题目描述
原题链接:二叉搜索树迭代器
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类 BSTIterator,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器,需包含 hasNext() 方法(返回下一个结点的值)、hasNext()方法(返回是否已遍历完整棵树)。
示例
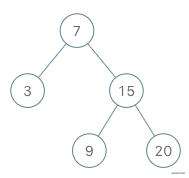
对于这棵树使用二叉搜索树迭代器应按如下返回:
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
进阶要求:next() 和 hasNext() 操作均摊时间复杂度为 O(1) ,并使用 O(h) 内存。其中 h 是树的高度。
解答
既然是二叉搜索树就必然离不开中序遍历,一般有递归和非递归的实现方式,其中中序遍历的递归实现相对简单:
function inorderTraversal(root){
if(root.left) inorderTraversal(root.left)
console.log(root.val) // 在这里操作结点
if(root.right) inorderTraversal(root.right)
}
如果使用递归遍历的方式可以在 BSTIterator 的构造函数里先遍历一遍整棵树,将所有节点保存在一个队列中,调用 next() 方法时出队一个节点并返回它的 val 值,调用 hasNext() 方法只需要返回队列是否为空即可。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
*/
const BSTIterator = function(root) {
this.queue = []
const inorderTraversal = (root) => {
if(root.left) inorderTraversal(root.left)
this.queue.push(root)
if(root.right) inorderTraversal(root.right)
}
inorderTraversal(root)
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.next = function() {
return this.queue.shift().val
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.hasNext = function() {
return !!this.queue.length
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new BSTIterator(root)
* var param_1 = obj.next()
* var param_2 = obj.hasNext()
*/
复杂度分析:这种解法用一个队列保存了所有结点,所以空间复杂度是 O(n),next() 方法和 hasNext() 方法的时间复杂度均为 O(1)。
如果采用非递归的方式去遍历这棵树,就不需要在构造函数里遍历完整棵树。非递归实现方法如下:
function inorderTraversal(root){
const stack = [];
let cur = root
while(cur){
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
}
while(stack.length){
const node = stack.pop()
console.log(node.val) // 在这里操作结点
cur = node.right
while(cur){
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
}
}
}
在本题中,若采用非递归的方式去遍历,仅需使用一个栈保存少量的结点即可:
var BSTIterator = function(root) {
this.stack = []
var cur = root
while(cur){
this.stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
}
};
BSTIterator.prototype.next = function() {
var node = this.stack.pop()
if(node.right){
var cur = node.right
while(cur){
this.stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
}
}
return node.val
};
BSTIterator.prototype.hasNext = function() {
return !!this.stack.length
};
复杂度分析:仅采用一个栈保存了数量最大为树高的结点,故空间复杂度为 O(h),next() 方法和 hasNext() 方法的时间复杂度均为 O(1)。
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?





发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!