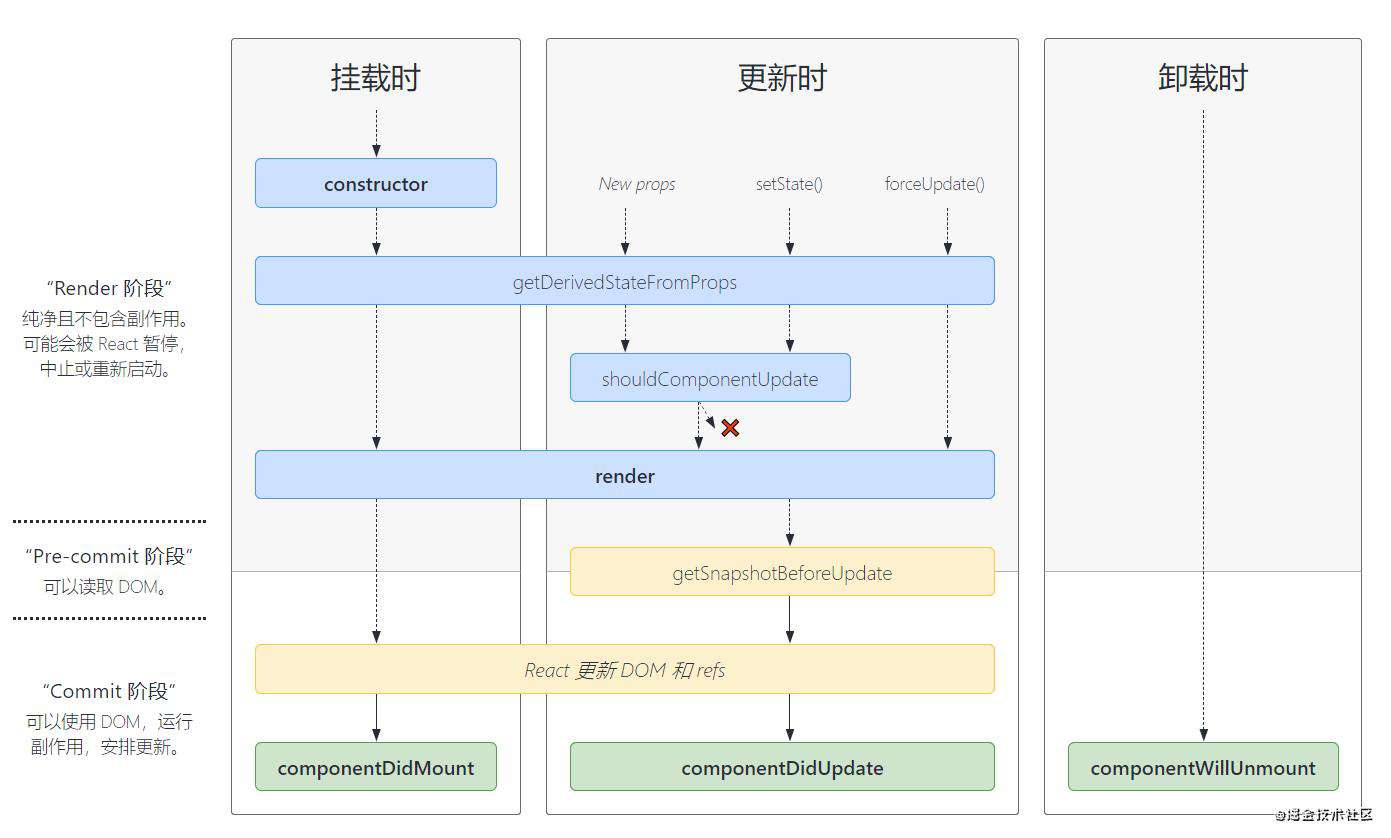
1、React组件挂载阶段
在React组件挂载阶段会按顺序调用constructor、getDerivedStateFromProps、componentDidMount、render这些钩子函数。
import React from 'react';
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { title: 'hello React' };
console.log('执行constructor')
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state){
console.log('执行getDerivedStateFromProps')
return null;
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log('执行componentDidMount')
}
render() {
console.log('执行render')
return (
<div>{this.state.title}</div>
);
}
}
export default HelloWorld;
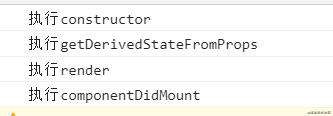
执行以上代码,在控制台的打印结果如下图所示:
1.1 constructor
constructor其实是React.Component 子类的构造函数。在其中我们一般做三件事情。
- 在其他语句之前前调用
super(props),否则this.props为undefined; - 通过给 this.state 赋值对象来初始化state;
- 为事件处理函数绑定实例,否在函数中无法使用
this。
import React from 'react';
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { title: 'hello React' };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
console.log(this)
}
render() {
return (
<div onClick={handleClick}>{this.state.title}</div>
);
}
}
export default HelloWorld;
此外要特别注意以下两点:
- 不能使用
this.setState()来初始内部state,如下所示:
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.setState({
title:'hello world'
})
}
- 不能将props直接赋值给state,然后使用state,而不直接使用props,这样做,当props更新时对应的state不会更新。
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state({
title:this.props.title
})
}
1.2 getDerivedStateFromProps
这是一个不常用的钩子函数,其作用是用组件的props来派生出一个新的state。getDerivedStateFromProps钩子函数接收组件的props和state作为参数,函数最后返回一个对象或者null,若返回一个对象,则用这个对象来更新state,若返回null,则不更新state。
import React from 'react';
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
constructor(props: any) {
super(props);
this.state={
info:'hello world'
};
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state){
let stateName = props.state == 1? '处理中':'已完成';
return {
stateName
};
}
render() {
return (
<div>{this.state.stateName}</div>
);
}
}
export default HelloWorld;
使用getDerivedStateFromProps钩子函数时要注意以下三点:
- 要派生出新的state,不要修改原来的state;
- 函数最后必须返回一个对象或者null;
- 钩子函数中无法使用
this。
1.3 render
render函数应该为纯函数,在其中不应该去修改state和props。在用JSX书写React元素时,通过state和props来给React元素绑定数据。最后必须返回一些React元素,且这些React元素必须只有一个根元素。若不想在DOM中额外增加一个无用的标签,可以使用<React.Fragment>作为根元素。
render() {
<React.Fragment>
<div>{this.state.title}</div>
<div>{this.props.info}</div>
</React.Fragment>
}
1.4 componentDidMount
componentDidMount钩子函数会在组件挂载后(插入 DOM 树中)立即调用,跟Vue中的mounted钩子函数的作用非常相似。
在其中我们一般可以做以下操作
- 获取DOM元素;
- 请求服务端数据;
- 监听事件,必须在
componentWillUnmount()中取消监听; - 可以调用
this.setState()来改变state数据。
componentDidMount(){
this.setState({
title:'hello world'
})
}
2、React组件更新阶段
在React组件更新阶段会按顺序调用getDerivedStateFromProps、shouldComponentUpdate、render、getSnapshotBeforeUpdate、componentDidUpdate这些钩子函数。
import React from 'react';
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
constructor(props: any) {
super(props);
this.state = {
title: 'hello world'
}
this.update = this.update.bind(this);
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
console.log('执行getDerivedStateFromProps');
return null;
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('执行shouldComponentUpdate');
return true;
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('执行getSnapshotBeforeUpdate');
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('执行componentDidUpdate')
}
update() {
this.setState({
title: 'hello react'
})
}
render() {
console.log('执行render')
return (
<div onClick={this.update}>{this.state.title}</div>
)
}
}
export default HelloWorld;
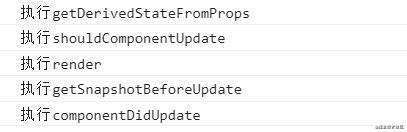
执行以上代码,在控制台的打印结果如下图所示:
在React中有三个操作会引起组件更新:
-
组件的props发生变化;
-
执行
this.setState();this.setState(updater, [callback])其中undater可以为一个对象或函数(state, props) => stateChange,stateChange中要返回一个对象,这个对象在React内部会和this.state进行合并来更新state。另外通过函数的参数state和props可以获取组件最新的state和props。执行
this.setState()并不总是立即更新组件,它会批量推迟更新。这使得在调用this.setState()后立即 读取this.state成为了隐患。所以this.setState的第二个参数callback为可选的回调函数,在回调函数去读取更新后的state。handleClick(){ this.setState((state,props) =>{ const count= state.count + 1; return { count, } },() =>{ console.log(this.state.count) }) } -
执行
this.forceUpdate()。执行
this.forceUpdate()强制让组件重新渲染,相当Vue中的vm.$forceUpdate()。handleClick(){ this.forceUpdate(); }执行
this.forceUpdate()引起组件更新,会跳过shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数。 但其子组件会触发正常的生命周期钩子函数,包括shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数。
2.1 getDerivedStateFromProps
getDerivedStateFromProps钩子函数在组件挂载阶段会被调用,在组件更新阶段也会被调用,且函数接收的state和props都是更新后的。
那么在其中派生出来的state,完全受props控制,即使用this.setState()改变也不起作用。
2.2 shouldComponentUpdate
shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数接收更新之后的state和props,通过和更新前的state和props对比,来判断是否更新组件,如果函数最后返回true则更新组件,反之返回false则不更新组件,一般用于性能优化。
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (this.props.color !== nextProps.color) {
return true;
}
if (this.state.count !== nextState.count) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
使用shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数时要注意以下三点:
-
在组件中执行
this.forceUpdate()触发组件更新,则不会执行该钩子函数; -
在其中执行
this.setState()时,必须在一个条件语句里中,否会陷入无限更新的死循环,导致程序崩溃。 -
函数最后必须返回
true或false,若返回false,后续render、getSnapshotBeforeUpdate、componentDidUpdate钩子函数不再被调用。
2.3 render
执行render()重新渲染组件。
2.4 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数相当Vue中beforeUpdate钩子函数。
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数调用时,props和state已经更新了,故该钩子函数接收更新前的props和state作为参数,作为比较使用。
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数最后返回一个值,该值会被componentDidUpdate钩子函数的第三个参数snapshot接收。
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数是在组件重新渲染后挂载到DOM之前被调用,故在该钩子函数中获取到的 DOM 还是更新的 DOM ,一般用组件UI更新前后的交互操作。
例如下面的示例,通过isOpen这个prop来看控制一个列表的显示隐藏,列表的高度自适应。当isOpen改变导致组件更新时,在getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数中可以获取到隐藏前的列表高度,用于UI交互。
import React from 'react';
class List extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.listRef = React.createRef();
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log(prevProps)
if (prevProps.isOpen) {
const listEl = this.listRef.current;
return listEl.height;
}
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log(snapshot)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.props.isOpen &&
<div
ref={this.listRef}
>
{/* ...contents... */}
</div>}
</div>
);
}
}
export default List;
使用getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数时要注意以下三点:
-
在其中执行
this.forceUpdate()或this.setState()时,必须在一个条件语句里中,否会陷入无限更新的死循环,导致程序崩溃; -
函数最后必须返回一个值或null,否则代码会报错;
-
必须和
componentDidUpdate钩子函数一起调用,否则代码会报错。
2.5 componentDidUpdate
componentDidUpdate钩子函数在组件重新渲染后并挂载到DOM中后才执行的,函数参数接收更新前的state和props,还用snapshot参数接收getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数返回值。
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot){
//...
}
使用componentDidUpdate钩子函数时要注意以下两点:
-
在其中执行
this.forceUpdate()或this.setState()时,必须在一个条件语句里中,否会陷入无限更新的死循环,导致程序崩溃; -
如果
shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数返回值为false,则不会调用componentDidUpdate钩子函数。
3、React组件卸载阶段
3.1 componentWillUnmount
componentWillUnmount会在组件卸载及销毁之前调用。我们一般在其中处理以下事项:
- 清除定时器;
- 取消网络请求;
- 解绑在
componentDidMount钩子函数中监听的事件。
componentWillUnmount(){
//...
}
4、React父组件挂载阶段
在React父组件挂载阶段,在调用父组件render函数后,会去调用子组件的constructor函数,直到子组件的componentDidMount钩子函数被调用后,才会去调用父组件的componentDidMount钩子函数。
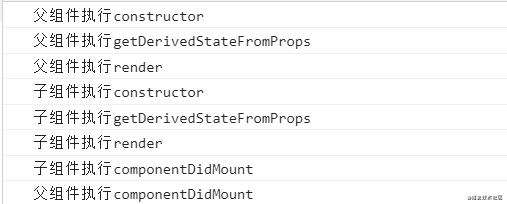
假如子组件中还有孙子组件,同理在调用子组件render函数后,会去调用孙子组件的constructor函数,直到孙子组件的componentDidMount钩子函数被调用后,才会去调用子组件的componentDidMount钩子函数,最后才调用父组件的componentDidMount钩子函数。
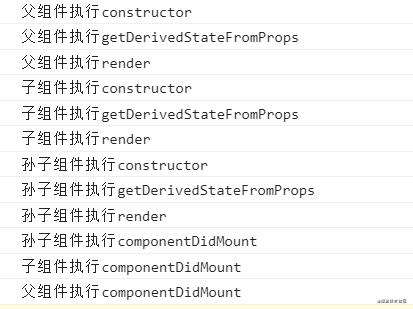
一层层调用下去,直到最后一个孙子组件的componentDidMount钩子函数被调用后,才会去调用父组件的componentDidMount钩子函数。
5、React父组件更新阶段
React更新是自顶向下的进行递归更新的,不管你嵌套了多少层组件,都会触发到最后一层组件的更新。
而Vue的更新只到当前组件,不会去触发子组件的更新,触发子组件的props发生了改变。
所以React父组件更新了,会引起子组件更新阶段的钩子函数的调用,如下图所示:
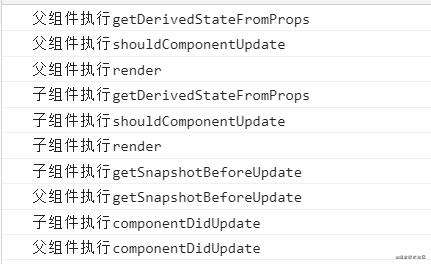
父组件更新时,在调用render函数后,会去调用子组件的getDerivedStateFromProps钩子函数,直到子组件的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数被调用后,再去调用父组件的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数,然后调用子组件的componentDidUpdate钩子函数,最后才调用父组件的componentDidUpdate钩子函数。
再来看子组件还有孙子组件的场景下,调用孙子组件的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数,接着调用子组件的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数,然后调用父组件的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate钩子函数,才会去调用各组件的componentDidUpdate钩子函数。
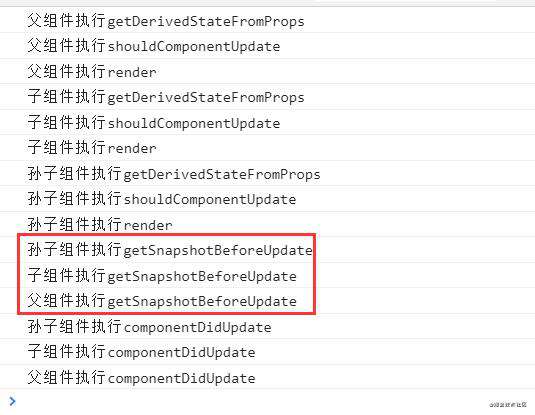
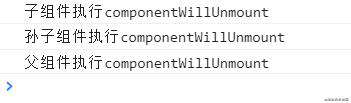
6、React父组件卸载阶段
React父组件卸载后。其内部嵌套最深一层组件先调用componentWillUnmount钩子函数,然后依次往外调用各组件的componentWillUnmount构造函数。
 +
+
7、React组件更新的优化
React中父组件更新,不管子组件的state和props是否发生变化,都会被迫更新。习惯了Vue开发,会感到非常不可思议,按常理是传递给子组件的props变化了,子组件才会更新。React这种更新机制可能导致性能问题,可以用React.PureComponent来创建那种更新计算开销很大的子组件,来优化性能。
React.PureComponent会创建一个自行调用shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数的组件,故在此组件中不能再次调用shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数。
在shouldComponentUpdate钩子函数中自动浅层对比props和state,若数据有变化,返回true,触发组件更新。
要注意只是浅层对比props和state,下面用一个例子来直观的解释什么是浅层对比。
import React from 'react';
class HelloWorld extends React.PureComponent {
constructor(props: any) {
super(props);
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('子组件执行componentDidUpdate')
}
render() {
const { title, arr, obj } = this.props;
return (
<div>
<div>{title}</div>
{arr.map((item,index) =>{
return (
<span key={index}>{item}</span>
)
})}
<div>{obj.a}</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default HelloWorld;
import React from 'react';
import HelloWorld from './HelloWorld';
class Index extends React.Component {
constructor(props: any) {
super(props);
this.state = {
title: 'hello world',
arr:[1,2,3],
obj:{
a:1
}
}
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
let {arr,obj} = this.state;
arr.push(4);
obj.a =4;
this.setState({
arr,
obj,
})
}
render() {
return (
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>
<HelloWorld title={this.state.title} arr={this.state.arr} obj={this.state.obj}></HelloWorld>
</div>
)
}
}
export default Index;
export default HelloWorld;
“浅层对比”:只对比到this.props的属性值的一层,比如属性值是数组或对象时不去对比里面的嵌套数据,
换句话来说,只要该属性值的引用地址不改变,就认为该属性值未改变。数组和对象都是引用类型。
在上述例子中给this.state.arr数组中添加一个4,将this.state.obj.a的值改变成4,都不会触发子组件的更新。
要触发组件的更新,要给this.state.arr或this.state.obj赋值个新数组或对象,也就是将其引用地址改变。
那么用React.PureComponent来创建的子组件,在父组件中,只有传递给子组件的props经过浅层对比后发现改变了,才会触发子组件的更新,避免父组件数据变动时子组件也被迫一起更新,从而优化了性能。
另外可以调用forceUpdate强制触发子组件的更新。
import React from 'react';
import HelloWorld from './HelloWorld';
export default class Index extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.myCom = React.createRef();
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.myCom.current.forceUpdate();
}
render() {
return (
<div onClick={this.handleClick} >
<HelloWorld ref={this.myCom}></HelloWorld>
</div>
)
}
}
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!