实现instanceof
function myInstanceof(left,right){
// 如果是基础类型直接返回false
if(typeof left !== 'object' && typeof left == null) return false;
// Object.getPrototypeOf() 方法返回指定对象的原型(内部[[Prototype]]属性的值)
let proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(left);
while(true){
if(!proto) return false;
if(proto == right.prototype) return true;
proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(proto);
}
}
实现深拷贝
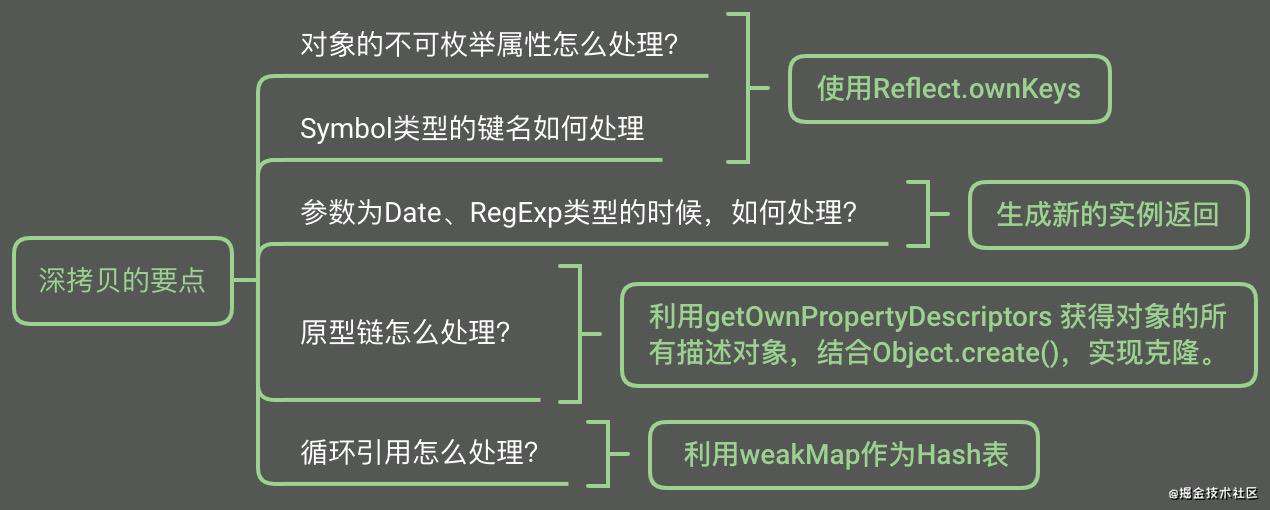
function deepClone(obj,map = new Map()){
if(obj instanceof Object){
if(obj instanceof Function) return obj;
if(obj instanceof Date) return new Date(obj);
if(obj instanceof RegExp) return new RegExp(obj);
// 解决循环引用
if(map.has(obj)) return map.get(obj);
// 拷贝原型链
let allDesc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(target);
let cloneObj = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(target), allDesc);
map.set(obj,cloneObj);
// Reflect.ownKeys可以拿到不可枚举属性和symbol类型的键名
for(let key of Reflect.ownKeys(obj)){
cloneObj[key] = deepClone(obj[key],map);
}
return cloneObj
}else{
return obj;
}
}
实现new
function myNew(ctor,...args){
if(typeof ctor !=='function'){
throw 'ctor must be function';
}
// 创建一个新对象
let obj = Object.create(ctor.prototype);
// 改变this指向,执行构造函数中的代码,
let res = ctor.apply(obj,[...args]);
let isObject = typeof res === 'object'&& typeof res !== null;
let isFunction = typeof res == 'function';
// 返回新对象
return isObject || isFunction? res : obj;
}
实现apply
Function.prototype.myApply =function(context = window,args){
// 利用symbol声明唯一变量
let fn = Symbol('fn')
// 为context绑定当前的方法,改变this指向
context[fn] = this;
// 执行当前的方法
var result = context[fn](args);
delete context.fn;
return result;
}
实现bind
Function.prototype.myBind =function(context = window,...args){
var self = this;
var fbound = function(...args1){
return self.apply(context,[...args,...args1]);
}
fbound.prototype = Object.create(this.prototype);
// 返回一个函数
return fbound;
}
实现softBind
为什么需要softBind,让我们一同来看一个例子。
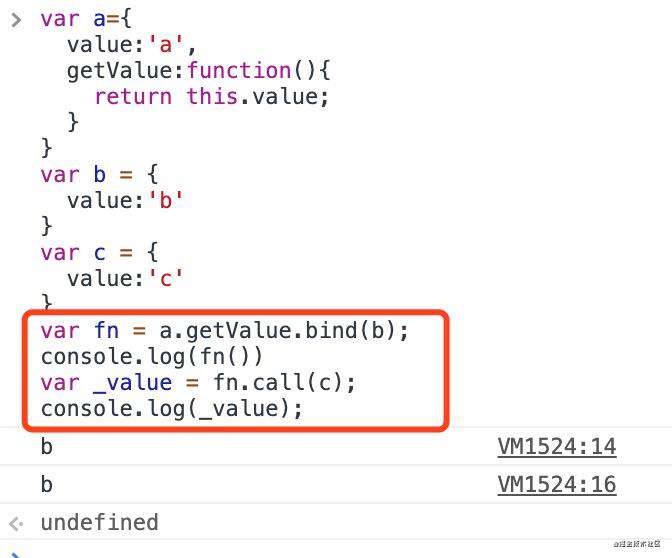 我们可以看到bind之后,无法通过call来再次改变this的指向。我们想要输出c的value,但是却依旧输出的是b的value。为了解决以上问题我们要实现一种软绑定。
我们可以看到bind之后,无法通过call来再次改变this的指向。我们想要输出c的value,但是却依旧输出的是b的value。为了解决以上问题我们要实现一种软绑定。
那如何更改this呢?如何区分直接调用还是通过call这两种情况呢?我们分析可以得到两种情况:
- fn直接执行的时候,this指向的window
- 调用fn.call的时候,this指向call的第一个参数,
Function.prototype.softBind = function(context = window,...args){
var self = this;
var fbound = function(...args1){
//此行逻辑是重点!结合上述分析可分析出原因
var _context = (!this||this==(window || global))?context:this;
return self.apply(_context,[...args,...args1]);
}
fbound.prototype = Object.create(this.prototype);
return fbound;
}
实现JSON.Stringify
看一下MDN上对规则的描述:

function jsonStringify(data){
let result = '';
var type = typeof data;
if(type !== 'object' || data === null ){
// 基础类型在此处理
result = data;
if(type == 'number' &&(Number.isNaN(data) || !Number.isFinite(data))){
// 规则8:NaN 和 Infinity格式的数值会被当做 null。
result = "null";
}else if(type == 'function' || type == 'undefined' || type == 'symbol'){
// 规则4:函数、undefined 被单独转换时,会返回 undefined,
result = "undefined";
}else if(type == 'string'){
result = `"${data}"`
}
result = String(result);
}else{
if(data.toJSON && typeof data.toJSON =='function'){
//规则1:转换值如果有 toJSON() 方法,该方法定义什么值将被序列化。
result+=jsonStringify(data.toJSON())
}else if(data instanceof Array){
result = [];
data.forEach((item,index)=>{
let itemType = typeof item;
// 规则4:undefined、任意的函数以及 symbol 值,出现在数组中时,被转换成 null
if(itemType == 'undefined' || itemType =='function' || itemType =='symbol'){
result[index]="null";
}else{
result[index]=jsonStringify(item);
}
})
result = `[${result}]`
}else{
result = [];
Object.keys(data).forEach((item,index)=>{
// 规则6:所有以 symbol 为属性键的属性都会被完全忽略掉,Object.keys返回包括对象自身的(不含继承的)所有可枚举属性(不含 Symbol 属性)的键名。
let valueType = typeof data[item];
if(valueType == 'undefined' || valueType =='function' || valueType =='symbol'){
// 规则4:undefined、任意的函数以及 symbol 值,在序列化过程中会被忽略(出现在非数组对象的属性值中时)
}else if(data[item] == data){
// 规则5:对包含循环引用的对象(对象之间相互引用,形成无限循环)执行此方法,会抛出错误。
throw "cycling";
}else{
result.push(`"${item}":${jsonStringify(data[item])}`);
}
})
result = `{${result}}`
}
}
return result;
}
常见问题FAQ
- 免费下载或者VIP会员专享资源能否直接商用?
- 本站所有资源版权均属于原作者所有,这里所提供资源均只能用于参考学习用,请勿直接商用。若由于商用引起版权纠纷,一切责任均由使用者承担。更多说明请参考 VIP介绍。
- 提示下载完但解压或打开不了?
- 找不到素材资源介绍文章里的示例图片?
- 模板不会安装或需要功能定制以及二次开发?






发表评论
还没有评论,快来抢沙发吧!