1. react 16 版本生命周期有哪些?
- 初始化阶段
- constructor 构造函数
- getDefaultProps props 默认值
- getDefaultState state 默认值
- 挂载阶段
- componentDidMount 组件已经被渲染到 DOM 中 (对应 mounted)
- render
- 更新阶段
- shouldComponentUpdate
- componentDidUpdate
- 卸载阶段
- componentWillUnmount (对应 destoryed)
- 错误处理
- componentDidCatch
2. props 和 state 的区别?
- props 是外部传入的数据参数, 不可变;
- state 是组件内部的状态, 可变;
- 没有 state 的是无状态组件, 有 state 的是有状态组件;
- 多用 props, 少用 state, 即多写无状态组件
3. setState 是同步的还是异步的?
-
结论: 原生事件, setTimeOut 是同步的, 合成事件, 生命周期中是异步的
-
异步示例
componentDidMound(){
this.setState({index: this.state.index + 1});
console.log(index)
}
- 同步示例
componentDidMound(){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(this.state.index)
this.setState({index: this.state.index + 1});
console.log(this.state.index)
})
}
4. react hook
- 基础示例:
import React, { useState } from "react";
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>点击{{ count }}次</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}></button>
</div>
);
}
- Hook 声明多个 state 变量
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [name, setName] = useState("xiaoming");
}
- Effect Hook
- 副作用: 如果在 react 组件中, 执行数据获取, 订阅或手动修改 DOM, 统一叫做副作用
- useEffect 钩子, 给函数组件增加了操作副作用的能力, 它跟 class 组件中的 componentDidMount、componentDidUpdate 和 componentWillUnmount 具有相同的用途,只不过被合并成了一个 API
// 示例:
import React, { useState } from "react";
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
document.title = `点击了${count}次`; // 完成对DOM的更改后执行useEffect中的代码
});
return (
<div>
<p>点击{count}次</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}></button>
</div>
);
}
清除副作用: 副作用函数可以通过返回一个函数来清除副作用.
// 下面的组件使用副作用来订阅好友的在线状态, 并通过取消订阅来清除操作;
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function FriendStatus(props) {
const [isOnline, setIsOnline] = useState(null);
function handleStatusChange(status) {
setIsOnline(status.isOnline);
}
useEffect(() => {
ChatAPI.subscribeToFriendStatus(props.friend.id, handleStatusChange);
return () => {
ChatAPI.unsubscribeFromFriendStatus(
props.friend.id,
handleStatusChange
);
};
});
if (isOnline === null) {
return "Loading...";
}
return isOnline ? "Online" : "Offline";
}
- 自定义 hook
- 如果在组件之间有一些重用的状态逻辑, 有两种主流方案可以解决, 高阶组件和 render props, 自定义 hook 可以让你在不增加组件的情况下实现
// 自定义hook示例:
function useFriendStatus(friendID) {
const [isOnline, setIsOnline] = useState(null);
function handleStatusChange(status) {
setIsOnline(status.isOnline);
}
useEffect(() => {
ChatAPI.subscribeToFriendStatus(friendID, handleStatusChange);
return () => {
ChatAPI.unsubscribeFromFriendStatus(friendID, handleStatusChange);
};
});
return isOnline;
}
// 以friendID为参数, 并返回该好友是否在线
// 在以下两个组件中使用
function findFriendStatus(props) {
const isOnline = useFriendStatus(props.friend.ID);
if (isOnline === null) {
return "Loading...";
}
return isOnline ? "Online" : "Offline";
}
function FriendListItem(props) {
const isOnline = useFriendStatus(props.friend.id);
return (
<li style={{ color: isOnline ? "green" : "black" }}>
{props.friend.name}
</li>
);
}
可以在自定义 hook 中传递数据
function transData() {
const [id, setId] = useState(0);
const isOnline = findFriendStatus(id);
}
-
hook 规则
-
- 不要在循环, 条件或嵌套函数中调用 hook, 确保总是在你的 React 函数的最顶层以及任何 return 之前调用他们. 遵循这条规则, 可以保证每一次渲染都按照同样的顺序被调用, 这让 React 能够在多次的 useState 和 useEffect 调用之间保持 hook 状态的正确
// 示例: function Form() { // 1. Use the name state variable const [name, setName] = useState("Mary"); // 2. Use an effect for persisting the form useEffect(function persistForm() { localStorage.setItem("formData", name); }); // 3. Use the surname state variable const [surname, setSurname] = useState("Poppins"); // 4. Use an effect for updating the title useEffect(function updateTitle() { document.title = name + " " + surname; }); // ... } -
- 只能在 react 函数中调用 hook
-
5. 高阶组件
// 示例:
const commentList = withSubscription(CommentList, DataSource =>
DataSource.getComment()
);
const BlogPost = withSubscription(BlogPost, (DataSource, props) => {
DataSource.getBlogPost(props.id);
});
function withSubscription(WrappedComponents, selectedData) {
return class extends React.components {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
this.state = {
data: selectedData(DataSource, props)
};
}
componentDidMount() {
// ...负责订阅相关的操作...
DataSource.addChangeListener(this.handleChange);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
DataSource.removeChangeListener(this.handleChange);
}
handleChange() {
this.setState({
data: selectData(DataSource, this.props)
});
}
render() {
return <WrappedComponents data={this.state.data} {...this.props} />;
}
};
}
6. render props
// 示例1:
<DataProvider render={data => <h1>{data.target}</h1>} />;
// 示例2
class Cat extends React.Component {
render() {
const mouse = this.props.mouse;
return (
<img
src="/cat.jpg"
style={{ position: "absolute", left: mouse.x, top: mouse.y }}
/>
);
}
}
class Mouse extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleMouseMove = this.handleMouseMove.bind(this);
this.state = { x: 0, y: 0 };
}
handleMouseMove(event) {
this.setState({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
});
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{ height: "100vh" }} onMouseMove={this.handleMouseMove}>
{/*
使用 `render`prop 动态决定要渲染的内容,
而不是给出一个 <Mouse> 渲染结果的静态表示
*/}
{this.props.render(this.state)}
</div>
);
}
}
class MouseTracker extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>移动鼠标!</h1>
<Mouse render={mouse => <Cat mouse={mouse} />} />
</div>
);
}
}
// 示例3:
// 如果你出于某种原因真的想要 HOC,那么你可以轻松实现
// 使用具有 render prop 的普通组件创建一个!
function withMouse(Component) {
return class extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Mouse
render={mouse => <Component {...this.props} mouse={mouse} />}
/>
);
}
};
}
7. react-redux
-
定义: 状态管理框架
-
流程图:
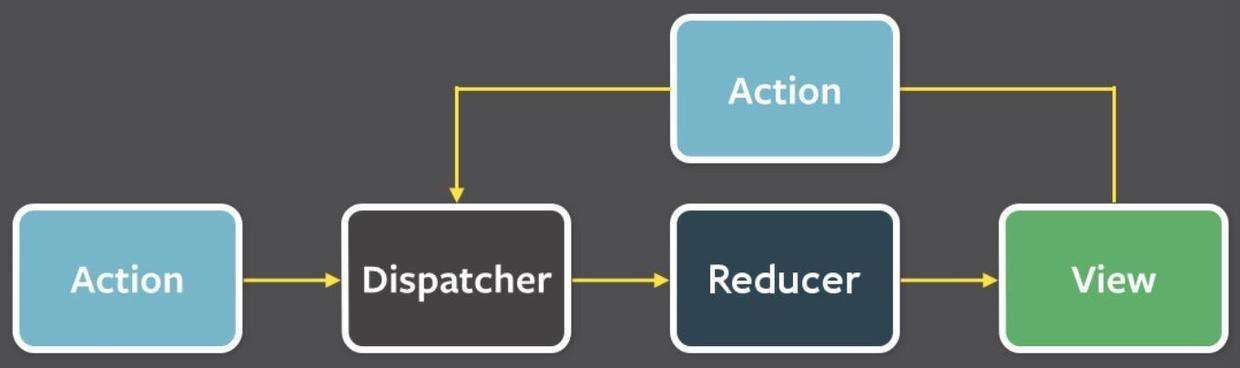
-
基本概念:
- store: react-redux 总的状态容器, 是一个对象
- action: 一个对象, 表明事件, 需要有 type 字段
- reducer: 一个函数, 根据不同的 action 返回不同的数据
根据上面流程图, view 层可以通过两种方式来更新
- view 发出 action => dispatcher 之后到达 reducer => reducer 处理后返回新的数据更新 View
- 其他层发出 action 后以同样的方式更新 view
-
总结: 发出 action => reducer 根据 action 返回不同数据 => store 被更新 => view 更新
组件分类: react-redux 将所有组件分为 UI 组件 和 容器组件
-
UI 组件:
- 只负责 UI 的展示
- 没有状态(state)
- 所有数据由 props 提供
- 不使用 redux 的所有 API
-
容器组件
- 负责管理数据和所有的交互逻辑
- 带有内部状态
- 可以使用 redux 的 API
-
计数器示例:
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import Count from "./Count";
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return {
count: state.count
};
}
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {
add: () => dispatch({ type: "ADD_COUNT" })
};
}
const newComponent = connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Count);
mapStateToProps
接收 state 参数, 返回 props 对象
mapDispatchToProps
接收 dispatch 参数, 定义一系列发送事件的方法(发送一个 action), 返回 props
Reducer
刚才我们发送了 action, 但是并未对事件进行处理, reducer 实际就是来处理 action 的 示例如下:
// counter-reducer
export default function reducer(state = { count: 0 }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "ADD-COUNT":
return {
count: state.count + 1
};
default:
return state;
}
}
store
// store示例
import { createStore, Provider } from "react-redux";
import React from "react";
import reducer from "./counter-reducer";
import Counter from "./components/Counter";
const store = createStore(reducer); // 创建store
ReactDOM.render(
// store注册到顶层, 所有组件可以共享
<Provider store={store}>
<Counter />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root") // 挂载到根节点
);
- redux 总结:
- dispatch(action) => reducer => new state => new props => update components
- 分为容器组件和 UI 组件, 传统组件需要使用 connect 处理
- reducer 处理 action 返回新的 state, 需要考虑 action 不匹配的情况(default)
- 使用 creatStore 函数创建 store,reducer 作为参数
- 使用 provider 作为顶层组件将全局 sotre 引入
8. react fiber
react 在进行组件渲染时, 从 setState 到渲染完成整个过程是同步的, 如果需要渲染的组件比价庞大, js 运行占用的主线程时间会比较长, 导致页面响应变差, 使得 react 在动画, 手势等应用中效果变差; 为了解决整个问题, react 团队经过两年时间, 重写了 react 的核心算法-reconciliation, 命名为 fiber
本文持续更新中~~~
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!